모델 학습- Train
-
Learning rate scheduler
- 초기 시점에 WarmUP에 도입해서 lr이 천천히 증가(PiecewiseConstantWarmUpDecay)
class PiecewiseConstantWarmUpDecay(tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.LearningRateSchedule):
def __init__(self, boundaries, values, warmup_steps, min_lr, name=None):
super(PiecewiseConstantWarmUpDecay, self).__init__()
if len(boundaries) != len(values) - 1:
raise ValueError(
"The length of boundaries should be 1 less than the"
"length of values")
self.boundaries = boundaries
self.values = values
self.name = name
self.warmup_steps = warmup_steps
self.min_lr = min_lr
def __call__(self, step):
with tf.name_scope(self.name or "PiecewiseConstantWarmUp"):
step = tf.cast(tf.convert_to_tensor(step), tf.float32)
pred_fn_pairs = []
warmup_steps = self.warmup_steps
boundaries = self.boundaries
values = self.values
min_lr = self.min_lr
pred_fn_pairs.append(
(step <= warmup_steps,
lambda: min_lr + step * (values[0] - min_lr) / warmup_steps))
pred_fn_pairs.append(
(tf.logical_and(step <= boundaries[0],
step > warmup_steps),
lambda: tf.constant(values[0])))
pred_fn_pairs.append(
(step > boundaries[-1], lambda: tf.constant(values[-1])))
for low, high, v in zip(boundaries[:-1], boundaries[1:],
values[1:-1]):
pred = (step > low) & (step <= high)
pred_fn_pairs.append((pred, lambda: tf.constant(v)))
return tf.case(pred_fn_pairs, lambda: tf.constant(values[0]),
exclusive=True)
-
Hard negative mining
- Object detection 모델 학습
- 학습 중, label은 negative
- confidence가 높게 나오는 샘플 재학습
- false negative오류가 강해짐
- loss만 따로 모아 계산해주는 방식
def hard_negative_mining(loss, class_truth, neg_ratio):
pos_idx = class_truth > 0
num_pos = tf.math.reduce_sum(tf.cast(pos_idx, tf.int32), axis=1)
num_neg = num_pos * neg_ratio
rank = tf.argsort(loss, axis=1, direction='DESCENDING')
rank = tf.argsort(rank, axis=1)
neg_idx = rank < tf.expand_dims(num_neg, 1)
return pos_idx, neg_idx
print('슝=3')Training
priors = prior_box()
train_dataset = load_dataset(priors, train=True)
print('슝=3')
model = SsdModel()
model.summary()
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
model,
to_file=os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'model.png'),
show_shapes=True,
show_layer_names=True
)사실 100으로 좋은 성능이 나오고 그렇지 않으면 크게 유의미한 결과를 얻진 못할 것입니다.
EPOCHS = 10
for epoch in range(0, EPOCHS):
for step, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(train_dataset.take(steps_per_epoch)):
load_t0 = time.time()
total_loss, losses = train_step(inputs, labels)
load_t1 = time.time()
batch_time = load_t1 - load_t0
print(f"\rEpoch: {epoch + 1}/{EPOCHS} | Batch {step + 1}/{steps_per_epoch} | Batch time {batch_time:.3f} || Loss: {total_loss:.6f} | loc loss:{losses['loc']:.6f} | class loss:{losses['class']:.6f} ",end = '',flush=True)
filepath = os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_PATH, f'weights_epoch_{(epoch + 1):03d}.h5')
model.save_weights(filepath)Inference -NMS-
Grid cell을 사용하는 Object detection의 inference 단계에서 하나의 object가 여러 개의 prior box에 걸쳐져 있을 때 가장 확률이 높은 1개의 prior box를 하나로 줄여주는 NMS(non-max suppression)이 필요합니다. 아래 코드를 확인해 주세요.
NMS를 통해 겹쳐진 box를 하나로 줄일 수 있게 되었다면, 이제 모델의 예측 결과를 해석해주는 함수를 작성합니다.
아래 함수에서는 모델의 예측 결과를 디코딩해서 예측 확률을 토대로 NMS를 통해 최종 box와 score 결과를 만들어 줍니다.
def parse_predict(predictions, priors):
label_classes = IMAGE_LABELS
bbox_predictions, confidences = tf.split(predictions[0], [4, -1], axis=-1)
boxes = decode_bbox_tf(bbox_predictions, priors)
scores = tf.math.softmax(confidences, axis=-1)
out_boxes = []
out_labels = []
out_scores = []
for c in range(1, len(label_classes)):
cls_scores = scores[:, c]
score_idx = cls_scores > 0.5
cls_boxes = boxes[score_idx]
cls_scores = cls_scores[score_idx]
nms_idx = compute_nms(cls_boxes, cls_scores)
cls_boxes = tf.gather(cls_boxes, nms_idx)
cls_scores = tf.gather(cls_scores, nms_idx)
cls_labels = [c] * cls_boxes.shape[0]
out_boxes.append(cls_boxes)
out_labels.extend(cls_labels)
out_scores.append(cls_scores)
out_boxes = tf.concat(out_boxes, axis=0)
out_scores = tf.concat(out_scores, axis=0)
boxes = tf.clip_by_value(out_boxes, 0.0, 1.0).numpy()
classes = np.array(out_labels)
scores = out_scores.numpy()
return boxes, classes, scores
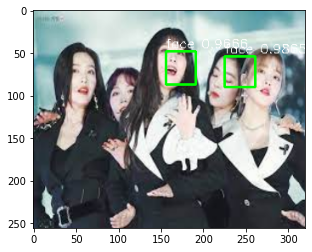
print('슝=3')Inference - 사진에서 얼굴 찾기-
TEST_IMAGE_PATH = os.path.join(PROJECT_PATH, 'image.jpg')
img_raw = cv2.imread(TEST_IMAGE_PATH)
img_raw = cv2.resize(img_raw, (IMAGE_WIDTH, IMAGE_HEIGHT))
img = np.float32(img_raw.copy())
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img, pad_params = pad_input_image(img, max_steps=max(PRIOR_STEPS))
img = img / 255.0
priors = prior_box()
priors = tf.cast(priors, tf.float32)
predictions = model.predict(img[np.newaxis, ...])
boxes, labels, scores = parse_predict(predictions, priors)
boxes = recover_pad(boxes, pad_params)
for prior_index in range(len(boxes)):
draw_box_on_face(img_raw, boxes, labels, scores, prior_index, IMAGE_LABELS)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(img_raw, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.show()