
1546
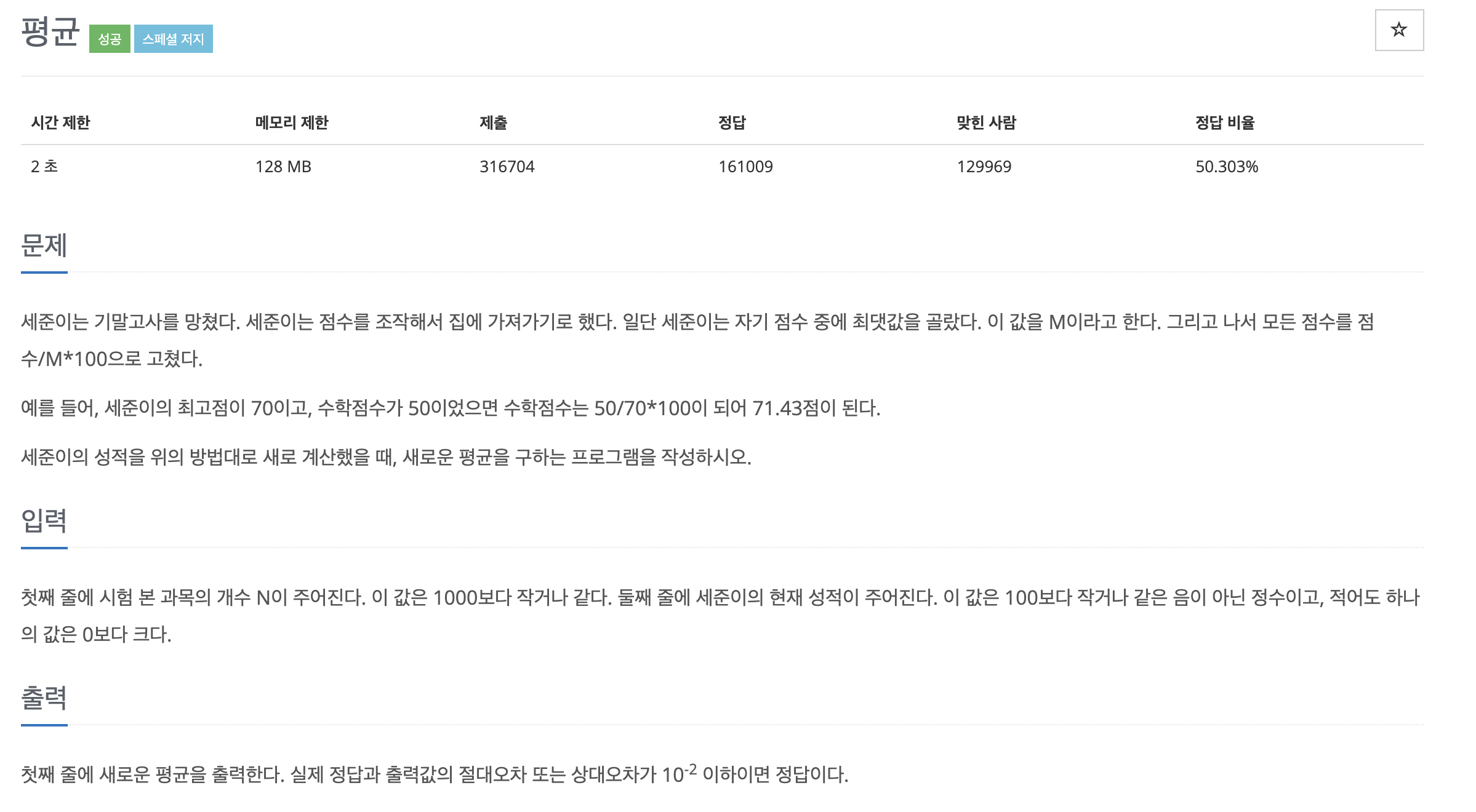
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[] subjects = new int[N];
int max = 0;
double sum = 0.0; // 실수로 변경하여 정수 나눗셈 문제 해결
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
subjects[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (subjects[i] > max) {
max = subjects[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
sum += (double) subjects[i] / max * 100;
}
System.out.println(sum / N);
}
}27866
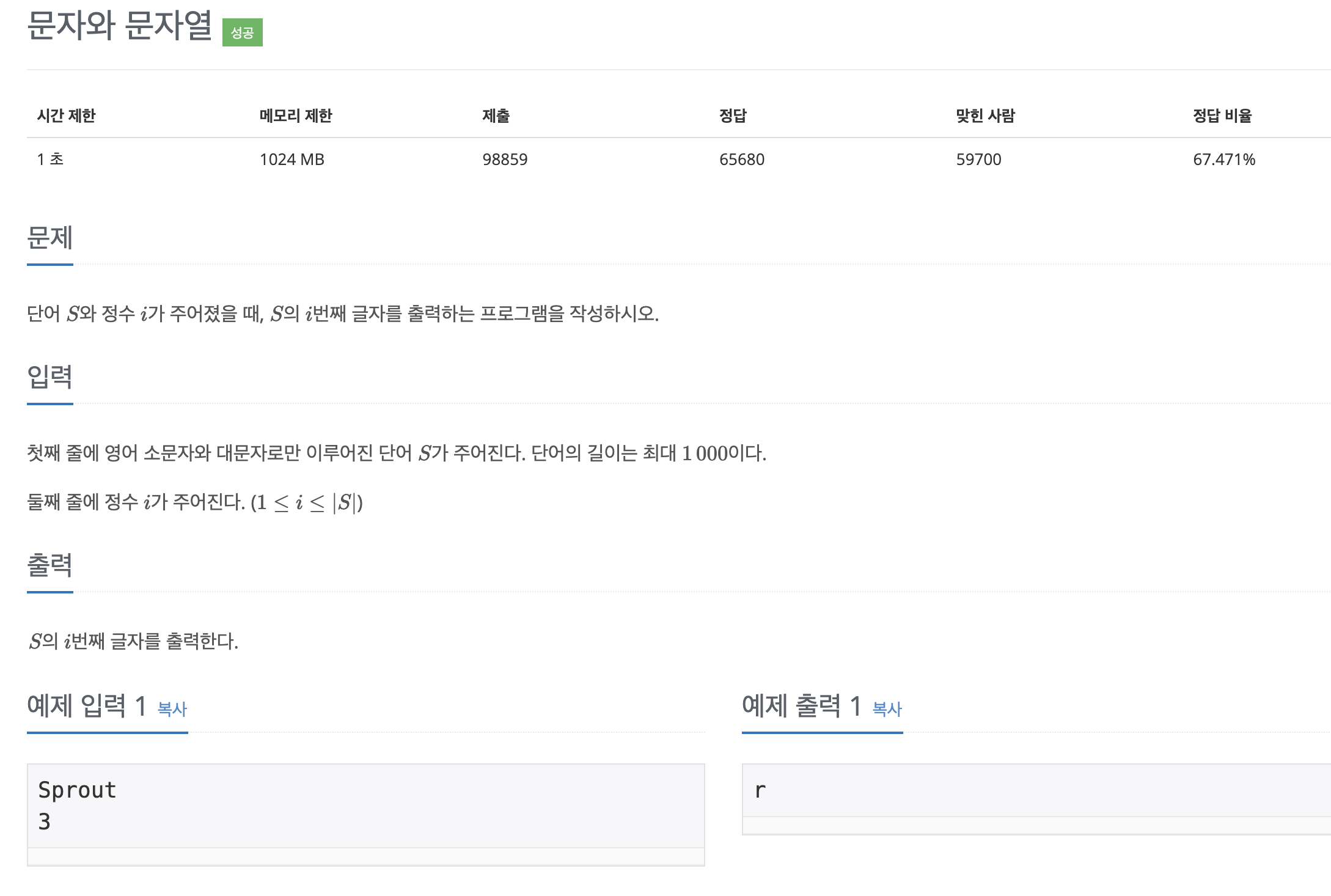
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
char charAt = s.charAt(sc.nextInt() -1);
System.out.println(charAt);
}
}간략화1
char charAt = sc.nextLine().charAt(sc.nextInt() -1);
System.out.println(charAt);간략화2
System.out.println(sc.nextLine().charAt(sc.nextInt() -1));2743
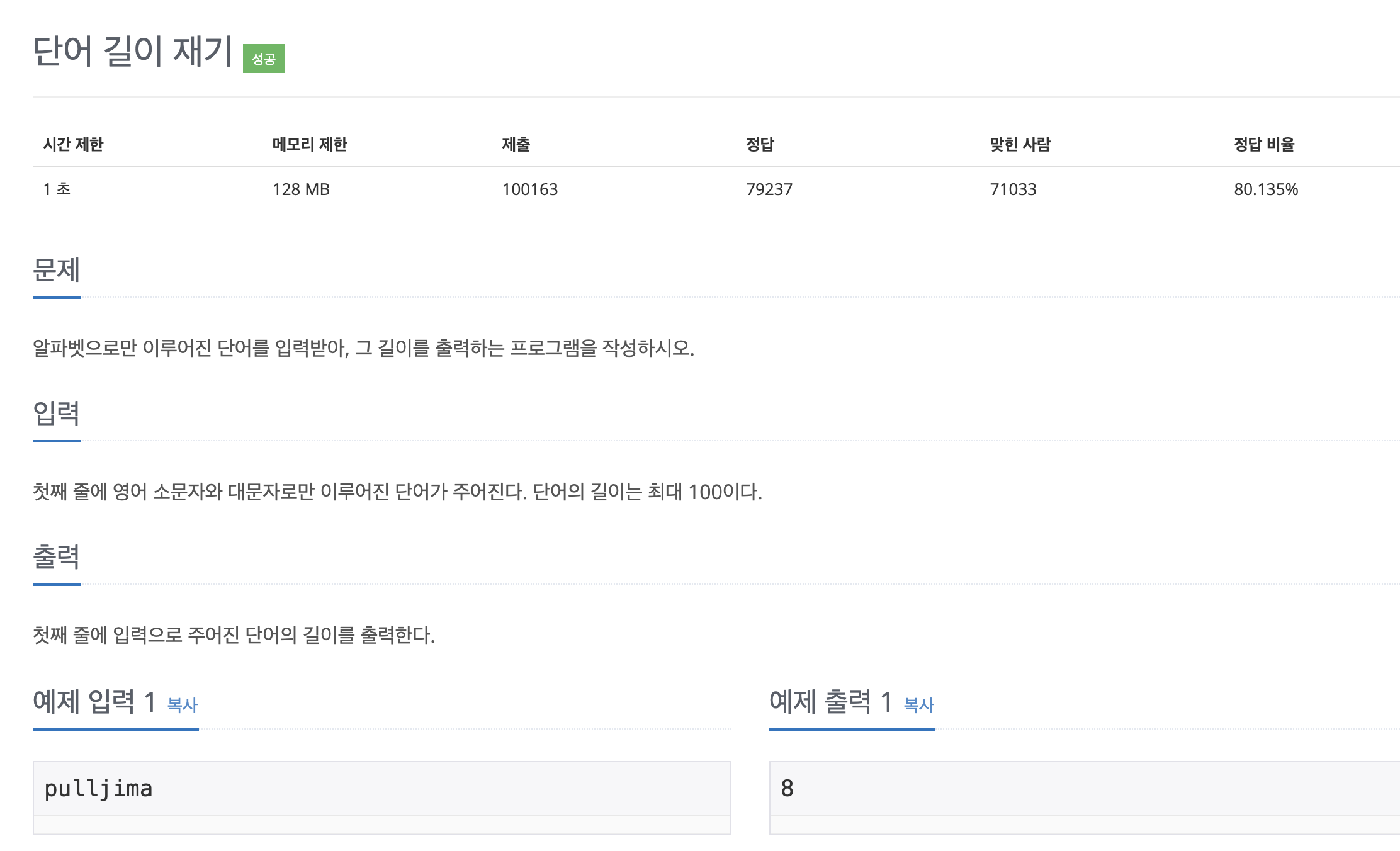
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(s.length());
}
}
9086
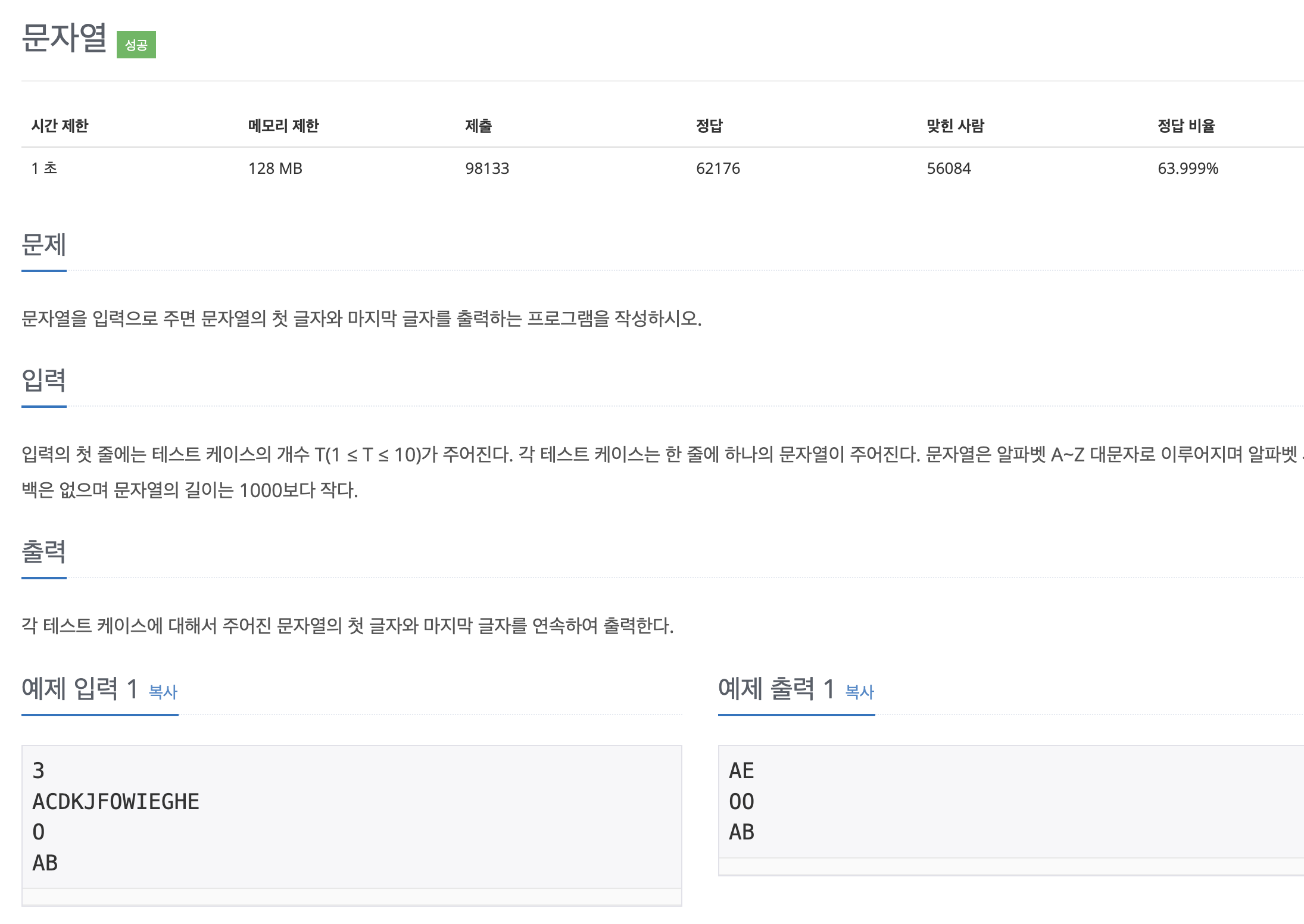
오류1 -StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: String index out of range: 0
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
char start = s.charAt(0);
char end = s.charAt(s.length());
System.out.println(start + end);
}
}
}StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: String index out of range: 0 라는 오류가 발생했다.
이는 문자열이 비어있을 때 ("") charAt(0) 또는 charAt(str.length(-1)을 호출해서 발생할 수 있는 문제다.
문제 원인
Scanner의 nextInt()를 사용하면 숫자만 읽고, 개행 문자(\n)는 버퍼에 남겨둔다.
이후 nextLine()을 호출하면 버퍼에 남아 있던 \n(개행 문자)을 읽어버리기 때문에, 실제로 입력을 받지 못하고 빈 문자열을 리턴하게 된다.
해결 방법
버퍼를 비워야 한다.
int num = sc.nextInt(); // 정수 입력 (개행 문자가 남는다)
sc.nextLine(); // 버퍼에 남아있는 `\n` 제거오류2
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
char start = s.charAt(0);
char end = s.charAt(s.length() - 1);
System.out.println(start + end);
}현재 출력은 char + char는 정수 연산(int)이 수행된다.(문자 코드 값을 더한 숫자가 출력)
원하는 값은 문자로 출력되야 하기 때문에 앞에 빈 문자를 넣어 문자로 인식하여 출력되게 해야한다.
정답
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
char start = s.charAt(0);
char end = s.charAt(s.length() - 1);
System.out.println("" + start + end);
}
}
}11654
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String next = sc.next();
System.out.println(next.charAt(0)-0);
}
}처음에는 이렇게 풀었지만 좀 더 명확하게 변환 연산을 해주는게 좋다.
System.out.println((int) next.charAt(0)); sc.next()는 문자열을 받지만, 숫자를 입력해도 문자열로 저장charAt(0)을 사용하면 첫 번째 문자가char타입으로 반환char타입을 정수로 변환할 때는 ASCII 코드 값으로 변환char - 0대신(int) char를 사용하면 코드 가독성이 더 좋다.