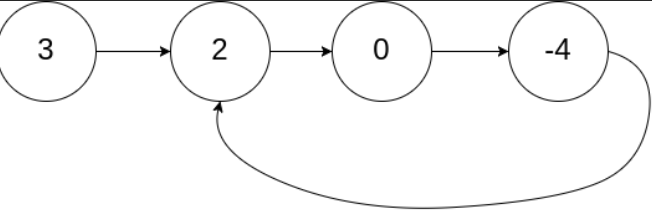
문제 - LeedCode 141. Liked List Cycle
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
참고 문제 - LeedCode 141. Liked List Cycle
링크드 리스트의 사이클 유무를 확인하는 알고리즘 - Floyd's algorithm
한칸씩 이동하는 slow 포인터와 두칸씩 이동하는 포인터 2개의 포인터를 이용하여 사이클을 찾는 방법이다.
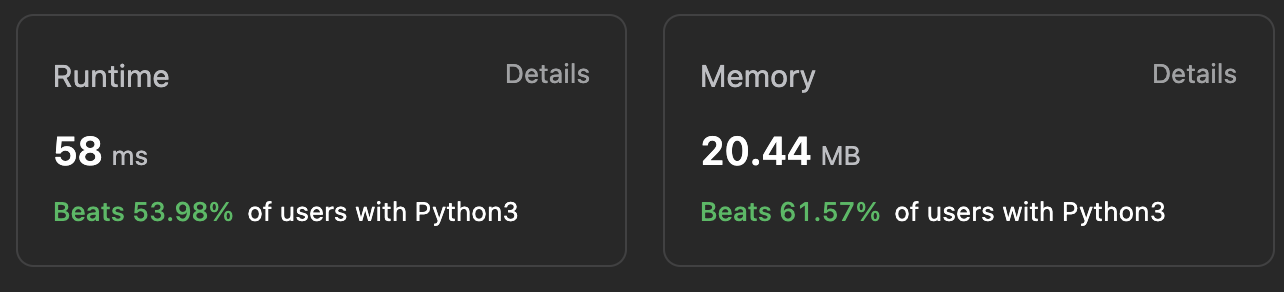
Floyd's 알고리즘을 사용하지 않았을때 - set() 이용
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
headSet = set()
if head == None: # 만약 linked list 가 주어지지 않으면 False 리턴
return False
while head.next != None: # 다음 노드가 존재하면 반복
if head in headSet: # 현재 노드가 set 에 존재한다면 사이클이 돈 것이니 True 리턴
return True
headSet.add(head) # 현재 노드가 set 에 존재하지 않았으니 set() 에 추가
head = head.next # 현재 노드를 다음 노드로 업데이트
return False # 갱신된 노드가 head.next == None 인 상태로 마지막 linked list 의 다음 노드가 None 인 상태라 False 리턴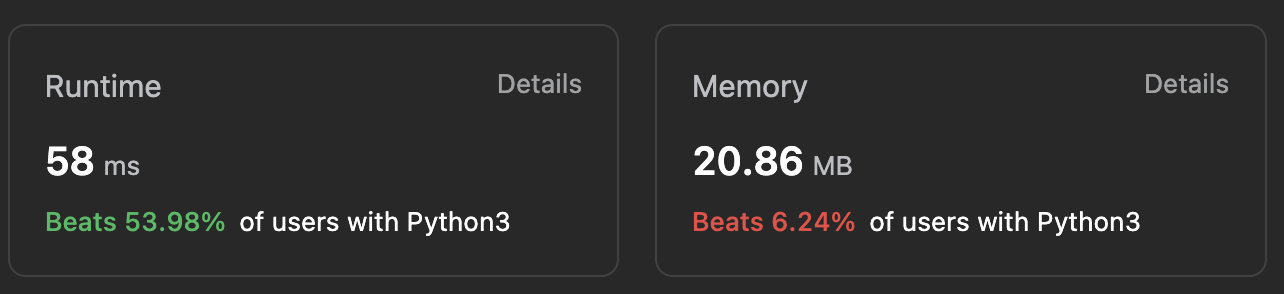
Floyd's 알고리즘을 사용했을 때
추가적인 링크드리스트 하나가 필요한 것 외에 별도의 메모리가 필요없다.
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if head == None or head.next == None:
return False
slow = head
fast = head.next.next
while fast != None and fast.next != None:
if fast == slow:
return True
else:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return False