기본 양식에 맞춰서 흐름 대로 작성하기
사실 dag은 어느정도 작성양식이 정해져있어 흐름에 따라서 작성해주면 되기때문에
재사용성이 높다.
기본DAG 양식
# package import
# function definition
#dag
# task1
# task2
# task3
# Task 간 의존성(실행 순서)
Debugging
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
Airflow webserver 에 dag을 올리기전에
에디터에서 debugging을 해주면 syntaxerror를 확인할 수 있다.
Airflow 내부에서 debugging 기능이 따로 없기에
사전에 체크하는게 중요하다.
python_callable=print_hello, # 함수지정
^SyntaxError: invalid syntax
bash + python operator
# package import
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
from airflow.operators.bash import BashOperator
# function definition
def print_hello() :
print("hello ")
def print_wolrd() :
print("world!! ")
'''
owner: DAG/Task 소유자 (Airflow UI에 표시됨).
depends_on_past:
True → 이전 Task 인스턴스가 성공해야 이번 실행이 수행됨.
False → 이전 실행과 관계없이 독립 실행.
start_date: DAG 실행 시작 시점.
Airflow는 이 날짜부터 schedule_interval을 따라 DAG Run을 생성.
email_on_failure: Task 실패 시 이메일 알림 보낼지 여부.
email_on_retry: Task 재시도할 때 이메일 알림 보낼지 여부.
retries: Task 실패 시 몇 번까지 재시도할지.
retry_delay: 재시도 간격(예: 5분 뒤 다시 시도).
'''
#default args 공통으로 적용되는 기본 설정값
default_args = {
'owner': 'chabao',
'depends_on_past': False,
'start_date': datetime(2025, 9, 24),
'email_on_failure': False,
'email_on_retry': False,
'retries': 1,
'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=5)
}
#dag
''''
catchup=True일 경우, DAG를 켰을 때 누락된 과거 run들을 전부 실행합니다.
catchup=False일 경우, 과거는 무시하고 **현재 시점(run_date 기준)**부터 실행합니다.
cron = 분/시/일/월/요일
| 표현식 | 의미 |
| -------------- | ------------------ |
| `0 0 * * *` | 매일 0시(자정) 실행 |
| `0 6 * * 1` | 매주 월요일 아침 6시 실행 |
| `*/15 * * * *` | 매 15분마다 실행 |
| `0 9,18 * * *` | 매일 오전 9시, 오후 6시 실행 |
| `0 0 1 * *` | 매월 1일 자정 실행 |
'''
# dag 작성
dag = DAG(
dag_id="hello_world_dag",
default_args=default_args,
description="This is my first dag for study Airflow",
schedule_interval="*/1 * * * *",
catchup=False,
tags=['example']
)
# task1
task1 = PythonOperator(
task_id = 'print_hello_task', # 식별자
python_callable=print_hello, # 함수지정
dag=dag # 이 task가 속할 객체 지정
)
# task2
task2 = PythonOperator(
task_id = 'print_world_task', # 식별자
python_callable=print_wolrd, # 함수지정
dag=dag # 이 task가 속할 객체 지정
)
#
task3 = BashOperator(
task_id='bash_task',
bash_command='echo "Hello from Bash!"',
dag=dag
)
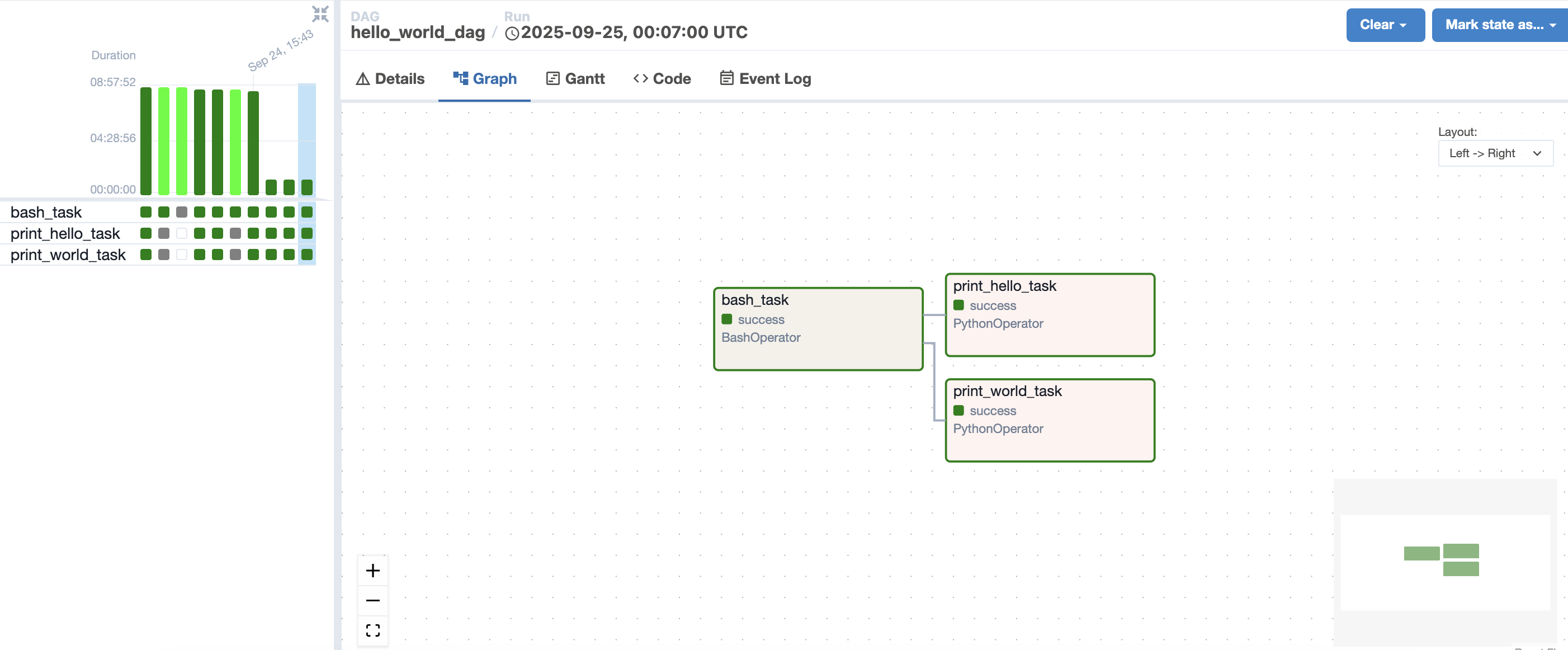
## Task 간 의존성(실행 순서)
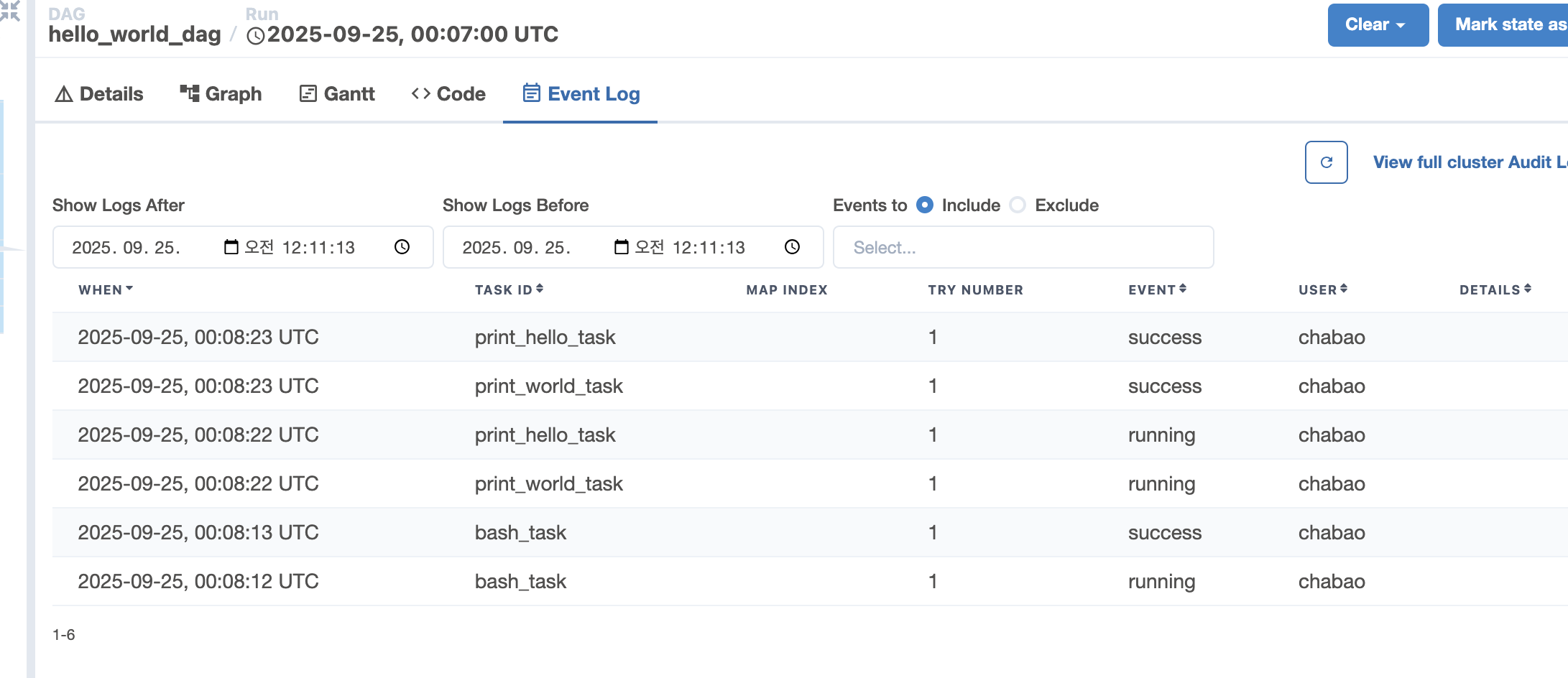
task3 >> [task1,task2]규칙에 맞춰서 bash commend 이후 Python 함수 병렬 실행
병렬처리 event log
task3 : 08:12 ~ 08 : 13
task1,task2 : 08:22 ~ 08:23