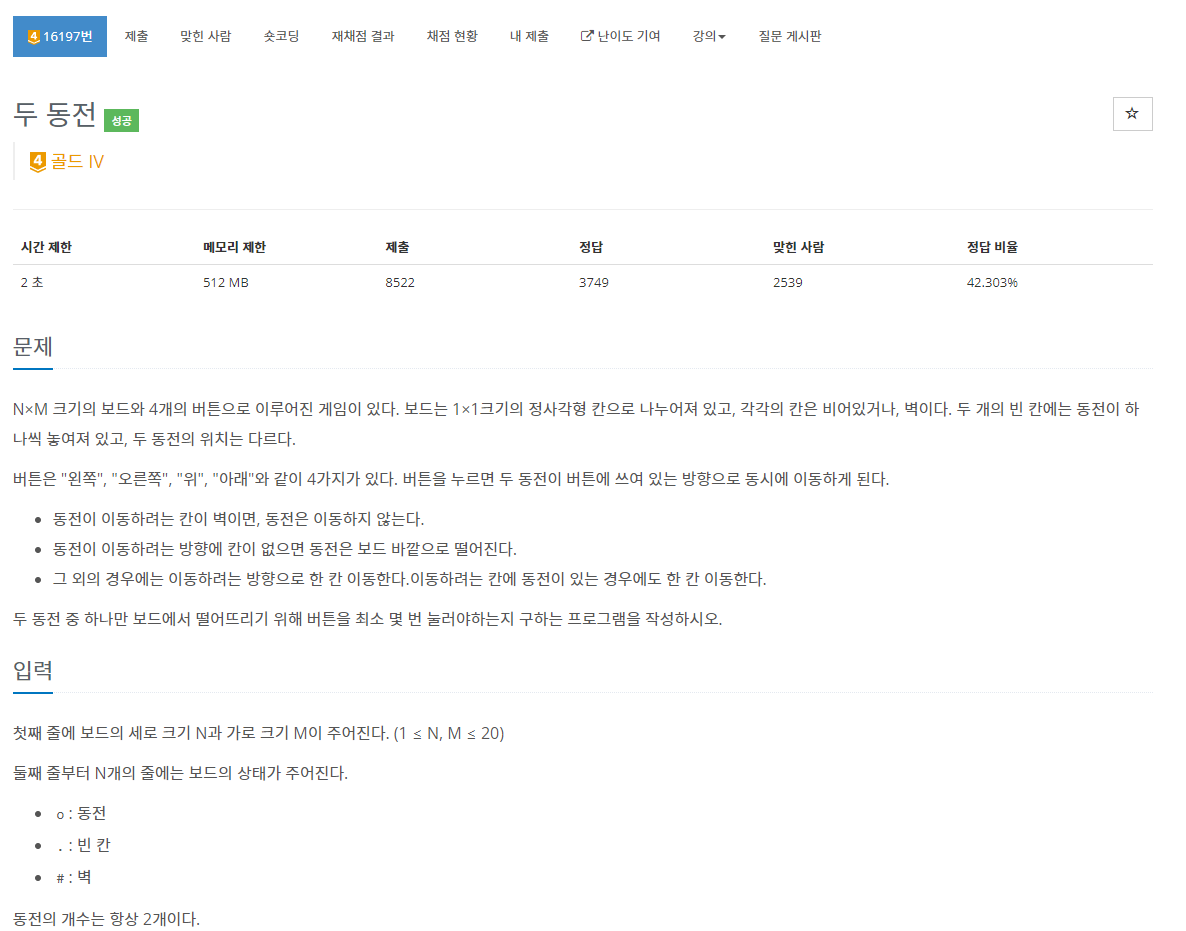
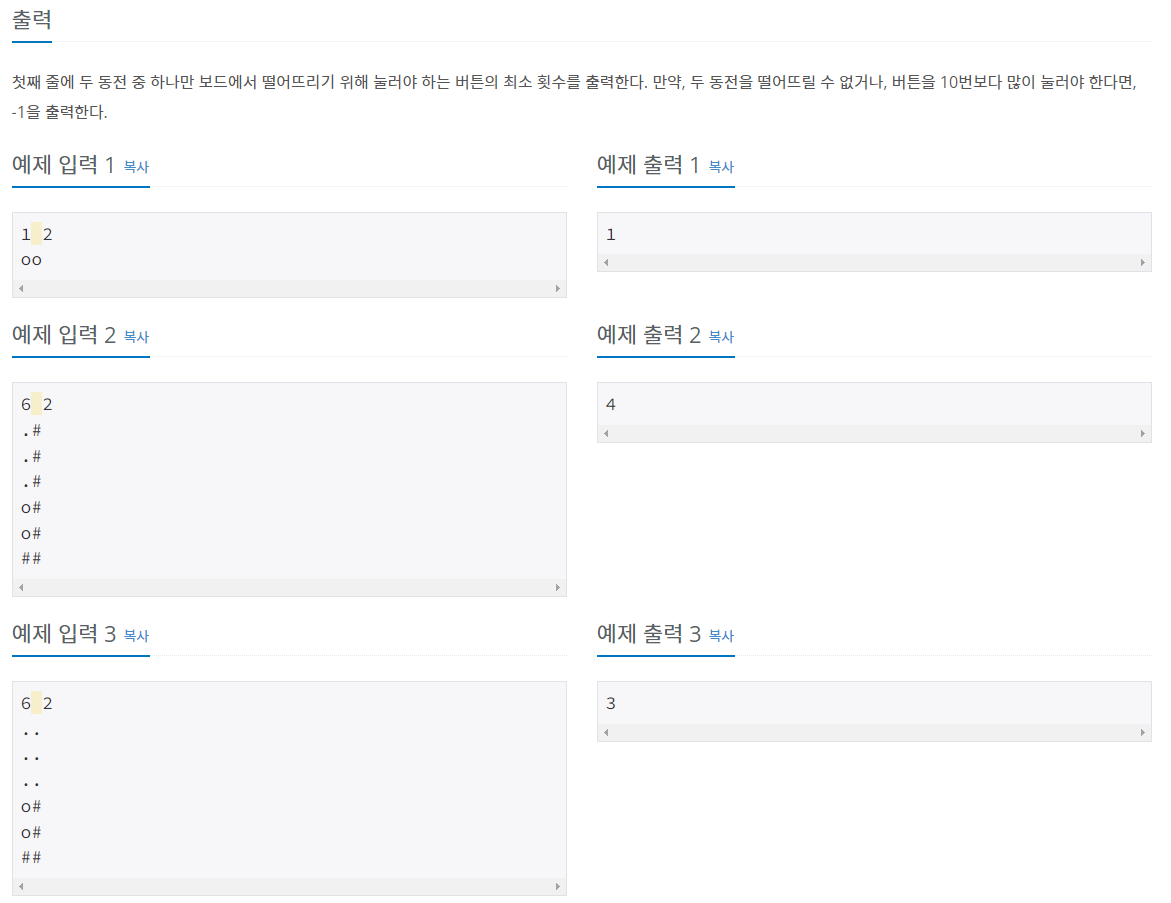
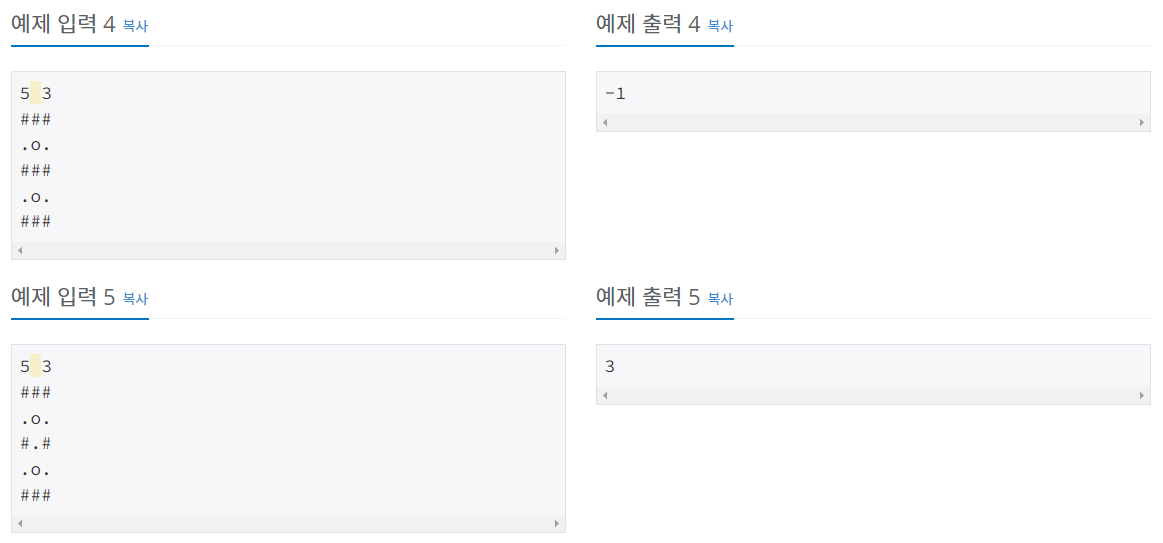
문제 설명
- https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/16197
- 두 동전을 같은 방향으로 움직입니다.
동전은 벽을 만나면 이동하지 않고 배열을 초과하면 떨어집니다.
동전을 하나만 남기기 위한 움직임의 최솟값을 구해야 합니다.
하나만 남기는게 불가능하거나 움직임이 10번을 초과하면 -1을 반환해야 합니다.
접근법
- DFS로 동전을 직접 움직여보면 됩니다.
- 두 동전의 위치를 나타내는 방문배열을 활용할 수 있습니다.
정답
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dx = {0,1,0,-1};
static int[] dy = {1,0,-1,0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
char[][] board = new char[N][M];
int[][] ballPosition = new int[2][2];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String s = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
board[i][j] = s.charAt(j);
if(board[i][j] == 'o') {
ballPosition[cnt++] = new int[] {i,j};
}
}
}
int answer = BFS(ballPosition,N,M,board);
System.out.println(answer);
}
public static int BFS(int[][] start, int N, int M, char[][] board) {
boolean[][][][] v = new boolean[N][M][N][M];
v[start[0][0]][start[0][1]][start[1][0]][start[1][1]] = true;
Queue<int[][]> q = new LinkedList<int[][]>();
q.add(start);
int time = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while(--size>=0) {
int[][] now = q.poll();
int[] ballOne = now[0];
int[] ballTwo = now[1];
// 처음 Validate검사를 한 곳
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int[][] next = new int[2][2];
int nx1 = ballOne[0]+dx[d];
int ny1 = ballOne[1]+dy[d];
int nx2 = ballTwo[0]+dx[d];
int ny2 = ballTwo[1]+dy[d];
if(0 <= nx1 && nx1 < N && 0 <= ny1 && ny1 < M && board[nx1][ny1] == '#') { // 벽을 만나면 위치가 그대로
next[0] = ballOne;
}else { // 벽이 아니면 이동
next[0] = new int[] {nx1,ny1};
}
if(0 <= nx2 && nx2 < N && 0 <= ny2 && ny2 < M && board[nx2][ny2] == '#') { // 벽을 만나면 위치가 그대로
next[1] = ballTwo;
}else { // 벽이 아니면 이동
next[1] = new int[] {nx2,ny2};
}
// Queue에 넣기 전에 Validate검사 실행
int ballCnt = Validate(next,N,M);
if(ballCnt == 1) return time+1; // 동전이 1나만 남은 정답인 경우
if(ballCnt == 0) continue; // 동전이 모두 떨어진 경우 -> Queue에 넣을 필요가 없음
// 위에서 ballCnt 0과1을 모두 처리했기 때문에 두 공이 모두 board위에 존재하는 경우만 남았기 때문에 visit배열을 활용할 수 있습니다.
// 공이 하나라도 밖에 나가있으면 배열의 범위를 초과해 visit을 사용할 수 없습니다.
if(v[next[0][0]][next[0][1]][next[1][0]][next[1][1]]) continue; // 이미 방문한 경우라면 패스
v[next[0][0]][next[0][1]][next[1][0]][next[1][1]] = true;
q.add(next);
}
}
time++;
if(time>=10) return -1;
}
return -1;
}
// 보드에 동전이 몇개 있는지 확인
public static int Validate(int[][] now, int N, int M) {
int cnt = 0;
if(0 <= now[0][0] && now[0][0] < N && 0 <= now[0][1] && now[0][1] < M) cnt++;
if(0 <= now[1][0] && now[1][0] < N && 0 <= now[1][1] && now[1][1] < M) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
}기타
처음 문제를 풀 때 시간과 메모리 모두 매우 비효율적이었습니다. 그 이유는 방문표시를 하지 않아 중복된 값을 계속 큐에 집어넣었기 때문입니다.
처음 사용한 코드(시간이 오래걸린 코드)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dx = {0,1,0,-1};
static int[] dy = {1,0,-1,0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
char[][] board = new char[N][M];
int[][] ballPosition = new int[2][2];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String s = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
board[i][j] = s.charAt(j);
if(board[i][j] == 'o') {
ballPosition[cnt++] = new int[] {i,j};
}
}
}
int answer = BFS(ballPosition,N,M,board);
System.out.println(answer);
}
public static int BFS(int[][] start, int N, int M, char[][] board) {
Queue<int[][]> q = new LinkedList<int[][]>();
q.add(start);
int time = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while(--size>=0) {
int[][] now = q.poll();
int[] ballOne = now[0];
int[] ballTwo = now[1];
int ballCnt = Validate(now,N,M);
if(ballCnt == 1) return time;
if(ballCnt == 0) continue;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int[][] next = new int[2][2];
int nx1 = ballOne[0]+dx[d];
int ny1 = ballOne[1]+dy[d];
int nx2 = ballTwo[0]+dx[d];
int ny2 = ballTwo[1]+dy[d];
if(0 <= nx1 && nx1 < N && 0 <= ny1 && ny1 < M && board[nx1][ny1] == '#') {
next[0] = ballOne;
}else {
next[0] = new int[] {nx1,ny1};
}
if(0 <= nx2 && nx2 < N && 0 <= ny2 && ny2 < M && board[nx2][ny2] == '#') {
next[1] = ballTwo;
}else {
next[1] = new int[] {nx2,ny2};
}
q.add(next);
}
}
time++;
if(time>10) return -1;
}
return -1;
}
public static int Validate(int[][] now, int N, int M) {
int cnt = 0;
if(0 <= now[0][0] && now[0][0] < N && 0 <= now[0][1] && now[0][1] < M) cnt++;
if(0 <= now[1][0] && now[1][0] < N && 0 <= now[1][1] && now[1][1] < M) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
}- 개선된 풀이와의 가장 큰 차이점은
방문배열을 사용했다는 점입니다. 그리고 방문배열을 사용하기 위해Validate검사를 queue에서 꺼낸 뒤가 아니라 queue에 집어넣기 전에 했다는 점이 가장 큰 차이입니다.

