데이터베이스 3일차
Relational Algebra
Relational Data Structure
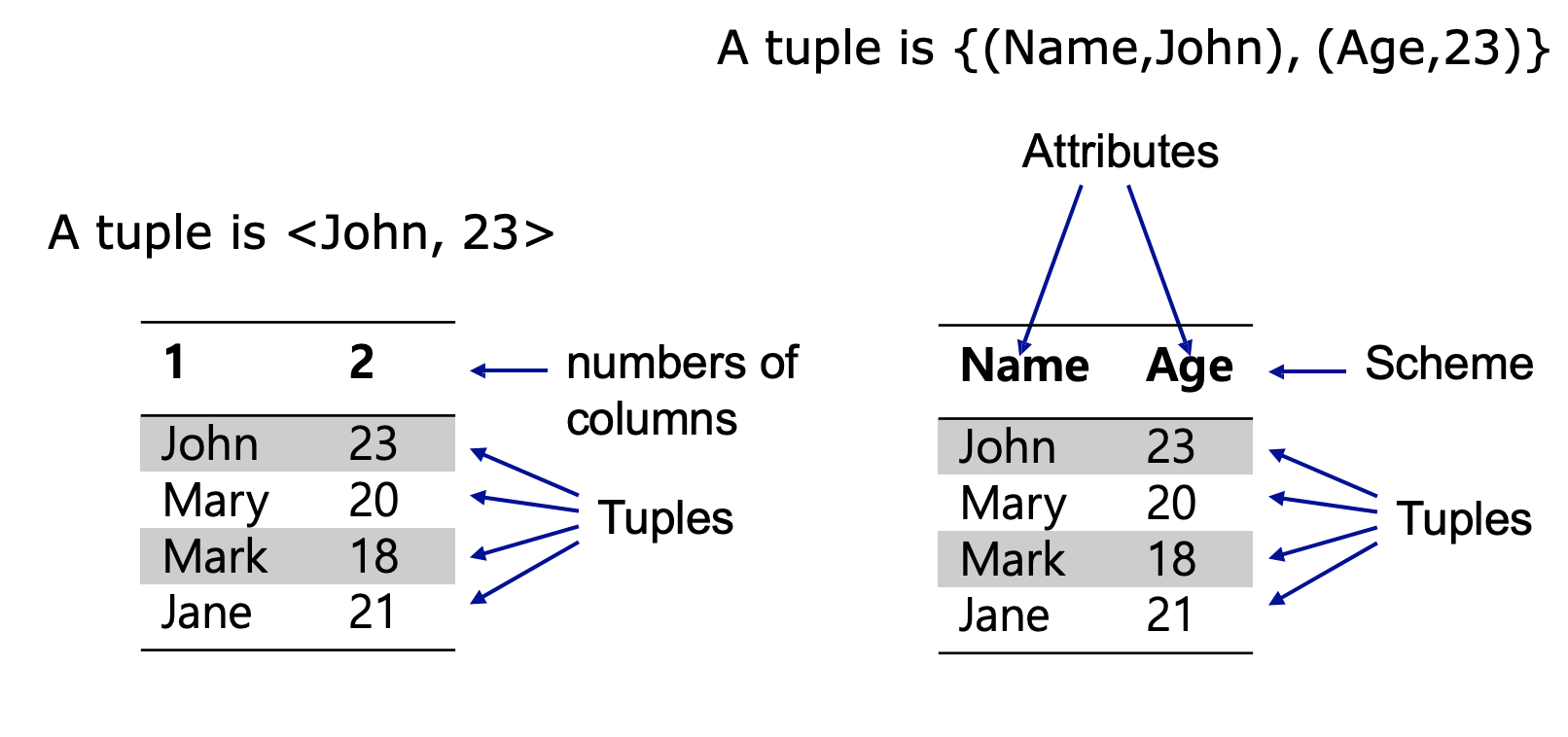
- Table == Relation: data is stored in relations
- set of tuples of the same schema
- Schema: each relation has a heading
- set of attributes
- Attributes: schema defines the columns
- rows contain tuples
- value assigned to each attributes
attribute 에다가 그냥 숫자가 아니라 의미있게 이름을 붙이자!
그렇게 index 가 아닌 의미 있는 이름을 attribute 라고 부르고,
그렇게 만들어진 테이블의 헤더를 Schema 라고 부른다.
index 숫자에다가 이름을 붙이는게 schema 라는 매우 혁명적인 아이디어이다.
Relational Algebra
-
예시: Renaming attributes (
AS쿼리) -
Relational Operations on Bags
- DBMS implements relational algebra that operates on bags (multisets) insetead of sets
- 왜 Bag 단위로 연산이 이루어지는가?
- Bag 는 tuple 의 duplication 을 허용하지만, 그냥 set 은 허용하지 않는다. 하지만 현실에서는 중복되는 tuple 이 생긴다.
Set Operations of Bags
Let’s assume tuple t appears n times in N and m times in M
- Union: n + m
- Intersection: min(n, m)
- Difference
- N\M: max(0, n - m)
- M\N: max(0, m - n)
Cartesian Product (Join)
- Cartesian Product 는 그냥 unconditioned Join 이다.
- Join 의 종류
- Natural join
- Theta join
- Semi-join
- Full outer join
- Right outer join
- Left outer join
Natural Join (R ⋈ S)
INNER JOIN
Cartesian Product, Selection, Projection 으로 Natural Join 을 구현 가능하다.

Theta θ-Joins (Theta-Joins)
- R⋈C S = σC (R × S), where c is a join condition
- It’s called equijoin if c contains only equality (=)
Semi-Join
LEFT INNER JOINRIGHT INNER JOIN
Extended Relational Algebra
- Operators
- Duplicate elimination
- Aggregation and grouping
- Sorting
- Outer join
Duplicate Elimination
- 중복 제거
- 단위가 Bag 라서 필요한 연산
Aggregation and grouping
SUM,AVG,MIN,MAX,COUNT
Elimination and grouping
- 그냥 grouping 한 것을 projection 한 것
Sorting
- 설명 생략
