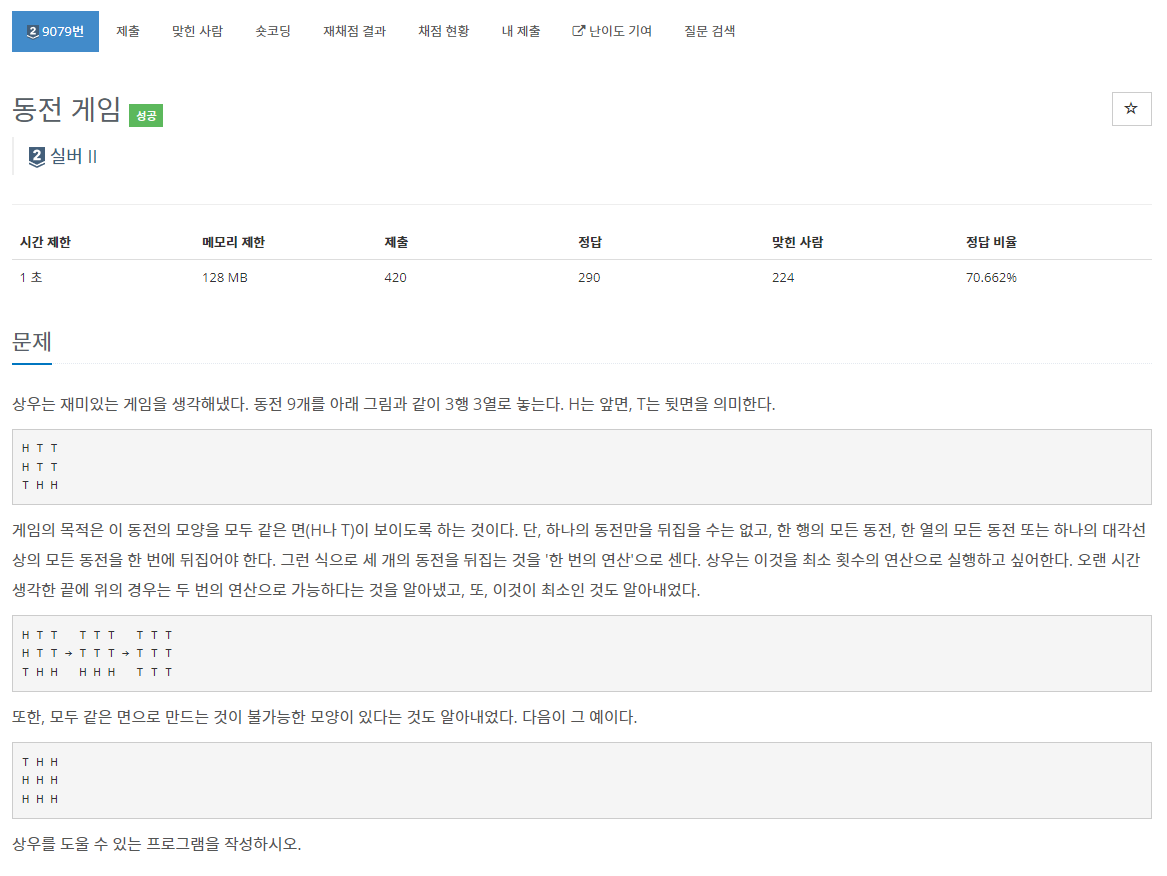
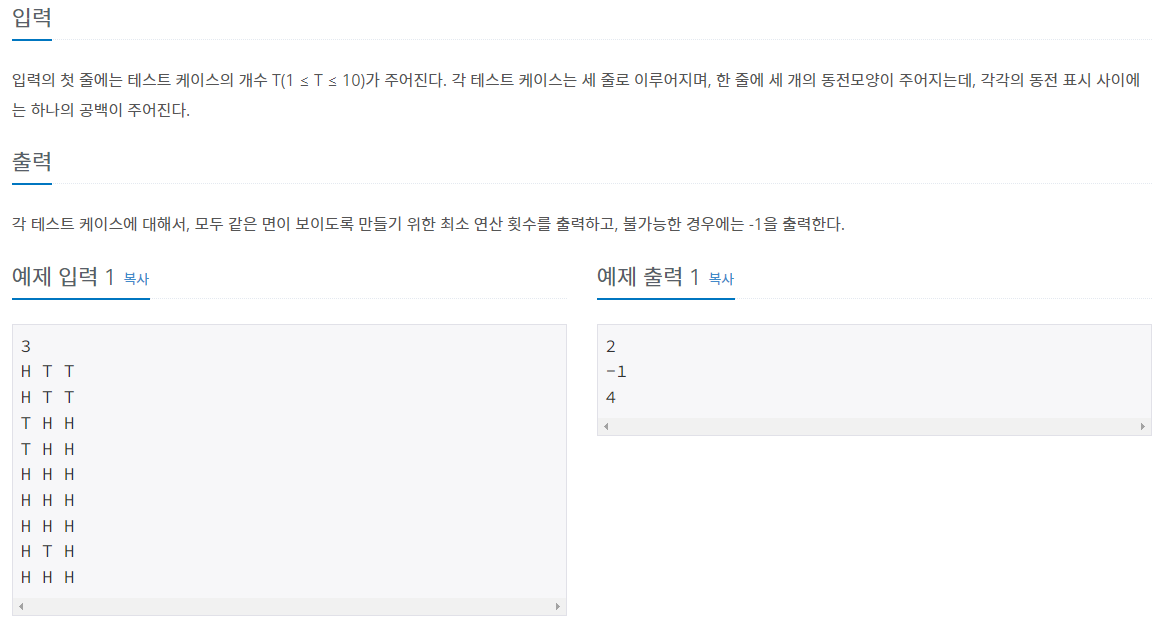
문제 설명
접근법
- 이전에 나왔던 배열의 상태(모양)가 반복되서 나타났다면 해당 경우는 더 이상 검사할 필요가 없습니다.
- 100 배열을 100011101(2)로 생각해 285라는 숫자로 치환할 수 있습니다.
011
101
- 3x3배열은 총 512개의 경우의 수가 존재하며 이는 9자리의 2진수로 모두 표현할 수 있습니다.
- 3x3배열을 뒤집는 경우의 수는 모두 8가지 입니다. 8가지 경우를 직접 입력해 주었습니다.
- 3x3배열을 새롭게 만드는 방법으로 백트래킹을 실행했습니다.
정답
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dx = { 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1 };
static int[] dy = { 1, 0, -1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1 };
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
int N = 3;
int[][] board = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine().trim());
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
if ("H".equals(st.nextToken())) {
board[i][j] = 1;
} else {
board[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
System.out.println(BFS(board));
}
}
public static int BFS(int[][] board) {
boolean[] v = new boolean[512];
v[findIndex(board)] = true;
Queue<int[][]> q = new LinkedList<int[][]>();
q.add(board);
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while (--size >= 0) {
board = q.poll();
if (Validate(board)) {
return cnt;
}
for (List<int[]> next : PossibleFlip()) {
int[][] nextBoard = Flip(next, board);
if (!v[findIndex(nextBoard)]) {
v[findIndex(nextBoard)] = true;
q.add(nextBoard);
}
}
}
cnt++;
}
return -1;
}
public static int findIndex(int[][] board) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
sb.append(board[i][j]);
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(sb.toString(), 2);
}
public static int[][] Flip(List<int[]> next, int[][] board) {
int[][] copyBoard = new int[3][3];
for (int i = 0; i < copyBoard.length; i++) {
copyBoard[i] = board[i].clone();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
copyBoard[next.get(i)[0]][next.get(i)[1]] = Math.abs(board[next.get(i)[0]][next.get(i)[1]] - 1);
}
return copyBoard;
}
public static boolean Validate(int[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != board[0][0])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static List<List<int[]>> PossibleFlip() {
List<List<int[]>> result = new ArrayList<List<int[]>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
List<int[]> temp = new ArrayList<int[]>();
temp.add(new int[] { 0, i });
temp.add(new int[] { 1, i });
temp.add(new int[] { 2, i });
result.add(temp);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
List<int[]> temp = new ArrayList<int[]>();
temp.add(new int[] { i, 0 });
temp.add(new int[] { i, 1 });
temp.add(new int[] { i, 2 });
result.add(temp);
}
List<int[]> temp = new ArrayList<int[]>();
temp.add(new int[] { 0, 0 });
temp.add(new int[] { 1, 1 });
temp.add(new int[] { 2, 2 });
result.add(temp);
List<int[]> temp2 = new ArrayList<int[]>();
temp2.add(new int[] { 0, 2 });
temp2.add(new int[] { 1, 1 });
temp2.add(new int[] { 2, 0 });
result.add(temp2);
return result;
}
}



