트리란?
비선형(순차적이지 않은)구조의 자료구조로써 계층적인구조를 갖는 자료구조이다.
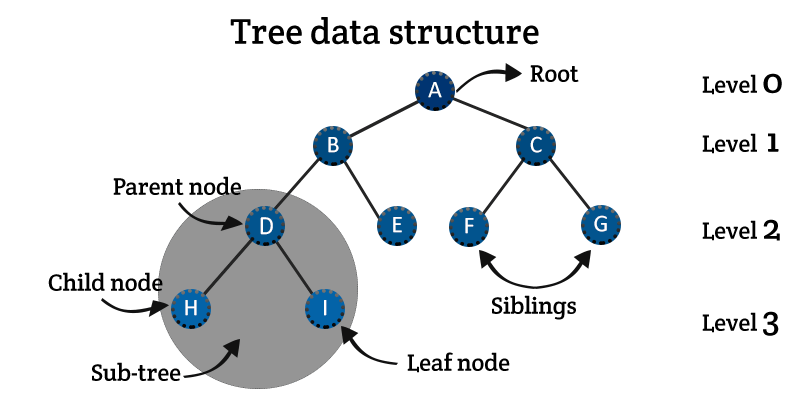
트리구조에서 최상위에 노드를 Root라고 하며, 이 Root로 부터 child그리고 마지막으로 leaf까지 가지치기한다.
이 Root 아래에는 값을 가진 노드들이 존재하며 노드와 노드사이는 link(edge)로 이어져있다.
트리의 특징
recursive data strucutre
트리는 특정 노드인 root와 몇 가지 sub-tree들로 이루어진 재귀적 구조이다.
n개의 노드 = n-1 엣지
Root를 제외한 모든 노드는 1개의 incoming edge가 있다.
그렇기 때문에 n개의 노드가 있다면 엣지는 n-1개 가 있다.
Depth & Height
Depth
: Root로 부터 노드 x까지의 경로의 길이이다.
(= Root로 부터 노드 x까지의 엣지의 수)
Height
: 노드 x로 부터 leaf 노드까지의 엣지의 수
활용사례
트리구조는 Maps, Sets, Databases, Queues, DOM(Document Object Model)등 여러곳에서 사용된다.
Storing naturally : 계층적 구조 ex.파일시스템
organize data : 퀵서치, 삽입, 삭제 ex.이진탐색트리
Tries : ex.사전
Network Routing Algorithm
트리 by JS
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.descendents = [];
}
}// create nodes with values
const abe = new TreeNode('Abe');
const homer = new TreeNode('Homer');
const bart = new TreeNode('Bart');
const lisa = new TreeNode('Lisa');
const maggie = new TreeNode('Maggie');
// associate root with is descendents
abe.descendents.push(homer);
homer.descendents.push(bart, lisa, maggie);
이진트리
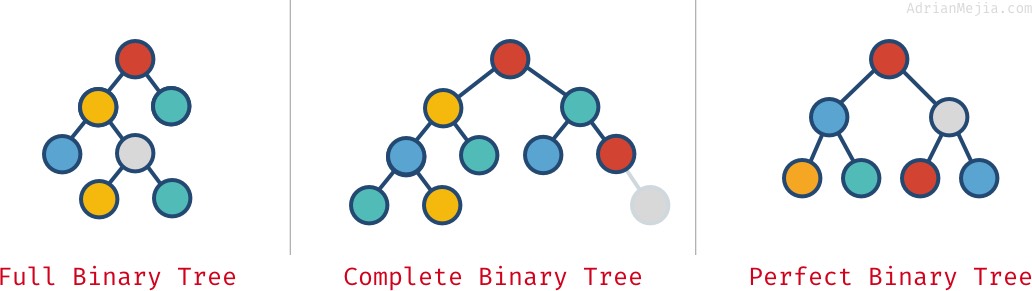
가장 많은 자식을 갖으면 자식의 수가 두개일 경우 binary tree이다.
종류는 Full, Complete, Perfect binary tree가 있다.
-
Full binary tree : 각 노드가 정확히 0 혹은 2개의 자식을 갖는 경우
-
Complete binary tree : 마지막 노드빼고 모든 레벨의 노드들이 full일 경우
-
Perfect binary tree : 모든 레벨의 노드들이 full일 경우
아래의 특징들은 중복될 수도 있다. -
A perfect tree is always complete and full
Perfect binary trees는 정확히 2k-1의 노드를 갖는다.
*k는 마지막 레벨의 트리(1부터 시작한다는 가정하에) -
A complete tree is not always full
위 사진의 Complete 예처럼, 하나의 child를 갖는 부모도 있다. 만약 이 노드를 제거하게 되면, complete & full tree가 되지만 perfect는 아니다. -
A full tree is not always complete and perfect
이진탐색트리
노드는 최대 2가지의 child를 갖는다(right/left)
노드의 값은 left < parent < right 순으로 정렬된다.
기존에 만들었던 트리구조와 비슷하지만 약간의 코드가 추가된다.
const LEFT = 0;
const RIGHT = 1;
class TreeNode {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.descendents = [];
this.parent = null;
}
get left() {
return this.descendents[LEFT];
}
set left(node) {
this.descendents[LEFT] = node;
if (node) {
node.parent = this;
}
}
get right() {
return this.descendents[RIGHT];
}
set right(node) {
this.descendents[RIGHT] = node;
if (node) {
node.parent = this;
}
}
}
left > parent > right 규칙을 적용할 수 있는 클래스를 생성한다.
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
this.size = 0;
}
add(value) { /* ... */ }
find(value) { /* ... */ }
remove(value) { /* ... */ }
getMax() { /* ... */ }
getMin() { /* ... */ }
}BST Node Insertion
이진트리에 노드를 추가하기 위해선, 아래와 같이 진행해야한다.
- 트리가 비었다면, 첫 번째 노드는 root가 될 것이다.
- root/부모의 값과 비교해서 크다면 오른쪽, 작다면 왼쪽으로 간다.
만약 값이 같다면 중복 카운트를 증가시킬 수 있다. - 빈 공간에 새로운 노드가 들어갈 때 까지 2번을 계속 반복한다.
add(value) {
const newNode = new TreeNode(value);
if (this.root) {
const { found, parent } = this.findNodeAndParent(value);
if (found) { // duplicated: value already exist on the tree
found.meta.multiplicity = (found.meta.multiplicity || 1) + 1;
} else if (value < parent.value) {
parent.left = newNode;
} else {
parent.right = newNode;
}
} else {
this.root = newNode;
}
this.size += 1;
return newNode;
}findNodeAndParent라는 함수를 이용해 트리의 노드가 이미 존재한다면 multiplicity 카운터를 증가 시킬것이다.
findNodeAndParent(value) {
let node = this.root;
let parent;
while (node) {
if (node.value === value) {
break;
}
parent = node;
node = ( value >= node.value) ? node.right : node.left;
}
return { found: node, parent };
}
findNodeAndParent 함수는 root부터 시작해서 값이 오른쪽/왼쪽 어디로 갈지 결정한다.
만약 값이 이미있다면 found 노드와 부모를 리턴해준다.
노드가 존재하지 않는다면 부모를 리턴해준다.
BST Node Deletion
노드를 추가하는것보다 약간 까다롭다.
Deleting a leaf node(0 children)
30 30
/ \ remove(12) / \
10 40 ---------> 10 40
\ / \ \ / \
15 35 50 15 35 50
/
12*부모 노드의 참조값을 null로 해주면 된다.
Deleting a node with one child
30 30
/ \ remove(10) / \
10* 40 ---------> 15 40
\ / \ / \
15 35 50 35 50부모노드(30)으로 가서 자식노드를 15로 바꿔준다.
Deleting a node with two children
30 30
/ \ remove(40) / \
15 40* ---------> 15 50
/ \ /
35 50 35부모노드(30)의 자식(40)과 40의 자식의 오른쪽(50)을 바꿔준다. 왼쪽 자식(35)를 같은자리에 두고, 50의 왼쪽 자식으로 만들어준다.
30
/ \
15 35
\
5040을 지워주고, 왼쪽 자식(35)를 위로 올려주고 오른쪽 자식을 그대로 납두는 경우도 있다.
트리구조의 특징인 left < parent < right만 지켜주면 둘다 상관없다.
Deleting the root
30* 50
/ \ remove(30) / \
15 50 ---------> 15 35
/
35root를 삭제하는 경우는 위에서 봤던 삭제와 매우 비슷하다.
한가지의 차이점은 root의 참조를 수정해줘야 하는 것이다.
remove(value) {
const nodeToRemove = this.find(value);
if (!nodeToRemove) return false;
// Combine left and right children into one subtree without nodeToRemove
const nodeToRemoveChildren = this.combineLeftIntoRightSubtree(nodeToRemove);
if (nodeToRemove.meta.multiplicity && nodeToRemove.meta.multiplicity > 1) {
nodeToRemove.meta.multiplicity -= 1; // handle duplicated
} else if (nodeToRemove === this.root) {
// Replace (root) node to delete with the combined subtree.
this.root = nodeToRemoveChildren;
this.root.parent = null; // clearing up old parent
} else {
const side = nodeToRemove.isParentLeftChild ? 'left' : 'right';
const { parent } = nodeToRemove; // get parent
// Replace node to delete with the combined subtree.
parent[side] = nodeToRemoveChildren;
}
this.size -= 1;
return true;
}- 노드 존재여부를 먼저 체크하고, 존재하지않으면 false를 리턴하고 끝낸다.
- 삭제할 노드가 존재한다면, 오른쪽이나 왼쪽 자식을 서브트리로 결합시켜야한다.
- 결합한 서브트리를 위해 노드를 대체해야 한다.
왼쪽을 오른쪽 서브트리로 결합시키는 함수는
combineLeftIntoRightSubtree(node) {
if (node.right) {
const leftmost = this.getLeftmost(node.right);
leftmost.left = node.left;
return node.right;
}
return node.left;
}아래 코드에서 트리를 합치고 노드 30을 지운다면, 30의 왼쪽 서브 트리를 오른쪽으로 합치길 원한다면
30* 40
/ \ / \
10 40 combine(30) 35 50
\ / \ -----------> /
15 35 50 10
\
15이제 새로운 루트의 서브트리를 만들고, 30은 더이상 존재하지 않는다.