출처 | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5JrEcPwwRFU&list=PLOSNUO27qFbtjCw-YHcmtfZAkE79HZSOO&index=55
함수형 프로그래밍의 이해(1/2)
-
함수형 프로그래밍을 이해하기 위해서는 우선 명령형(imperative) 프로그래밍과 선언형(declarative) 프로그래밍에 대한 이해가 필요하다.
-
명령형 프로그래밍은 특정 기능을 수행하기 위해 어떻게(How)에 집중하는 방식하다.
-
선언형 프로그래밍은 특정 기능을 수행하기 위해 무엇(what)에 집중하는 방식을 의미한다.
-
함수형 프로그래밍은 선언형 프로그래밍을 따르는 대표적인 프로그래밍 패러다임이다.

함수형 프로그래밍의 이해(2/2)
-
함수형 프로그래밍은 함수들의 집합으로 프로그램을 구성하는 것을 의미한다.
-
자바는 함수형 프로그래밍 도입은 프로그램 구현 방식에 큰 변화를 가져왔다.
-
함수형 프로그래밍의 함수는 순수 함수(Pure Function), 일급 객체(First-Class), 불변의 자료구조 혹은 영속 자료구조 등과 같은 특성을 갖는다.
- 순수함수 :
-
함수의 수행 결과는 오로지 입력에 따라 결정
-
함수의 실행에 따른 부수효과(side-effect)가 발생하지 않음.
- 일급객체
-
함수를 변수 혹은 특정 데이터 구조에 담을 수 있음
-
함수를 파라미터를 통해 전달할 수 있고, 결과로 반환 할 수 있다.
- 영속 자료구조
- 특정 변수/객체의 자료를 직접 변경하지 않고 새로운 인스턴스를 통해 의도하지 않은 변경을 방지
람다(Lambda)의 이해와 활용 (1/5) - 개요(1/2)
-
Java 8에서 가장 중요한 변화라 할 수 있는 람다 표현식의 등장은 불필요한 코드를 줄이고, 코드의 이해를 돕는다.
-
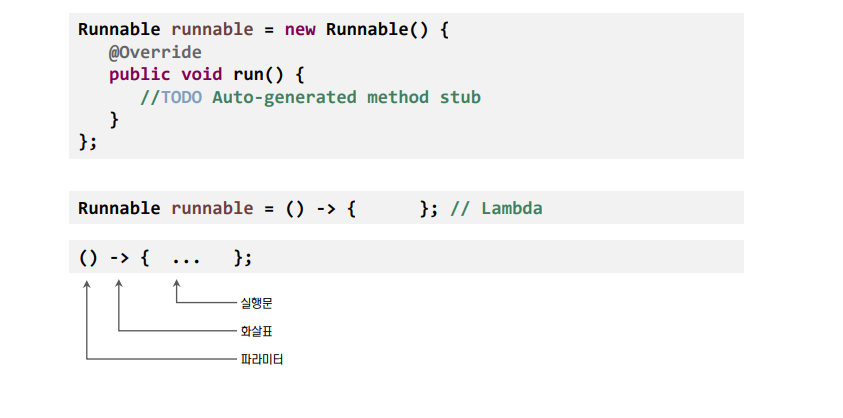
람다 표현식은 메소드로 전달할 수 있는 익명 함수를 단순화한 코드의 블록이다.
-
람다 표현식은 특정 클래스에 종속되지 않으며 함수라는 이름으로 명명한다.
-
람다 표현식은 함수 자체를 전달 인자로 보내거나 변수에 저장하는 것이 가능하다.
예제 Step-1
Gender
package com.home_object;
public enum Gender {
Male, Female
}
FunctionalAssist
package com.home_object;
import java.util.List;
public class FunctionalAssist {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomerService service = new CustomerService();
initData(service);
// 요구사항 1. 지역으로 검색한다.
List<Customer> result = service.searchCustomersByLocation("Seoul");
for(Customer cus : result)
{
System.out.println(cus);
}
}
private static void initData(CustomerService service)
{
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS01","Seoul",Gender.Male , 30));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS02","Busan",Gender.Female , 55));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS03","Seoul",Gender.Female , 13));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS04","Gwangju",Gender.Male , 27));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS05","Gwangju",Gender.Female , 61));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS06","Incheon",Gender.Male , 29));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS07","Seoul",Gender.Male , 42));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS08","Seoul",Gender.Female , 45));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS09","Seoul",Gender.Female , 33));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS10","Busan",Gender.Male , 20));
}
}
----------------------------------------------
Customer [id=CUS01, location=Seoul, gender=Male, age=30]
Customer [id=CUS03, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=13]
Customer [id=CUS07, location=Seoul, gender=Male, age=42]
Customer [id=CUS08, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=45]
Customer [id=CUS09, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=33]CustomerService
package com.home_object;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomerService {
private List<Customer> customers;
public CustomerService() {this.customers = new ArrayList<>();}
public void addCustomer (Customer newCustomer) {this.customers.add(newCustomer);}
// 요구사항 1) 지역으로 검색한다.
/*
* 같은 지역에 사는 customer들을 찾아서 반환하기 위한 foundCustomers 리스트 선언
* 반복문을 돌면서 customer의 로테이션 값을 얻으면서 그 받은 값이 == location이 같냐?
* 같으면 foundCustomers.add로 해서 더한다.
* 그래서 마지막은 foundCustomers를 반환한다.
*/
public List<Customer> searchCustomersByLocation(String location)
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(customer.getLocation().equals(location))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
}
Customer
package com.home_object;
public class Customer {
private String id;
private String location;
private Gender gender;
private int age;
public Customer(String id, String location, Gender gender, int age)
{
this.id = id;
this.location = location;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public Gender getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Gender gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [id=" + id + ", location=" + location + ", gender=" + gender + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
// @Override
// public String toString() {
// StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
// return builder.append(id).append(" : "),
// append(location).append(" : "),
// append(gender).append(" : "),
// append(age).toString();
//
// }
//
//
}
예제 Step2
- 요구사항 2) 성별을 통해서 검색을 하고 싶다.
CustomerService
package com.home_object;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomerService {
private List<Customer> customers;
public CustomerService() {this.customers = new ArrayList<>();}
public void addCustomer (Customer newCustomer) {this.customers.add(newCustomer);}
/*
* 같은 지역에 사는 customer들을 찾아서 반환하기 위한 foundCustomers 리스트 선언
* 반복문을 돌면서 customer의 로테이션 값을 얻으면서 그 받은 값이 == location이 같냐?
* 같으면 foundCustomers.add로 해서 더한다.
* 그래서 마지막은 foundCustomers를 반환한다.
*/
// 요구사항 1) 지역으로 검색한다.
public List<Customer> searchCustomersByLocation(String location)
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(customer.getLocation().equals(location))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
//요구사항 2) 성별로 검색한다.
public List<Customer> searchCustomerByGender(Gender gender)
{
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(customer.getGender().equals(gender))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
}
}
searchCustomerByGender
public List<Customer> searchCustomerByGender(Gender gender)
{
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(customer.getGender().equals(gender))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
FunctionalAssist
package com.home_object;
import java.util.List;
public class FunctionalAssist {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomerService service = new CustomerService();
initData(service);
// 요구사항 1. 지역으로 검색한다.
List<Customer> result = service.searchCustomersByLocation("Seoul");
for(Customer cus : result)
{
System.out.println(cus);
}
//요구사항 2. 성별로 검색 -> CustomerService 에 들어가서 성별로 검색하는 메소드를 만든다.
List<Customer> result1 = service.searchCustomerByGender(Gender.Female);
System.out.println("======================성별 추가====================");
for(Customer cus:result1)
{
System.out.println(cus);
}
}
private static void initData(CustomerService service)
{
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS01","Seoul",Gender.Male , 30));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS02","Busan",Gender.Female , 55));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS03","Seoul",Gender.Female , 13));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS04","Gwangju",Gender.Male , 27));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS05","Gwangju",Gender.Female , 61));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS06","Incheon",Gender.Male , 29));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS07","Seoul",Gender.Male , 42));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS08","Seoul",Gender.Female , 45));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS09","Seoul",Gender.Female , 33));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS10","Busan",Gender.Male , 20));
}
}
---------------------------------------------
Customer [id=CUS01, location=Seoul, gender=Male, age=30]
Customer [id=CUS03, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=13]
Customer [id=CUS07, location=Seoul, gender=Male, age=42]
Customer [id=CUS08, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=45]
Customer [id=CUS09, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=33]
======================성별 추가====================
Customer [id=CUS02, location=Busan, gender=Female, age=55]
Customer [id=CUS03, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=13]
Customer [id=CUS05, location=Gwangju, gender=Female, age=61]
Customer [id=CUS08, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=45]
Customer [id=CUS09, location=Seoul, gender=Female, age=33]
+ 추가적인 요구사항이 발생하게 되면 일일이 대응하기 힘들다. 여러가지의 상황이 발생할 때마다 여러 사항의 메서드가 아니라, 하나의 메소드를 만들어놓고 파라미터로 어떤 값을 원하는지를 구현하면 된다.
Step3
FunctionalAssist
package com.home_object;
import java.util.List;
public class FunctionalAssist {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CustomerService service = new CustomerService();
initData(service);
// 요구사항 1. 지역으로 검색한다.
List<Customer> result = service.searchCustomersByLocation("Seoul");
// for(Customer cus : result)
// {
// System.out.println(cus);
// }
// //요구사항 2. 성별로 검색 -> CustomerService 에 들어가서 성별로 검색하는 메소드를 만든다.
// List<Customer> result1 = service.searchCustomerByGender(Gender.Female);
// System.out.println("======================성별 추가====================");
// for(Customer cus:result1)
// {
//
// System.out.println(cus);
// }
result = service.searchCustomersBy(SearchOption.Location, "Busan");
for(Customer cus : result)
{
System.out.println(cus);
}
}
private static void initData(CustomerService service)
{
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS01","Seoul",Gender.Male , 30));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS02","Busan",Gender.Female , 55));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS03","Seoul",Gender.Female , 13));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS04","Gwangju",Gender.Male , 27));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS05","Gwangju",Gender.Female , 61));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS06","Incheon",Gender.Male , 29));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS07","Seoul",Gender.Male , 42));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS08","Seoul",Gender.Female , 45));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS09","Seoul",Gender.Female , 33));
service.addCustomer(new Customer("CUS10","Busan",Gender.Male , 20));
}
}
CustomerService
package com.home_object;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomerService {
private List<Customer> customers;
public CustomerService() {this.customers = new ArrayList<>();}
public void addCustomer (Customer newCustomer) {this.customers.add(newCustomer);}
/*
* 같은 지역에 사는 customer들을 찾아서 반환하기 위한 foundCustomers 리스트 선언
* 반복문을 돌면서 customer의 로테이션 값을 얻으면서 그 받은 값이 == location이 같냐?
* 같으면 foundCustomers.add로 해서 더한다.
* 그래서 마지막은 foundCustomers를 반환한다.
*/
// 요구사항 1) 지역으로 검색한다.
public List<Customer> searchCustomersByLocation(String location)
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(customer.getLocation().equals(location))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
//요구사항 2) 성별로 검색한다.
public List<Customer> searchCustomerByGender(Gender gender)
{
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(customer.getGender().equals(gender))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
}
// 하나의 메소드로 간다.
public List<Customer> searchCustomersBy(SearchOption searchOption, String searchValue)
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(searchOption.equals(SearchOption.Location))
{
if (customer.getLocation().equals(searchValue))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
else if(searchOption.equals(SearchOption.Gender));
{
if(customer.getGender().name().equals(searchValue))
{
}
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
}
+
public List<Customer> searchCustomersBy(SearchOption searchOption, String searchValue)
{
List<Customer> foundCustomers = new ArrayList<>();
for(Customer customer : customers)
{
if(searchOption.equals(SearchOption.Location))
{
if (customer.getLocation().equals(searchValue))
{
foundCustomers.add(customer);
}
}
else if(searchOption.equals(SearchOption.Gender));
{
if(customer.getGender().name().equals(searchValue))
{
}
}
}
return foundCustomers;
}
}
