Static 메소드와 Static 변수
예외처리
- 예외&에러: 실행이 정상적으로 되지 않는 상황
(1) 에러(Error): 메모리와 같은 하드웨어상에서의 문제, 개발자와 자바 프로그램이 control할 수 없음 -> JVM이 프로그램을 반드시 종료시켜야 함
ex. OutOfMemoryError, StackOverflowError
(2) 예외(Exception): 개발자가 control할 수 있는 문제, 예외는 JVM이 처리해줌(예외 메시지 출력 및 프로그램 종료)
(i) Checked Exception: 반드시 예외 처리를 해야하는 예외로 처리하지 않으면 컴파일 에러 발생
ex. IOExeption
(ii) Runtime Exception: 반드시 예외 처리를 할 필요는 없음
ex. ArithmeticExceptionA. try-catch-finally
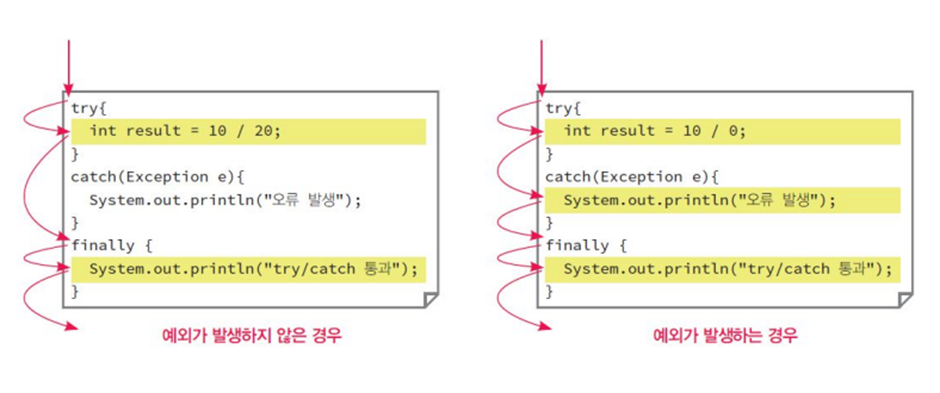
- try문에서 error가 발생하면 try문에서 그 이후를 실행하지 않고 catch문을 실행
- finally문은 항상 실행 -> 에러 발생과 상관없이 반드시 실행해야하는 구문을 finally문에 넣기
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.print("a/b... a? ");
int n1 = kb.nextInt();
System.out.print("a/b... b? ");
int n2 = kb.nextInt();
System.out.printf("%d / %d = %d \n", n1, n2, n1 / n2);
} catch (Exception e){
// Exception도 객체임
// 에러가 발생했을 때 처리하는 구문
e.printStackTrace(); // 에러났을 때의 문구를 뿌려줌, 디버깅을 위해서 넣어줌
// JVM이 Exception이라는 객체 생성을 시켜줌 -> 객체의 printStackTrace를 사용할 수 있게 함
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally 실행");}
- JVM이 Exception 객체를 생성함 -> Exception의 메소드인 printStackTrace()나 getMessage()를 호출해서 에러 메시지를 불러낼 수 있음
B. throws
- 특정 메소드에서 throws를 처리하면 그 메소드를 호출하는 곳으로 에러가 전달됨 -> 메소드를 호출한 곳에서 에러를 처리
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
md1(); // md1에서 발생한 에러가 넘어옴
} catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void md1() throws IOException {
md2(); // md2에서 말생한 에러가 넘어옴
}
public static void md2() throws IOException {
Path file = Paths.get("C:\\javastudy\\Simple.txt");
BufferedWriter writer = null;
writer = Files.newBufferedWriter(file);
writer.write('A');
writer.write('Z');
if(writer != null){
writer.close();
}
}
- main에서 예외를 throws하면 JVM에서 예외를 처리함: JVM이 에러메시지를 띄우고 프로그램을 종료함 -> Checked Exception으로 인해 발생하는 컴파일 에러를 무시하고 코드를 실행하기 위해서 사용할 수 있음
cf) throw: exception을 발생시키는 키워드, 예를 들어 parseInt의 경우 정수가 아닌 다른 문자열을 받으면 exception을 발생시켜 프로그램이 중단된다.
int num = Integer.parseInt(numStr);parseInt의 소스코드의 throw -> 적절하지 않은 인자(string 등)가 전달되었을 때 예외를 출력하도록 함
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException
{
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
....
}C. 예외 클래스
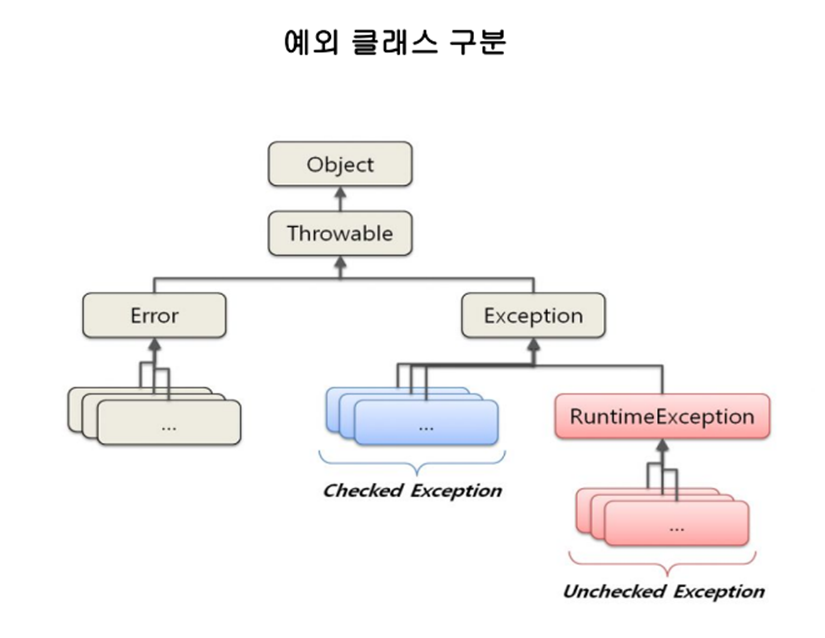
- 모든 종류의 Exception의 부모 클래스가 Exception이므로 Exception을 통해 모든 Exception을 처리할 수 있음
public class Example1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.print("a/b... a? ");
int n1 = kb.nextInt();
System.out.print("a/b... b? ");
int n2 = kb.nextInt();
System.out.printf("%d / %d = %d \n", n1, n2, n1 / n2); // 이 값은 안 뿌림
} catch (ArithmeticException e){
e.printStackTrace(); // 에러났을 때의 문구를 뿌려줌, 디버깅을 위해서 넣어줌
// JVM이 ArithmeticException이라는 객체 생성을 시켜줌 -> 객체의 printStackTrace를 사용할 수 있게 함
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (InputMismatchException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e){
// Exception도 객체임
// 에러가 발생했을 때 처리하는 구문
// Exception은 Exception들의 부모 클래스 -> 모든 에러를 처리할 수 있음
// JVM이 위에서 부터 순서대로 확인 Arithmatic -> Input -> 전체 exception
// 제일 마지막으로 배치해야함
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally 실행");
// 예외가 없으면 catch 구문을 실행하지 않고 finally를 실행
// 예외가 있어도 catch 구문을 실행한 후 finally 실행
// 에러가 있던 없던 실행해야하는 사항을 finally에 넣어줌
}
// try-catch로 묶어주면 죽지는 않음
System.out.println("try-catch 바깥");
System.out.println("Good bye~~!");
}
}
따라서 제일 처음에 Exception을 이용해서 예외를 처리하면 오류가 발생할 수 있음
try {
System.out.print("a/b... a? ");
int n1 = kb.nextInt();
System.out.print("a/b... b? ");
int n2 = kb.nextInt();
System.out.printf("%d / %d = %d \n", n1, n2, n1 / n2);
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (InputMismatchException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
//컴파일 에러 발생
}
-
RuntimeException에 속하는 exception은 Unchecked Exception이고 그 외는 전부 CheckedException이다.
-
암기!
(a) RuntimeException: JVM의 정상적인 작동 중에 발생할 수 있는 예외, 코드 실행 중에 인풋 값이 잘못된 경우나 특정 조건에 부합할 때 발생하게 된다.
(b) ArithmeticException: 정수를 0으로 나누었을 경우
(c) ClassCastException: Class 형변환을 적절하지 않게 실행한 경우
(d) ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 배열에 대한(배열을 참조하는) 인덱스가 잘못된 경우
