10181
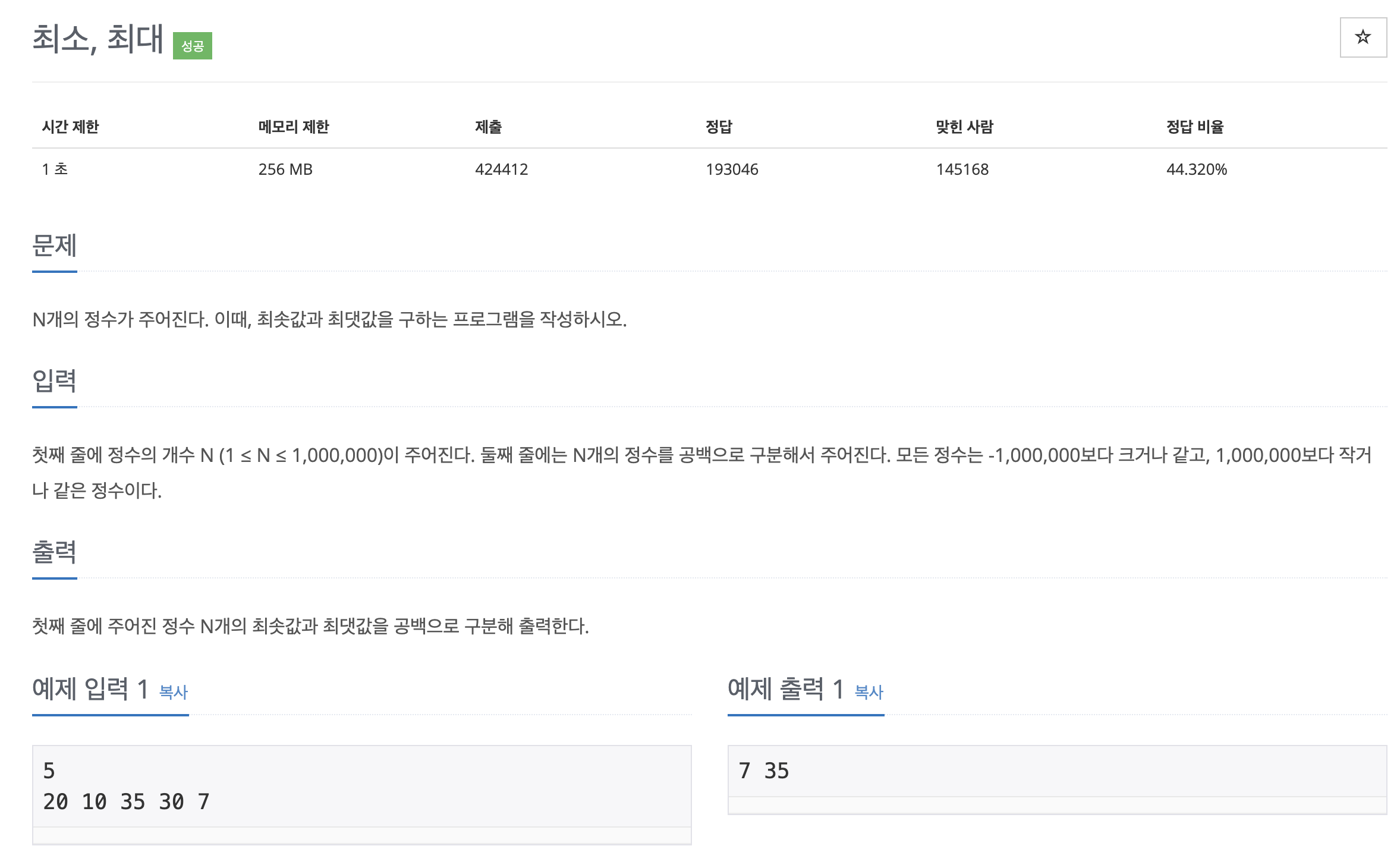
처음 코드 - 오답
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[] X = new int[N];
int max = 0;
int min = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
X[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (X[i] > max) {
max = X[i];
}
min = X[0];
if (min > X[i]) {
min = X[i];
}
}
System.out.println(min + " " + max);
}
} int min = X[0];
int max = X[0];중간에 이렇게 첫번째 값으로 초기화 해야겠다 싶어 초기화 방법을 바꿨다.
- max 값은 잘 들어가는데 min 값은 어떻게 초기화 해줘야할지 모르겠어서 여기 저기 넣어봤다.
- 어느정도 고민을 해봐도 답이 안나와 찾아보니 아래와 같이 초기화 하신분이 있었다.
정답이긴 한 코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[] X = new int[N];
int max = -1000000;
int min = 1000000;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
X[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (X[i] > max) {
max = X[i];
}
if (X[i] < min) {
min = X[i];
}
}
System.out.println(min + " " + max);
}
}- 정답 코드로 돌리면 맞다고는 하지만 뭔가 이렇게 초기화 하는건 아닌 것 같아 조금 더 고민해보고 찾아보다가
- 아래와 같이 입력을 받은 후 초기화를 하고 다시 for문을 돌려 max값과 min 값을 찾았다.
정답 코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[] X = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
X[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int min = X[0];
int max = X[0];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (X[i] > max) {
max = X[i];
}
if (X[i] < min) {
min = X[i];
}
}
System.out.println(min + " " + max);
}
}- 입력받는 for문이 끝난 후 초기화 하는 방법 처럼 조금 더 시야를 넓게 볼 수 있도록 하자.
- 입력값을 복사해서 넣으면 한번에 들어가서인지 min 오류가 계속 났는데 디버깅을 하면 min값이 제대로 나오고 디버깅을 안할 땐 min값이 계속 7이 나와서 직접 입력하니 제대로 나왔다. 값을 한번에 넣으면 오류가 좀 나는 것 같다.
2562
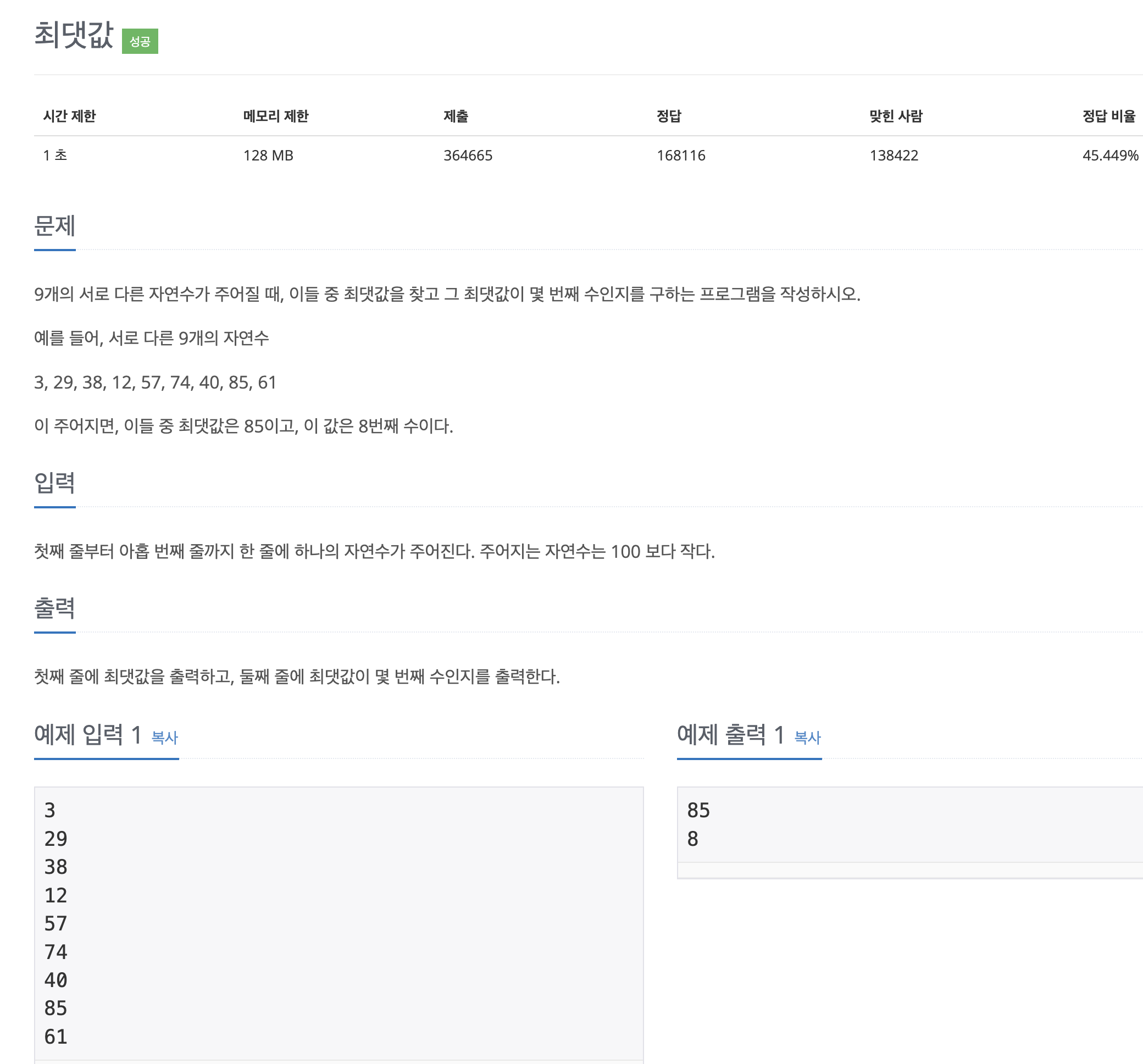
!! 입력받는 값이 9개라고 나와 있다 => 입력받을 N개를 만들 필요 없이 9개의 값을 가지는 배열을 만들면 된다.
런타임 에러
처음에는 max이던 아니던 카운트를 올려줘야 된다 생각해서 첫 번째와 같이 코드를 작성했다.
그랬더니 정답은 나오지만 런타임에러가 뜬다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N[] = new int[9];
int max = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N.length; i++) {
N[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (max != N[i]) {
count++;
}
if (N[i] > max) {
max = N[i];
}
}
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(count - 1);
}
}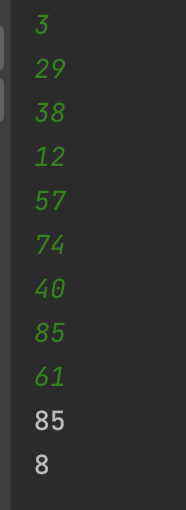
정답은 맞게 나오지만 컴파일 에러가 나서 다른 방법을 찾아봤다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N[] = new int[9];
int max = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N.length; i++) {
N[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (N[i] > max) {
max = N[i];
count = i + 1;
}
}
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println(count);
}
}- max값을 변경해 줄 때 해당하는 i값에 +1을 하여 저장해준다. 배열의 첫 번째 인자는 0으로 시작하기 때문에 +1을 해주어 위치가 어디인지 저장해 주는 것이다.
10810
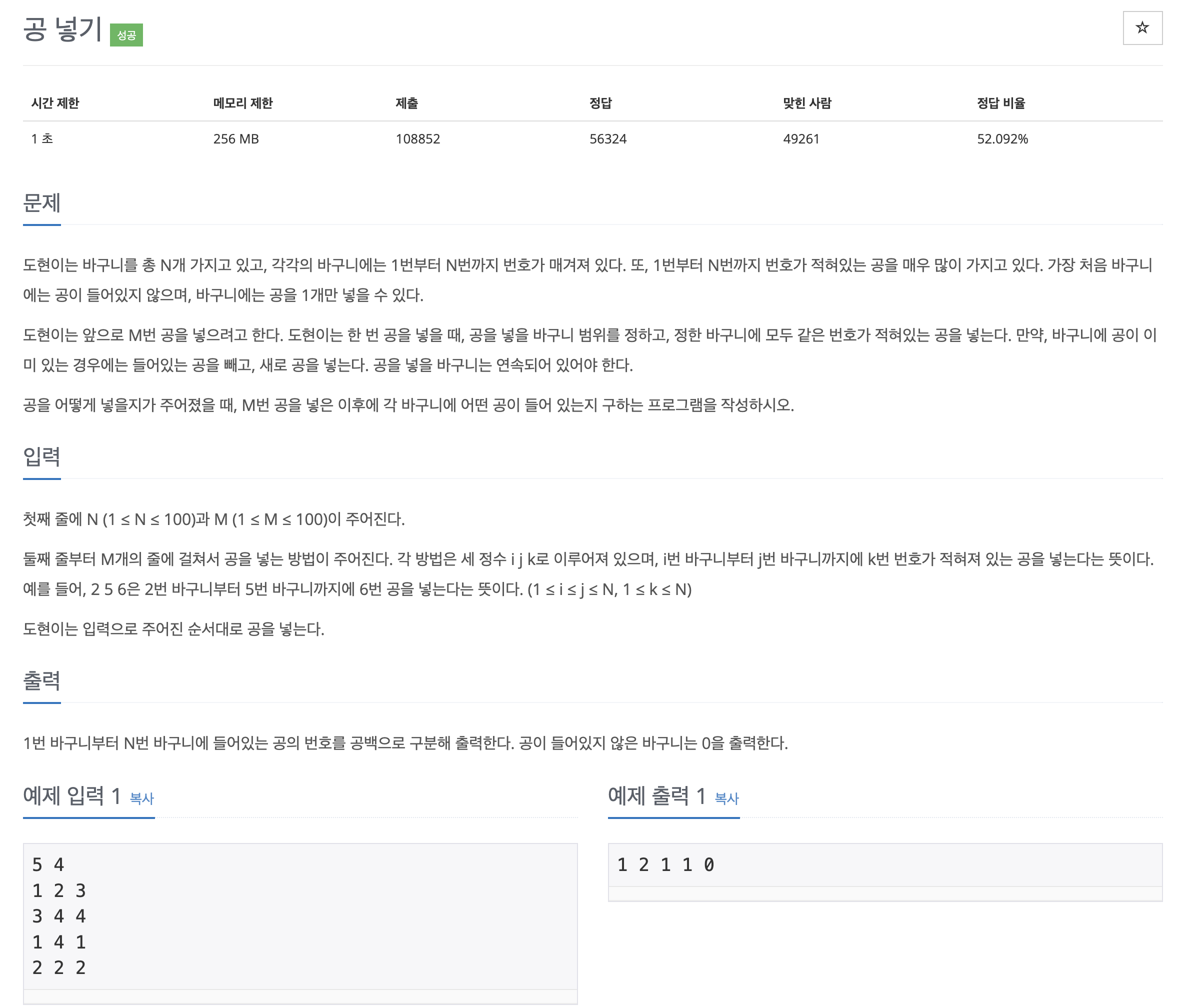
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int[] baskets = new int[N]; //크기가 N인 배열 생성 (초기값 0)
//M번의 공 넣기 작업 수행
for (int m = 0; m < M; m++) {
int i = sc.nextInt(); // 시작 바구니 번호
int j = sc.nextInt(); // 끝 바구니 번호
int k = sc.nextInt(); // 넣을 공 번호
//i부터 j까지 바구니에 공 번호 k를 넣음
for (int index = i - 1; index < j; index++) {
baskets[index] = k;
}
}
for (int basket : baskets) {
System.out.print(basket + " ");
}
}
}문제가 조금 복잡해지니 문제를 풀면서 조금씩 헷갈려 코드 짜기가 어려웠다.
무엇을 할 것인지 주석을 하면서 해보니 조금 정리가 되는 것 같았다.
다음에 다시 풀어봐야겠다.
10813
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
//바구니에 각 번호가 담긴 공 세팅
int[] baskets = new int[N];
for (int n = 0; n < N; n++) {
baskets[n] = n + 1;
}
//M번의 공 바꾸기 작업
for (int m = 0; m < M; m++) {
int i = sc.nextInt(); // 첫 번째 바구니 번호
int j = sc.nextInt(); // 두 번째 바구니 번호
//i와 j 바구니 공을 서로 바꾸어 넣음
int temp = baskets[i-1];
baskets[i - 1] = baskets[j - 1];
baskets[j - 1] = temp;
}
for (int basket : baskets) {
System.out.print(basket + " ");
}
}
}오류 - i와 j의 값을 바꿀 때 새로운 for문 안에서 작업해야 한다는 생각이 들어 조금 헤멨다.
i-1, j-1같이 인덱스 값이 0부터 시작한다는 것을 꼭 기억하고 적용해야 한다.