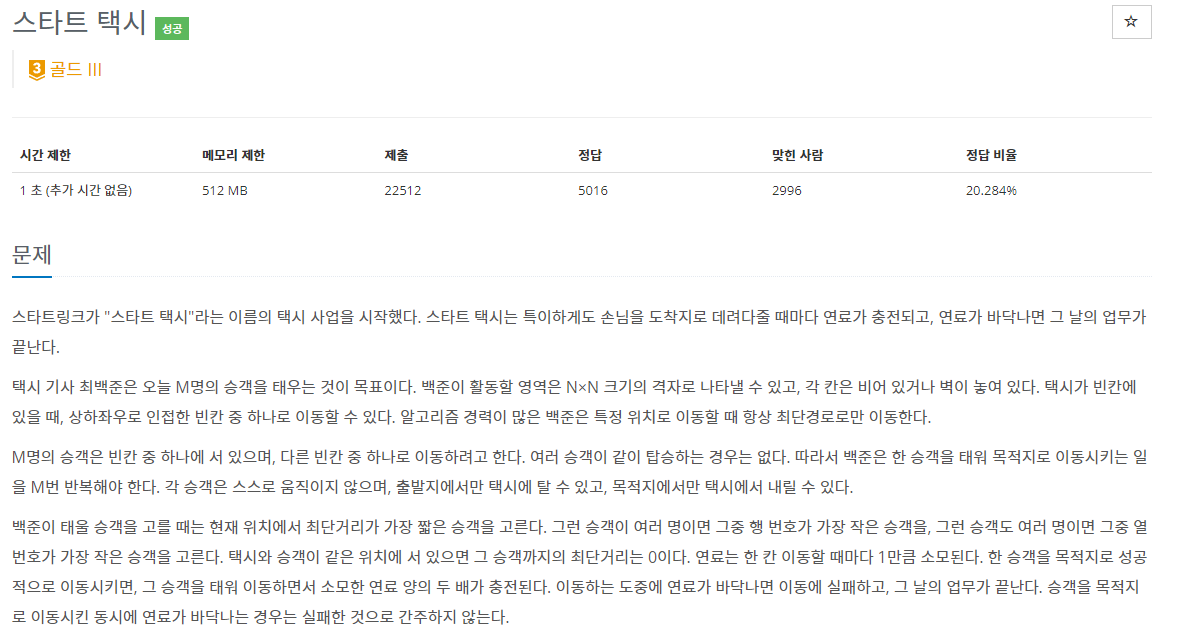
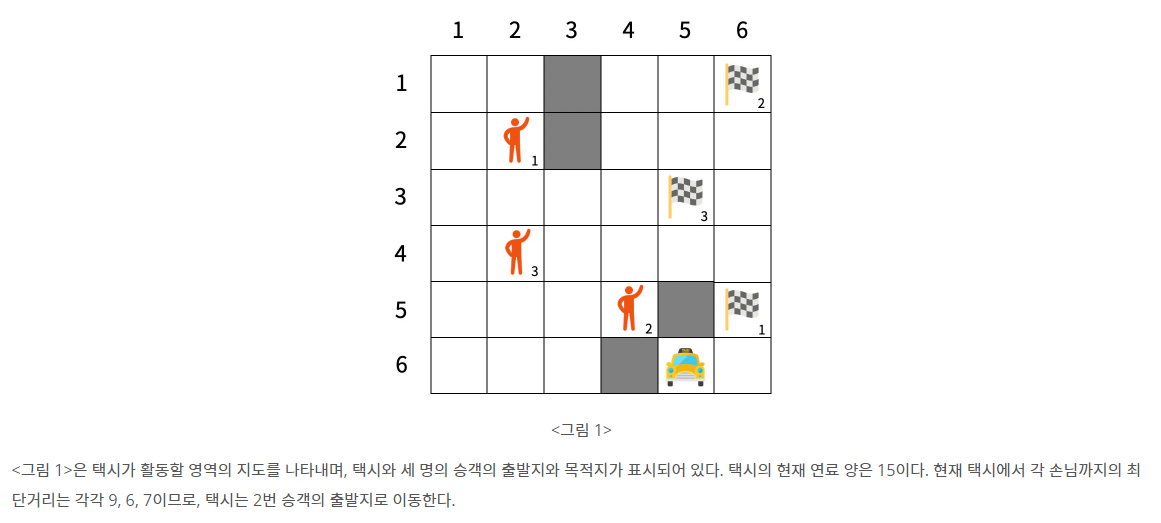
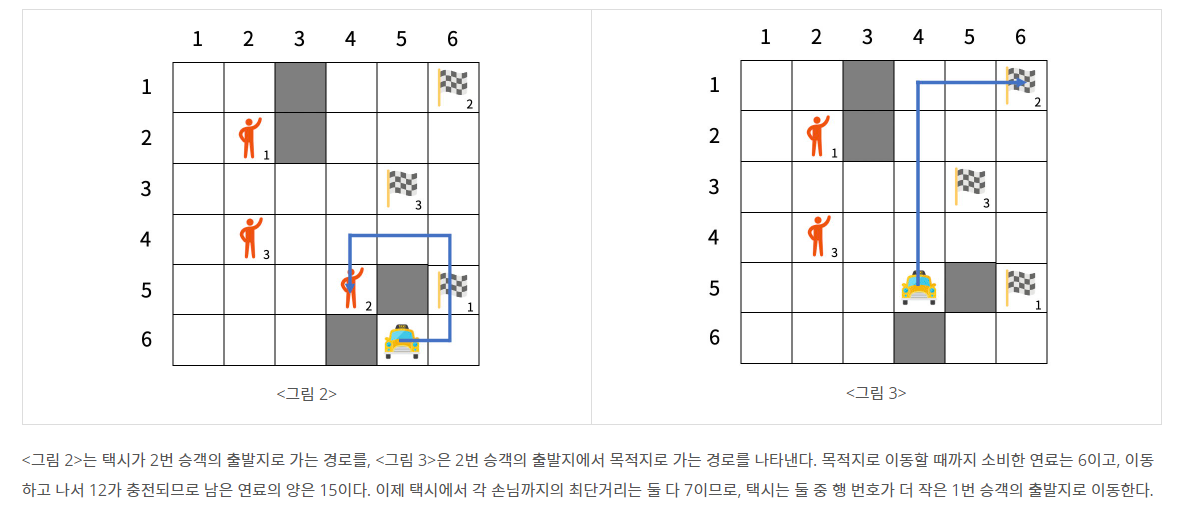
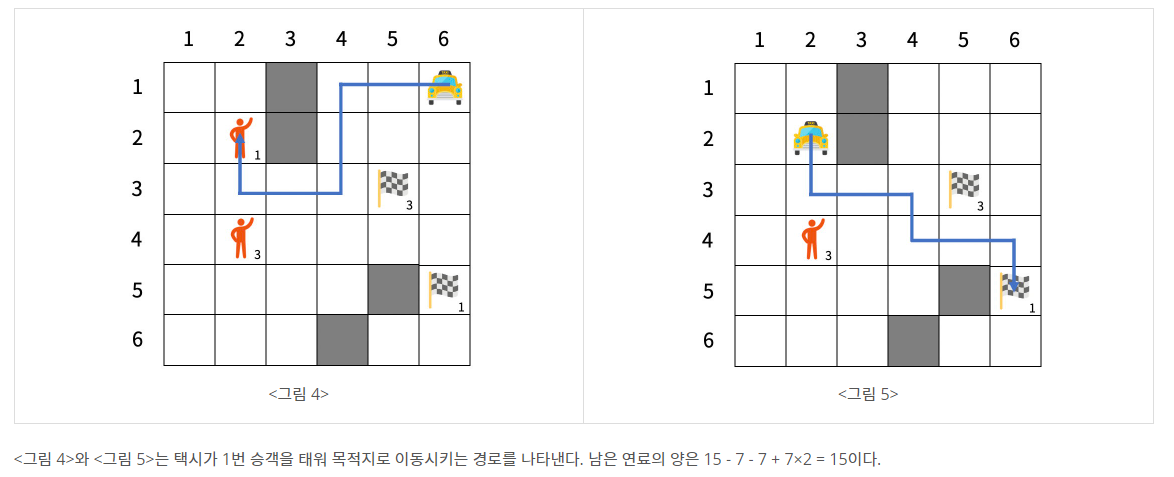
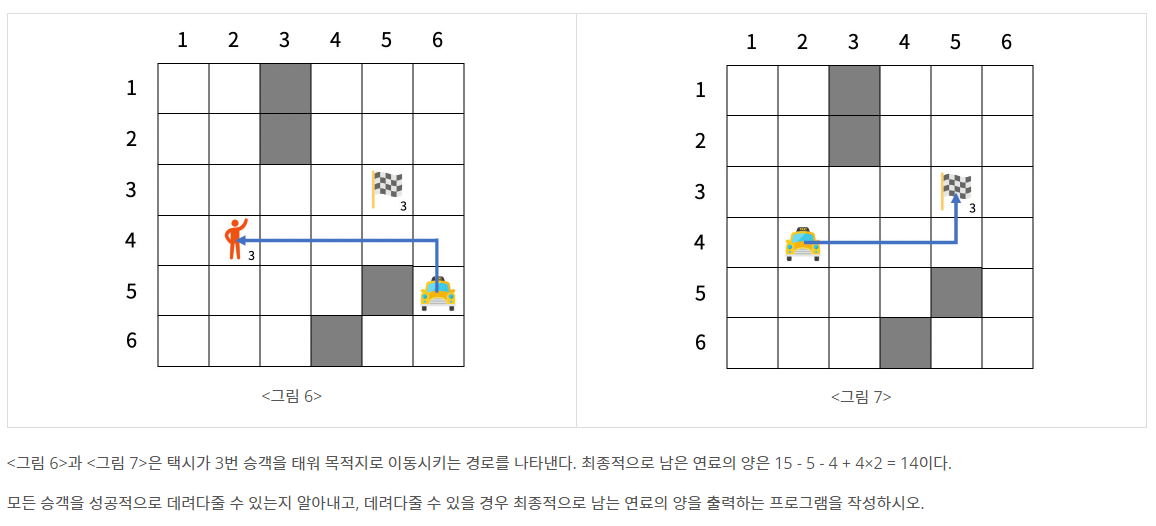
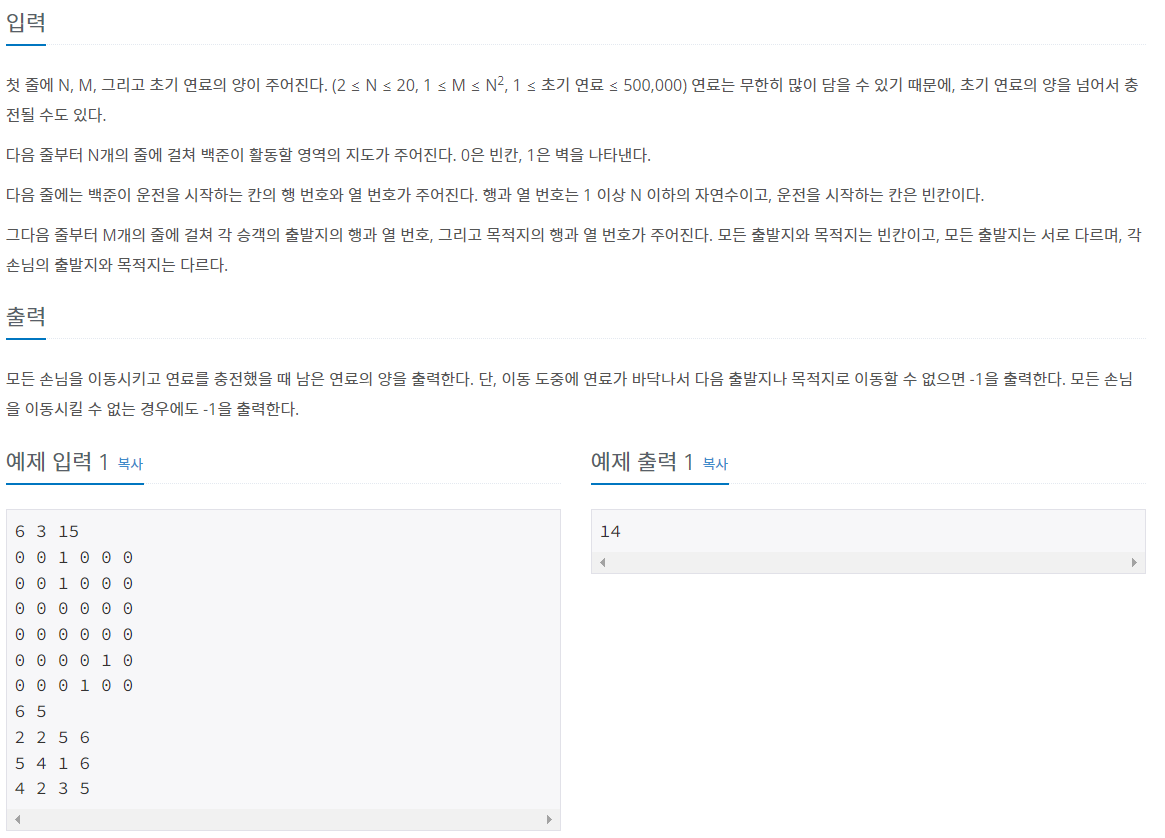
문제 설명
-
- 현재 위치에서 가장 가까이에 있는 사람을 태웁니다.
- 해당 사람을 목적지에 내려다 줍니다.
택시는 한 칸을 움직일 때 연료를 1 소비합니다. 사람을 목적지에 내려다주면 해당거리x2만큼 연료를 충전받습니다.
주행 도중 연료가 바닥나면 -1을 반환합니다.
1과 2를 반복해 모든 사람을 옮길 수 있다면 모두 옮긴 뒤 남은 연료를, 그럴 수 없다면 -1을 반환합니다.
접근법
- 'A가 서있는 위치가 B의 도착지' 인 경우가 있을 수 있다 생각해 도착지와 목적지를 모두 배열에 표현하지 않았습니다.
- 대신 도착지 좌표에 목적지 Node를 갖는 pBoard를 만들어 활용했습니다.
- pBoard에서 벽의 유뮤를 확인하지 않았고 board배열에서 벽의 유무를 확인했습니다.
- 현재 위치에서 가장 가까운 사람을 찾는 BFS, 어떤 사람을 목적지까지 태우는 BFS를 따로 구현했습니다.
주행 도중 연료가 바닥나면 -1을 반환한다라는 조건을 BFS도중 확인하지 않고 BFS를 끝낸 후 연료의 양을 계산했습니다.행이 낮은 순서로, 행이 같다면 열이 낮은 순서로라는 조건은 단순히위,좌,우,아래순서로 탐색하는 방법으로 만족시킬 수 없습니다.- 그 이유는
위,좌,우,아래순서는 거리가 1일 경우에만 유효하기 때문입니다. - 그래서 BFS를 위한 큐 대신 우선순위 큐를 사용했습니다.
- 그 이유는
정답
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dx = { -1, 0, 0, 1 };
static int[] dy = { 0, -1, 1, 0 };
static int[] position;
static int P;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
P = sc.nextInt();
int[][] board = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
board[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
position = new int[] { sc.nextInt() - 1, sc.nextInt() - 1 };
Node[][] pBoard = new Node[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int sx = sc.nextInt() - 1;
int sy = sc.nextInt() - 1;
int ex = sc.nextInt() - 1;
int ey = sc.nextInt() - 1;
pBoard[sx][sy] = new Node(ex,ey);
}
System.out.println(answer(N,M,board,pBoard));
}
public static int answer(int N, int M, int[][] board, Node[][] pBoard) {
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int result = BFS_findSomething(board, pBoard, N);
if(result<0) return -1; // 사람을 못찾으면
P-=result;
if(P<0) return -1; // 연료가 바닥나면
int result2 = BFS_toDestination(board, pBoard, N);
if(result2<0) return -1; // 목적지에 못대려다주면
P-=result2;
if(P<0) return -1; // 연료가 바닥나면
P+=result2*2;
}
return P;
}
public static int BFS_findSomething(int[][] board, Node[][] pBoard, int N) {
boolean[][] v = new boolean[N][N];
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((a,b) -> (a[0]==b[0])?(a[1]-b[1]):(a[0]-b[0]));
v[position[0]][position[1]] = true;
q.add(position);
int pure = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
List<int[]> tempQ = new LinkedList<int[]>();
while(--size>=0) {
int[] now = q.poll();
if(pBoard[now[0]][now[1]] != null) {
position = new int[] {now[0],now[1]};
return pure;
}
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = now[0] + dx[d];
int ny = now[1] + dy[d];
if(0 <= nx && nx < N && 0 <= ny && ny < N && board[nx][ny] != 1 && !v[nx][ny]) {
v[nx][ny] = true;
tempQ.add(new int[] {nx,ny});
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < tempQ.size(); i++) {
q.add(tempQ.get(i));
}
pure++;
}
return -1;
}
public static int BFS_toDestination(int[][] board, Node[][] pBoard, int N) {
boolean[][] v = new boolean[N][N];
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((a,b) -> (a[0]==b[0])?(a[1]-b[1]):(a[0]-b[0]));
v[position[0]][position[1]] = true;
q.add(position);
int[] start = new int[] {position[0],position[1]};
int[] destination = new int[] {pBoard[position[0]][position[1]].x,pBoard[position[0]][position[1]].y};
int pure = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
List<int[]> tempQ = new LinkedList<int[]>();
while(--size>=0) {
int[] now = q.poll();
if(now[0] == destination[0] && now[1] == destination[1]) {
position = new int[] {now[0],now[1]};
pBoard[start[0]][start[1]] = null;
return pure;
}
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = now[0] + dx[d];
int ny = now[1] + dy[d];
if(0 <= nx && nx < N && 0 <= ny && ny < N && board[nx][ny] != 1 && !v[nx][ny]) {
v[nx][ny] = true;
tempQ.add(new int[] {nx,ny});
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < tempQ.size(); i++) {
q.add(tempQ.get(i));
}
pure++;
}
return -1;
}
static class Node{
int x;
int y;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [x=" + x + ", y=" + y + "]";
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}

