백준 1260번: DFS와 BFS

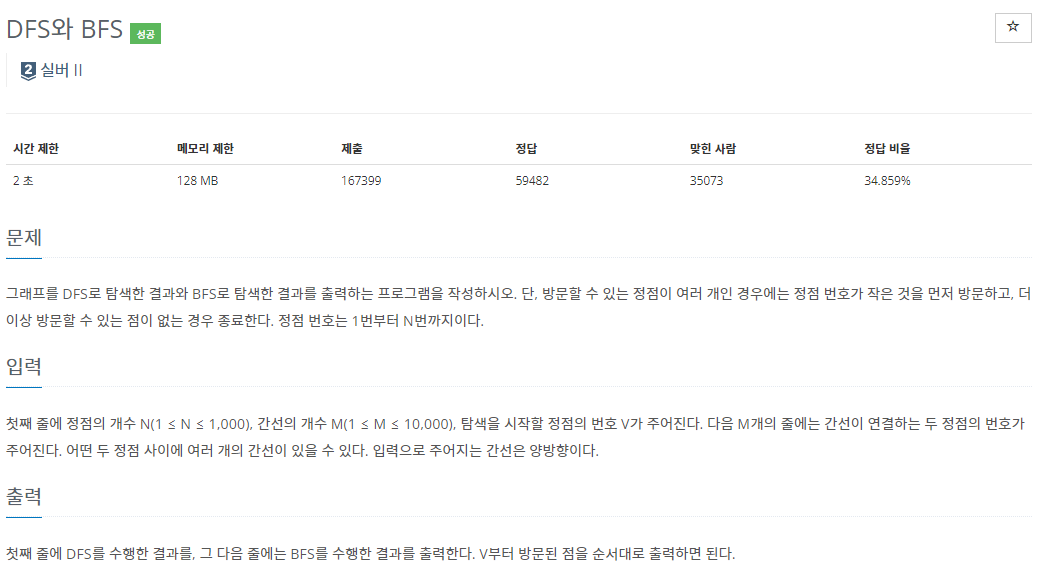
문제 설명
- DFS와 BFS를 구현하는 문제입니다.
접근법
- 인접리스트로 데이터를 받았습니다.
- Map에 key로 int값을, value로 list값을 활용했습니다.
- 번호가 낮은 정점부터 방문하기 위해 value인 list를 오름차순 정렬했습니다.
- 재귀호출 방식으로 DFS를 구현했습니다.
- Queue를 활용해 BFS를 구현했습니다.
정답
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N;
static int M;
static StringBuilder sb;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
sb = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int V = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
HashMap<Integer,List> graph = new HashMap<Integer,List>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int key = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int val = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(graph.keySet().contains(key)) {
graph.get(key).add(val);
}else {
List<Integer>temp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
temp.add(val);
graph.put(key, temp);
}
//양방향이라서
if(graph.keySet().contains(val)) {
graph.get(val).add(key);
}else {
List<Integer>temp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
temp.add(key);
graph.put(val, temp);
}
}
//숫자가 작은 정점부터 방문하기 위해 오름차순 정렬했습니다.
for (List<Integer> g: graph.values()) {
Collections.sort(g);
}
//System.out.println(graph.toString());
if(M==0) {//예외1. 아무런 연결이 없을 때
return;
}else if(graph.get(V)==null) {//예외2. 시작점에서 연결된 노드가 없을 때
System.out.println(V);
System.out.println(V);
}else{
DFS(V,new boolean[N+1],graph);
sb.append("\n");
BFS(V,graph);
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
public static void DFS(int V,boolean[] v,HashMap<Integer,List>graph) {
v[V] = true;
sb.append(V+" ");
List<Integer> lst = graph.get(V);
for (int i = 0; i < lst.size(); i++) {
if(!v[lst.get(i)]) {
DFS(lst.get(i),v,graph);
}
}
}
public static void BFS(int V,HashMap<Integer,List>graph) {
boolean[] v = new boolean[N+1];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
v[V] = true;
q.add(V);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int current = q.poll();
sb.append(current+" ");
List<Integer> lst = graph.get(current);
for (int i = 0; i < lst.size(); i++) {
if(!v[lst.get(i)]) {
q.add(lst.get(i));
v[lst.get(i)] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
기타
- 처음 틀렸을 때 반례를 직접 찾지 못해 검색을 통해 반례를 찾았습니다.
- 실제 문제였다면 틀렸을 거라는 얘기 -> 조금 더 반례찾는걸 연습하자
- 일반적인 DFS와 BFS가 실행되지 않는 두 가지 예외상황(시작지점에서 갈 수 있는 곳이 없음, 간선이 존재하지 않음)을 if-else로 처리했습니다.
- DFS와 BFS를 잘짜면 예외처리 없이 문제를 통과할 수 있는지 궁금합니다.
