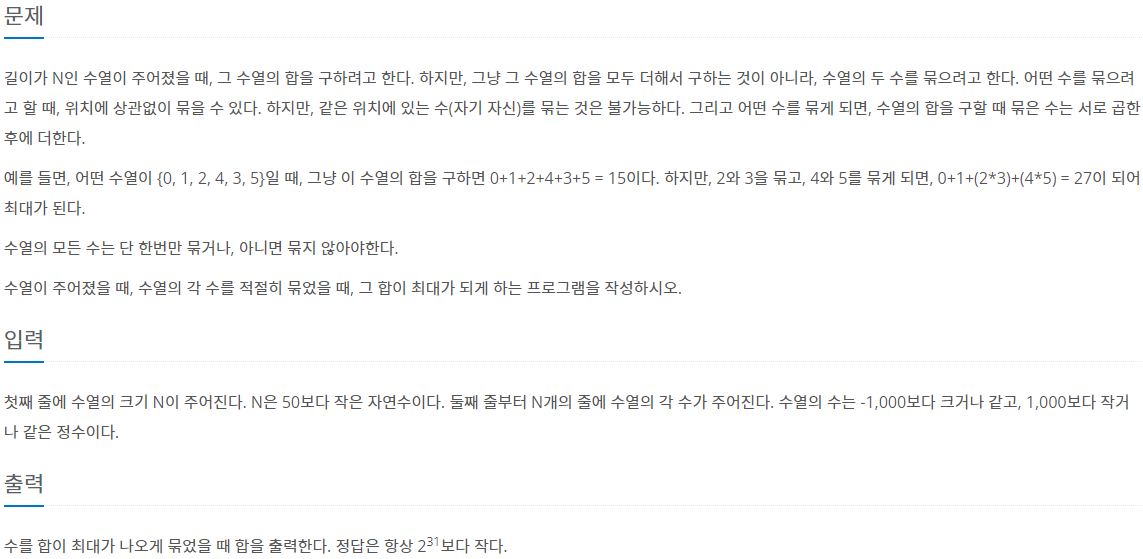
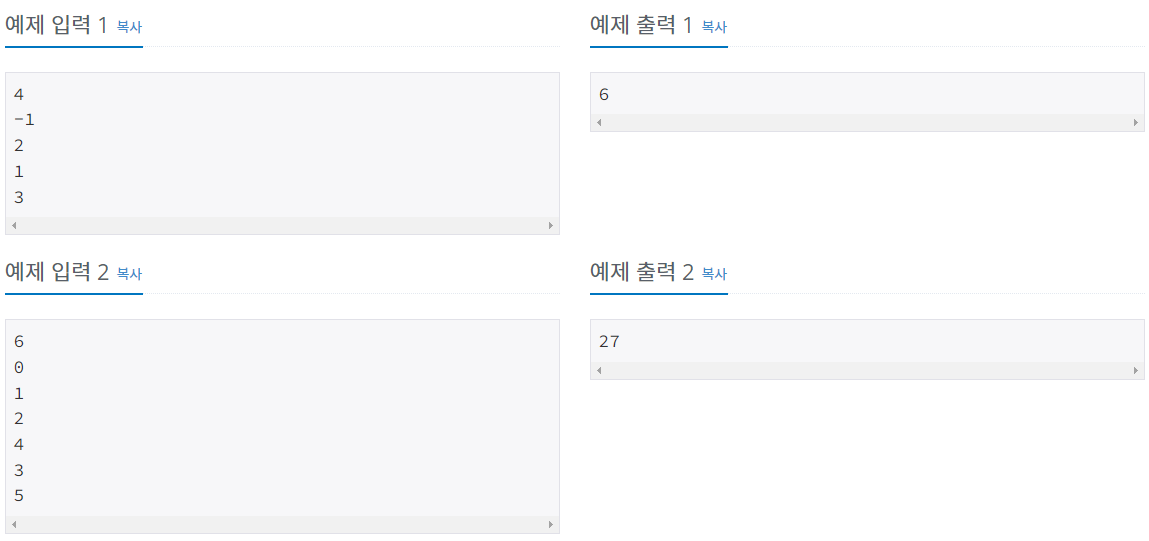
문제

풀이
public class Q1744_수묶기 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
// 양수의 경우 큰 수부터 묶어 연산해주는게 최대값을 구할 수 있으므로 내림차순으로 정렬
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b) -> {
return b - a;
});
// 음수의 경우 작은 값부터 묶어 곱하면 최대값을 만들 수 있으므로 오름차순 정렬
PriorityQueue<Integer> mq = new PriorityQueue<>();
int one = 0;
int zero = 0;
// 4가지 경우의 수로 나눠서 연산
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int tmp = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
// 1보다 클 때
if (tmp > 1) {
pq.add(tmp);
// 1일때
// 1은 곱하는 것보다 더하는게 더 큰 수를 만들 수 있음
} else if (tmp == 1) {
one++;
// 0일때
// 남은 음수와 0을 곱할 때 사용
} else if (tmp == 0) {
zero++;
// 음수일 때
} else {
mq.add(tmp);
}
}
int sum = 0;
// 양수의 경우부터 연산
while (pq.size() > 1) {
int a = pq.poll();
int b = pq.poll();
sum += a * b;
}
// 양수의 나머지 값 누적
if (!pq.isEmpty()) {
sum += pq.remove();
}
// 1의 개수만큼 누적
sum += one;
// 음수를 연산
while (mq.size() > 1) {
int a = mq.remove();
int b = mq.remove();
sum += a * b;
}
// 음수에 남은 수가 있을 때
if (!mq.isEmpty()) {
// 0이 남았다면
if (zero != 0) {
// 누적하지 않고 제거
mq.remove();
// 0이 없을 경우
} else {
// 결과에 누적
sum += mq.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}리뷰
내 풀이
4가지 경우의 수로 문제를 풀수 있었다.
- 1보다 큰 수의 경우
- 양수는 큰 수끼리 곱을 해야 최대값을 뽑을 수 있으므로 큰 순서대로 묶어주기 위해 내림차순 정렬을 해준다.
- 기본적으로 우선순위 큐는 오름차순으로 정렬을 하기 때문에 위의 풀이처럼 람다식을 이용해 정렬 방식을 바꿔주거나,
Collections.reverseOrder()를 이용해 내림차순 정렬로 바꿔주자.
- 1인 경우
- 1인 경우 곱을 하는 것보다 결과값에 누적을 해주는게 더 큰 값을 구할 수 있으므로 1의 개수는 따로 세준다.
- 0인 경우
- 음수의 개수가 홀수일 경우 값들을 묶고 나서는 음수가 하나 남게 되는데, 0이 있다면 0과 묶어 곱해줌으로 0으로 만들어준다.
- 음수의 경우
- 음수끼리 묶어 곱해주면 양수로 바뀌는데, 음수의 경우도 곱했을 때 큰 수가 나오도록 하기 위해 오름차순 정렬을 해준다.
- poll() vs remove()
둘 다 우선순위 큐의 최상위 값을 제거하고 반환하는 메서드인데
poll의 경우 null을 반환
remove의 경우 NoSuchElementException을 반환
