서론
앞선 mocking방식의 unit 테스트가 실제 db연동이 잘 되는지 확인하기 힘들고, TDD를 적용하기가 상당히 까다롭다는 판단 + 멘토님의 의견으로
unit 테스트 대신 e2e(end-to-end) 테스트를 작성하여 TDD를 하도록 전략을 바꿔 보았습니다.
TDD 방식은 흔히 사용되는 RED-GREEN-REFACTOR 방식을 학습하여 적용해 보았습니다.
간단히 설명드리자면 각 기능별로 다음의 순서로 개발을 진행하는 것입니다.
- 실패하는 테스트 코드 작성 (RED)
- 테스트가 통과하도록 구현 (GREEN)
- 코드 정리 (리팩토링, REFACTOR)
그럼 바로 가시죠
목표
e2e 방식의 TDD으로 다음의 이슈 해결
다음 이슈를 분석해 요구사항을 구체화하고 e2e 테스트로 만들자
- #12 [02-05] 서버는 아이디 중복을 검사하고 결과를 클라이언트에 전송한다.
- #16 [02-09] 서버는 회원가입 데이터를 받아 형식 검사와 아이디 중복검사를 진행한다.
- #17 [02-10] 검사에 통과하면 회원 정보를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
- #45 [06-08] 서버는 좋아요 / 좋아요 취소 요청을 받아 데이터베이스의 데이터를 수정한다.
- #39 [06-02] 서버는 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
- #60 [08-06] 서버는 전송 받은 데이터를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
- #65 [09-03] 서버는 검색된 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
Entity를 최소 컬럼으로 해서 CRUD를 구현한 후, 필요에 따라 컬럼을 추가하는 방식으로 구현
- 각 이슈에 요구되는 Entity의 최소 컬럼을 식별하고 구현하자
- SWAGGER로 API 명세 자동화!
체크리스트
- 이슈 분석
- board e2e, 실패하는 테스트 코드 작성 계획
- POST /board 실패하는 테스트 작성, 성공하도록 구현
- GET /board/:id (RED, GREEN, REFACTOR)
이슈 분석
auth 모듈과 관련 e2e 테스트 구상
- #12 [02-05] 서버는 아이디 중복을 검사하고 결과를 클라이언트에 전송한다.
- 회원 가입 전 아이디 중복 검사 버튼에 대한 처리
- GET /auth/check-available-username
- Request Parameters
- username: string
- Response JSON Properties
- success: boolean
- message: string
- #16 [02-09] 서버는 회원가입 데이터를 받아 형식 검사와 아이디 중복검사를 진행한다.
- #17 [02-10] 검사에 통과하면 회원 정보를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
- 회원가입 요청 처리. 하나의 API에서 validate 및 DB 저장 (#16, #17)
- POST /auth/register
- Request JSON Properties
- username: string
- password: string
- nickname: string
- Response JSON Properties
- success: boolean
- message: string
board 모듈과 관련 e2e 테스트 구상
- #45 [06-08] 서버는 좋아요 / 좋아요 취소 요청을 받아 데이터베이스의 데이터를 수정한다.
- 좋아요 업데이트. like, unlike 두 개의 API로 처리
- PUT /board/:id/like
- PUT /board/:id/unlike
- Request Parameters
- username: string
- Response JSON Properties
- like_cnt: number
- #39 [06-02] 서버는 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
- board id로 글 검색하여 전송 (findOne)
- GET /board/:id
- Response
- board: Board
- (추가 필요) 서버는 사용자의 글 목록을 전송한다.
- user로 필터링하여 글 목록 전송 (findAllBy)
- GET /board
- Response
- board: Board[]
- #60 [08-06] 서버는 전송 받은 데이터를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
- 작성한 글을 데이터베이스에 저장 (create, save)
- POST /board
- Request JSON Properties
- title: string
- content: string
- author: string
- Response
- board: Board
- #65 [09-03] 서버는 검색된 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
- 사용자 username으로 글 리스트 필터하여 전송 (findAllBy)
- GET /board/boards-by-author
- Request Parameters
- author: string
- Response
- boards: Board[]
- (추가 필요) 서버는 사용자의 요청에 따라 글을 수정한다.
- board id에 해당하는 글 수정
- PUT /board/:id
- Request Parameters
- title: string
- content: string
- author: string
- Response
- board: Board
- (추가 필요) 서버는 사용자의 요청에 따라 글을 삭제한다.
- board id에 해당하는 글 수정
- DELETE /board/:id
- Response JSON Properties
- success: boolean
방법론
학습메모 4를 참고하여, Red-Green-Refactor 방식을 준용해 보았다.
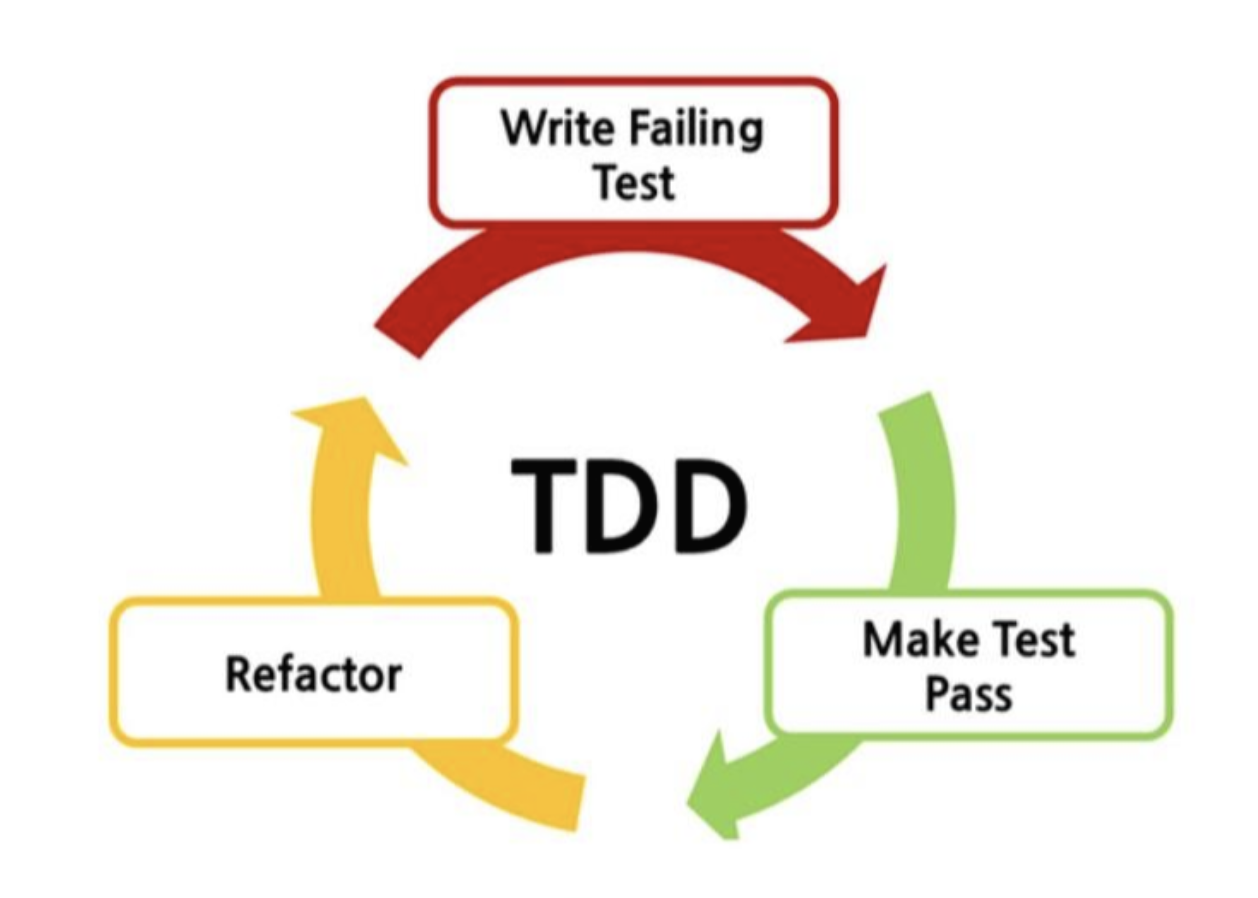
- Red (실패하는 테스트 코드 작성)
- Green (테스트를 통과하도록 구현)
- Refactor (리팩토링)
board e2e, 실패하는 테스트 코드 작성 계획
board가 단순 CRUD에 더 가까우므로 먼저 해보기로 했다.
test/board에 board.e2e-spec.ts 파일 생성
import { Test, TestingModule } from '@nestjs/testing';
import { INestApplication } from '@nestjs/common';
import * as request from 'supertest';
import { AppModule } from '../../src/app.module';
describe('BoardController (e2e)', () => {
let app: INestApplication;
beforeEach(async () => {
const moduleFixture: TestingModule = await Test.createTestingModule({
imports: [AppModule],
}).compile();
app = moduleFixture.createNestApplication();
await app.init();
});
describe('/board', () => {
// #39 [06-02] 서버는 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
it.todo('GET /board/:id');
// (추가 필요) 서버는 사용자의 글 목록을 전송한다.
it.todo('GET /board');
// #45 [06-08] 서버는 좋아요 / 좋아요 취소 요청을 받아 데이터베이스의 데이터를 수정한다.
it.todo('PUT /board/:id/like');
it.todo('PUT /board/:id/unlike');
// #60 [08-06] 서버는 전송 받은 데이터를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
it.todo('POST /board');
// #65 [09-03] 서버는 검색된 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
it.todo('GET /board/by-author');
// (추가 필요) 서버는 사용자의 요청에 따라 글을 수정한다.
it.todo('PUT /board/:id');
// (추가 필요) 서버는 사용자의 요청에 따라 글을 삭제한다.
it.todo('DELETE /board/:id');
});
});todo로 우선 요구사항 및 API 명세를 등록했다.
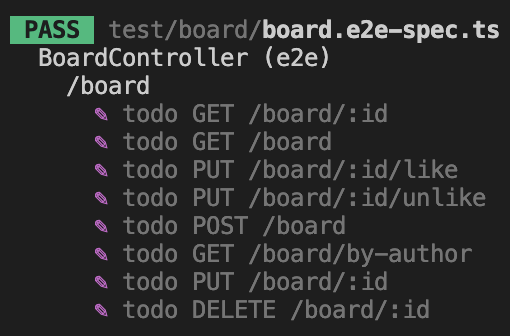
POST /board 실패하는 테스트 작성, 성공하도록 구현
실패하는 테스트 작성
POST /board에 대해 테스트 코드를 작성해보자.
// #60 [08-06] 서버는 전송 받은 데이터를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
it('POST /board', () => {
const board = {
title: 'test',
content: 'test',
author: 'test',
};
return request(app.getHttpServer())
.post('/board')
.send(board)
.expect(201, {
id: 1,
...board,
});
});yarn workspace server test '.../board.e2e-spec.ts'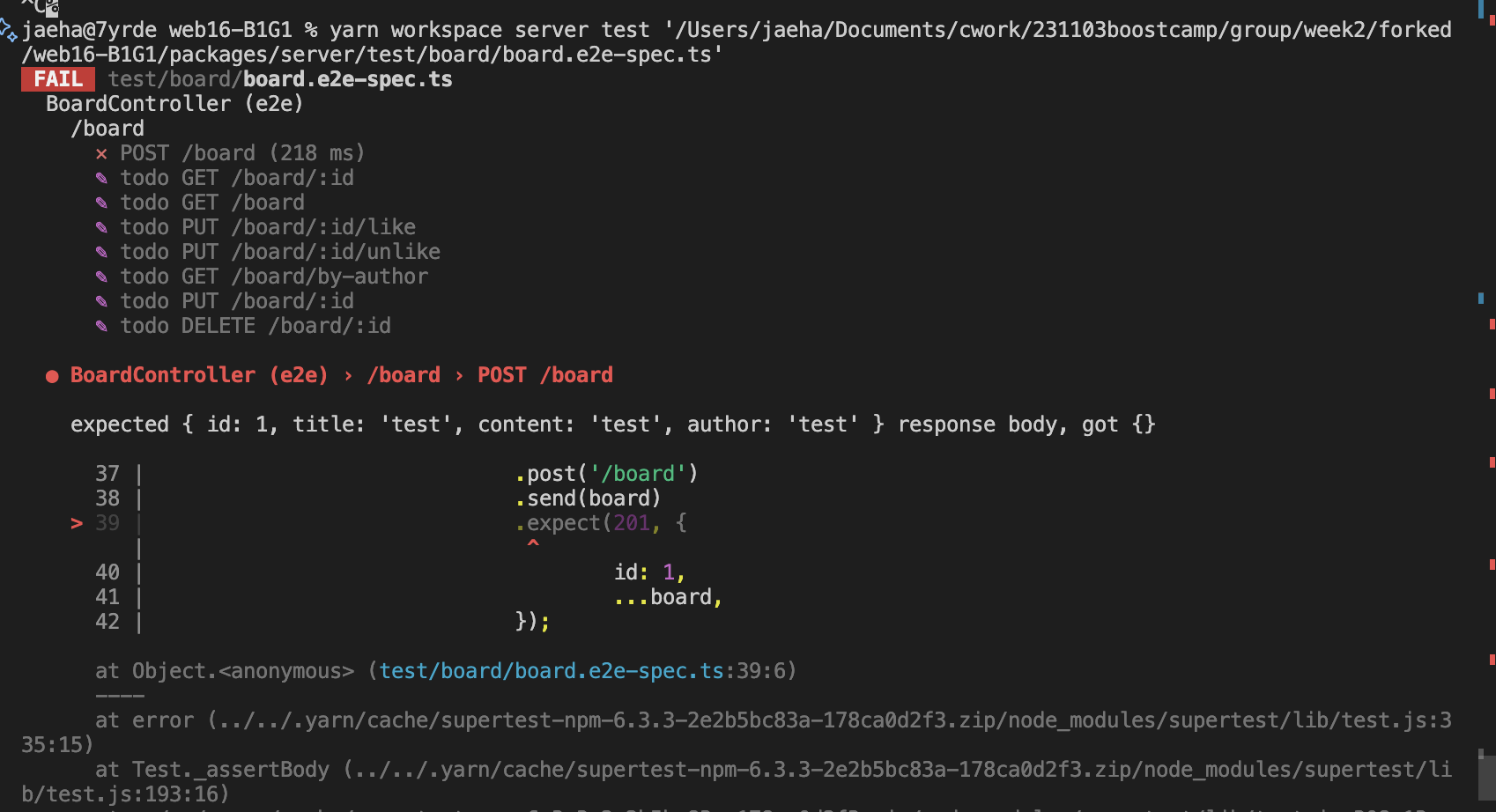
재밌는게 Nest에서 201 응답은 이미 처리해줘버림ㅋ 이제 여기를 통과하게 Entity랑 DTO 만들고 Controller, Service 코드를 수정해보자.
성공하도록 구현
// board.entity.ts
import { BaseEntity, Column, Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn } from 'typeorm';
@Entity()
export class Board extends BaseEntity {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column({ type: 'varchar', length: 255, nullable: false })
title: string;
@Column({ type: 'text', nullable: true })
content: string;
@Column({ type: 'varchar', length: 50, nullable: false })
author: string;
@Column({ type: 'timestamp', default: () => 'CURRENT_TIMESTAMP' })
created_at: Date;
@Column({ type: 'timestamp', default: () => 'CURRENT_TIMESTAMP' })
updated_at: Date;
}// create-board.dto.ts
export class CreateBoardDto {
title: string;
content: string;
author: string;
}이제 컨트롤러, 서비스를 수정해주자. DB까지 연동!
// board.controller.ts
@Controller('board')
export class BoardController {
constructor(private readonly boardService: BoardService) {}
@Post()
create(@Body() createBoardDto: CreateBoardDto): Promise<Board> {
return this.boardService.create(createBoardDto);
}
...
}// board.service.ts
...
@Injectable()
export class BoardService {
constructor(
@InjectRepository(Board)
private boardRepository: Repository<Board>,
) {}
async create(createBoardDto: CreateBoardDto): Promise<Board> {
const { title, content, author } = createBoardDto;
const board = await this.boardRepository.create({
title,
content,
author,
});
const created: Board = await this.boardRepository.save(board);
return created;
}
...
}repository도 주입해주고, 생성한 Board 인스턴스를 리턴하도록 해 id값을 얻을 수 있게 해줬다.
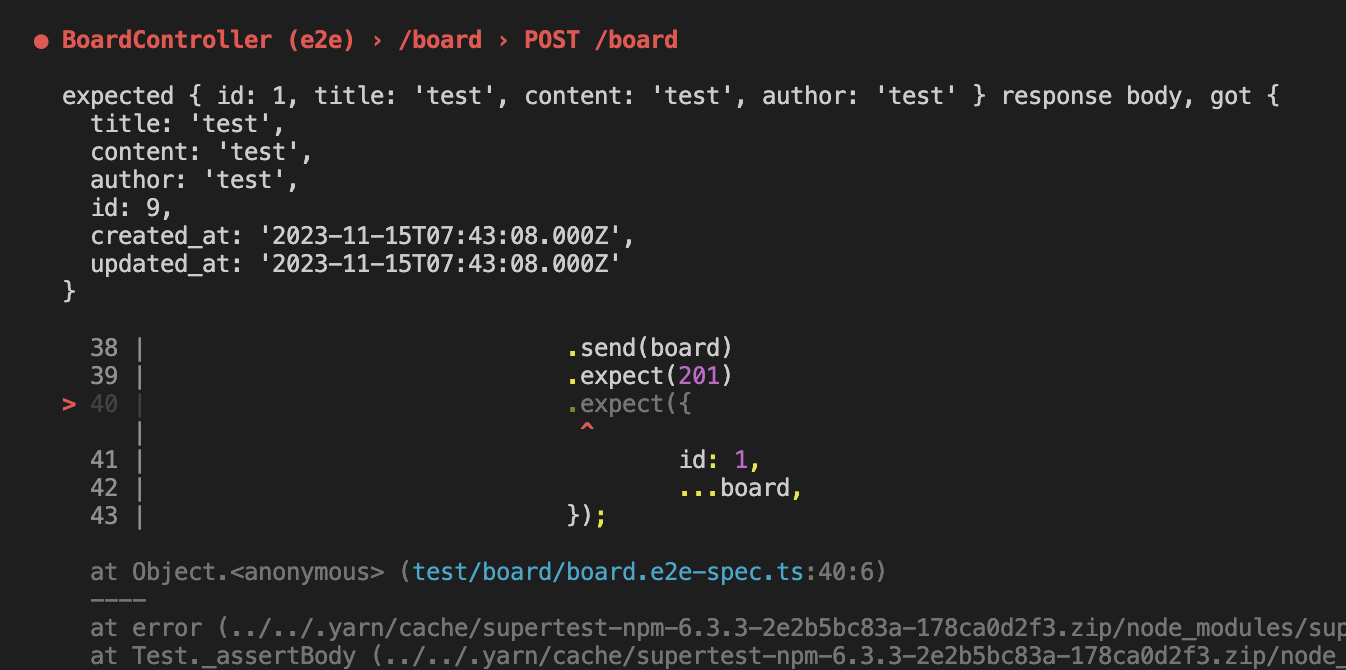
여기까지 테스트하니 id를 1으로 고정시켜놓은 것도 그렇고, created_at 등 추가된 컬럼과
앞으로 추가될 컬럼까지 고려해서 수정하지 않아도 되는 테스트를 만들고 싶었다.
// #60 [08-06] 서버는 전송 받은 데이터를 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
it('POST /board', async () => {
const board = {
title: 'test',
content: 'test',
author: 'test',
};
const response = await request(app.getHttpServer())
.post('/board')
.send(board)
.expect(201);
expect(response).toHaveProperty('body');
expect((response as any).body).toMatchObject(board);
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('id');
expect(typeof response.body.id).toBe('number');
});그래서 위와 같이 테스트코드를 수정함.
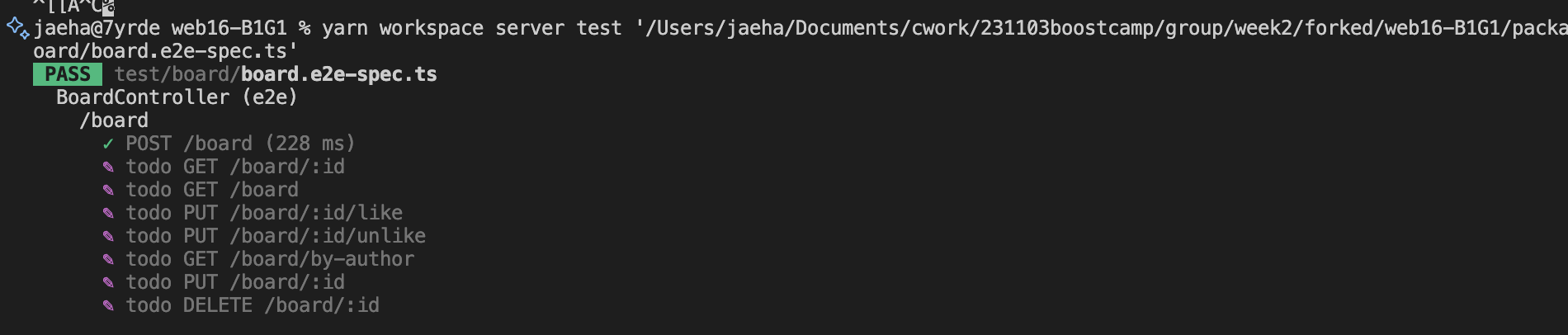
아름답게 통과된다! 리팩토링은 따로 필요없을 것 같아 생략.
GET /board/:id
이후부터는 방법론 명칭대로 다음과 같이 간략히 기재하겠음.
- RED : 실패하는 테스트코드 작성
- GREEN : 테스트 통과하도록 구현
- REFACTOR : 리팩토링
RED
// board.e2e-spec.ts
// #39 [06-02] 서버는 사용자의 글 데이터를 전송한다.
it('GET /board/:id', async () => {
const response = await request(app.getHttpServer())
.get('/board/1')
.expect(200);
expect(response).toHaveProperty('body');
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('id');
expect(response.body.id).toBe(1);
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('title');
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('content');
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('author');
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('created_at');
expect((response as any).body).toHaveProperty('updated_at');
});실패하는 테스트 코드를 작성해준다.
id가 일치해야 하며, 다음 기대되는 속성들을 받아올 수 있어야 함:
id, title, content, author, created_at, updated_at
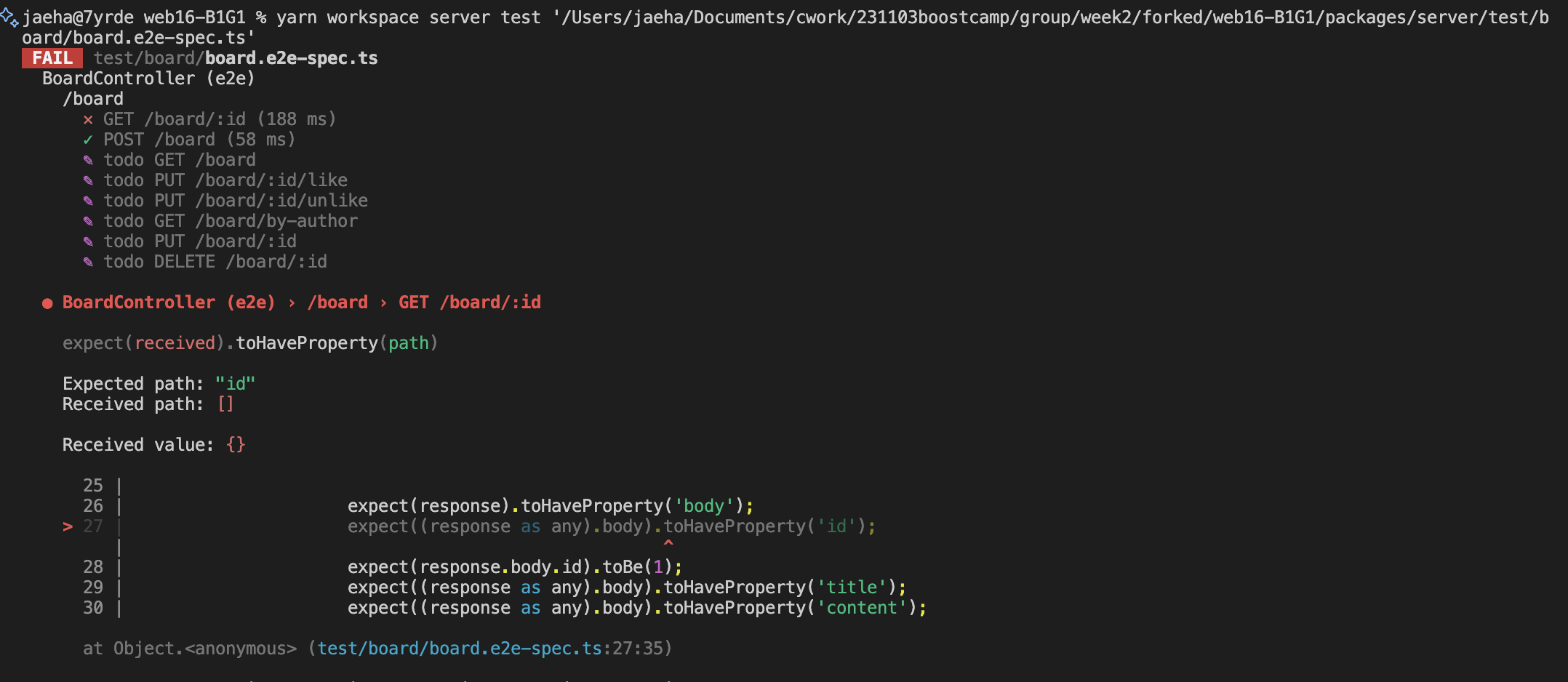
GREEN
// board.service.ts
async findOne(id: number) {
const found: Board = await this.boardRepository.findOneBy({ id });
return found;
}서비스 메소드인 findOne()을 위와 같이 수정해주면 된다.
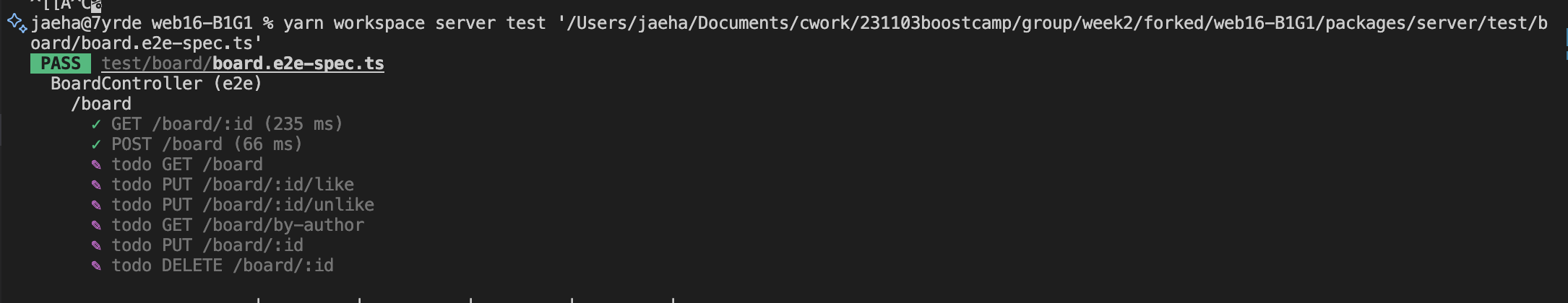
REFACTOR
예외처리와 적절한 함수이름으로의 변경, 타입 명시 등을 추가로 처리해줬다.
참고로 입력값에 대한 유효성 검증 등은 기본기능 구현 후 추가할 예정.
// board.controller.ts
@Get(':id')
getBoardById(@Param('id') id: string): Promise<Board> {
return this.boardService.getBoardById(+id);
}// board.service.ts
async getBoardById(id: number): Promise<Board> {
const found: Board = await this.boardRepository.findOneBy({ id });
if (!found) {
throw new NotFoundException(`Not found board with id: ${id}`);
}
return found;
}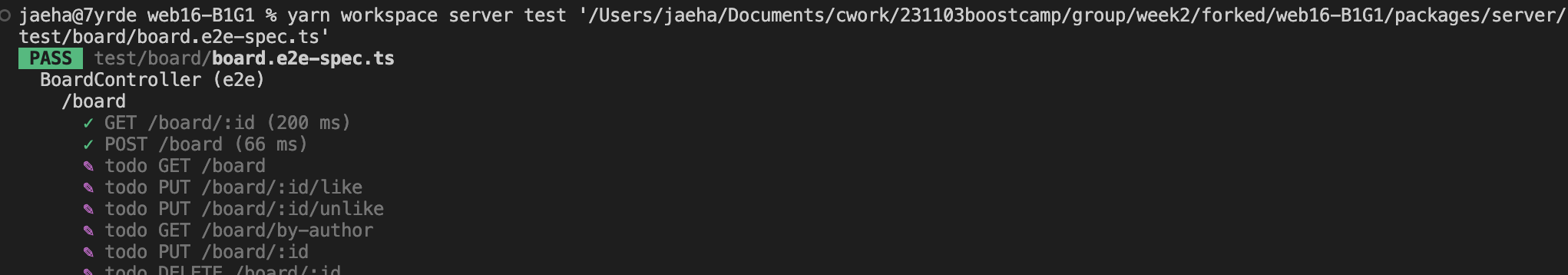
통과는 마찬가지로 잘 된다.
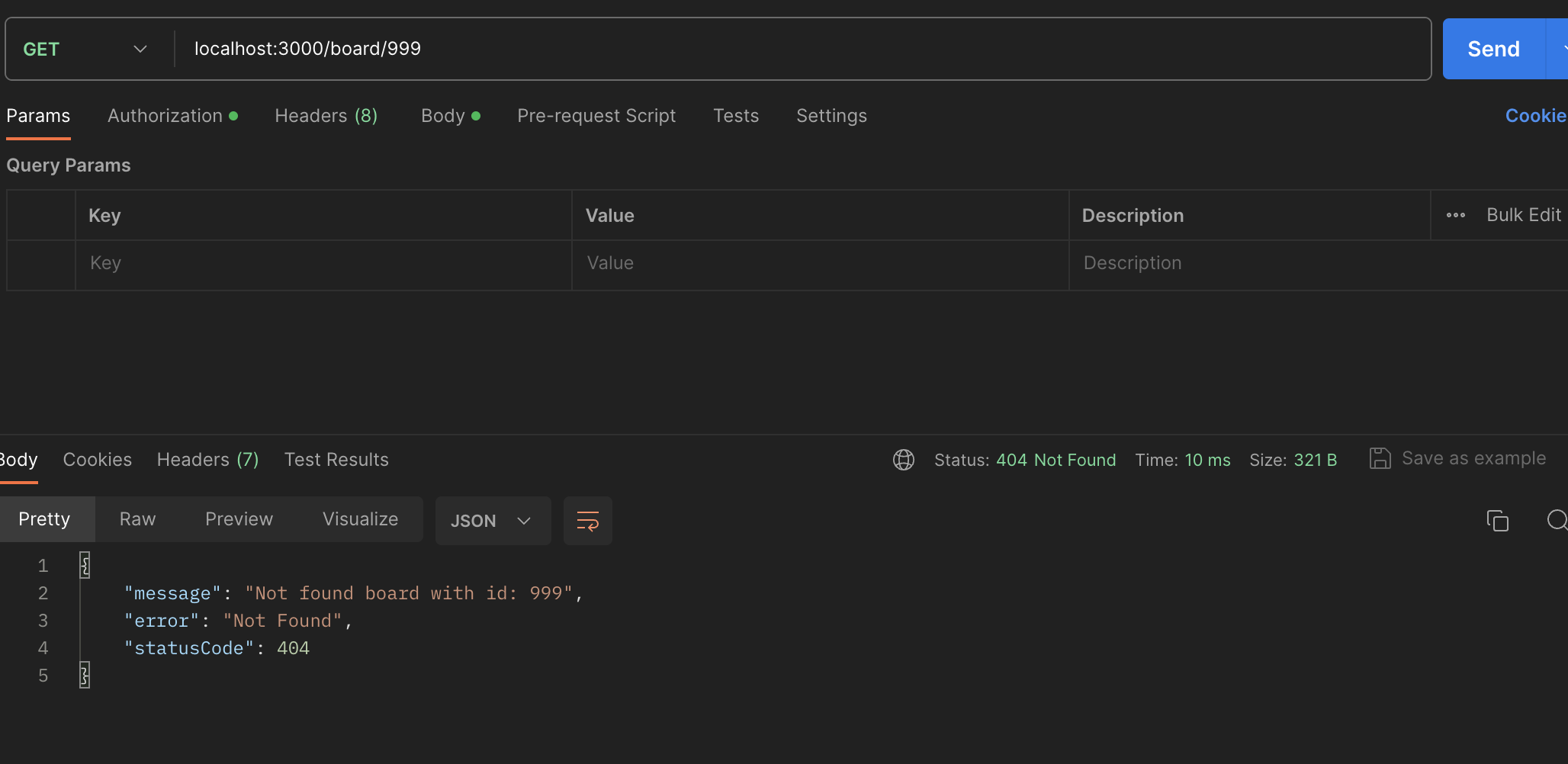
Not Found Exception 처리도 확인 (이것도 추후 테스트 추가해주면 좋을 듯 하다)
