
토큰과 렉서 추가확장
토큰
-,/,*,<,> 와 같은 문자와
== , != 같은 수식
return 과 같은 예약어를 추가한다.token.h
#pragma once
#define ILLEGAL_TOKEN "ILLEGAL_TOKEN"
#define EOF_TOKEN "EOF"
#define IDENT_TOKEN "IDENT"
#define INT "INT"
// 연산자
#define ASSIGN_TOKEN "="
#define PLUS_TOKEN "+"
#define MINUS_TOKEN "-"
#define BANG_TOKEN "!"
#define ASTERISK_TOKEN "*"
#define SLASH_TOKEN "/"
#define LT_TOKEN "<"
#define GT_TOKEN ">"
#define EQ_TOKEN "=="
#define NOT_EQ_TOKEN "!="
// 구분자
#define COMMA_TOKEN ","
#define SEMICOLON_TOKEN ";"
#define LPAREN_TOKEN "("
#define RPAREN_TOKEN ")"
#define LBRACE_TOKEN "{"
#define RBRACE_TOKEN "}"
// 예약어
#define FUNCTION_TOKEN "FUNCTION"
#define LET_TOKEN "LET"
#define TRUE_TOKEN "TRUE"
#define FALSE_TOKEN "FALSE"
#define IF_TOKEN "IF"
#define ELSE_TOKEN "ELSE"
#define RETURN_TOKEN "RETURN"
typedef const char* TokenType;
typedef struct _token {
TokenType type;
char* literal;
//type은 enum으로 저장해 두다가 나중에 필요하면 TokenType으로 사용하고
//literal은 어떤건지 특정하게 받아오는것 얘를 들어 5가 저장되고 이걸 INT로 나중에 토큰 타입으로 두기
}Token;
또한 lexer.c에 추가된 토큰을 다룰수 있게 바꿔준다.
#include "lexer.h"
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
Lexer* New(char* input)
{
//인풋 받으면 새롭게 Lexer 구조체 만들어서 input 저장해두는 함수
Lexer* l = (Lexer*)malloc(sizeof(Lexer));
l->input = _strdup(input);
if (!l->input) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed for input string\n");
free(l);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}//인풋이 없을때 오류메시지 생성과 종료
l->ch = 0;
l->position = 0;
l->readPosition = 0;
readChar(l);
return l;
}
void readChar(Lexer* lexer)
{
if (lexer->readPosition > strlen(lexer->input)){
lexer->ch = 0;//참조를 넘어가면 ch에 0넣기
}
else {
lexer->ch = lexer->input[lexer->readPosition];
}
lexer->position = lexer->readPosition;
(lexer->readPosition)++;
//미리 살펴보고 해도 되나 검사
//또한 현재 문자를 일단 보관을 해야하니
}
char peekChar(Lexer* l)
{
if (l->readPosition >= strlen(l->input)) {
return 0;//참조를 넘어가면 0 리턴
}
else {
return l->input[l->readPosition];
}
}
char* readNumber(Lexer* lexer)
{
int position = lexer->position;
while (isDigit(lexer->ch)) {
readChar(lexer);
}
const int len = lexer->position - position;
char* str = (char*)malloc(len + 1);
if (str == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed\n");
return;
}
strncpy_s(str, len + 1, lexer->input + position, len);
return str;
}
Token* NextToken(Lexer* lexer)
{
Token *tok=NULL;
skipWhitespace(lexer);
char lch = lexer->ch;
switch (lch)
{
case '=':
if (peekChar(lexer) == '=') {
readChar(lexer);
tok = (Token*)malloc(sizeof(Token));
tok->type = EQ_TOKEN;
tok->literal = "==";
}else tok = newToken(ASSIGN_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case ';':
tok = newToken(SEMICOLON_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '(':
tok = newToken(LPAREN_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case ')':
tok = newToken(RPAREN_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case ',':
tok = newToken(COMMA_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '+':
tok = newToken(PLUS_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '-':
tok = newToken(MINUS_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '!':
if (peekChar(lexer) == '=') {
readChar(lexer);
tok = (Token*)malloc(sizeof(Token));
tok->type = NOT_EQ_TOKEN;
tok->literal = "!=";
}
else tok = newToken(BANG_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '*':
tok = newToken(ASTERISK_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '/':
tok = newToken(SLASH_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '<':
tok = newToken(LT_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '>':
tok = newToken(GT_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '{':
tok = newToken(LBRACE_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case '}':
tok = newToken(RBRACE_TOKEN, lch);
break;
case 0:
tok = (Token*)malloc(sizeof(Token));
if (tok == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed for tok.\n");
exit(1); // 프로그램 종료
}
tok->type = EOF_TOKEN;
tok->literal = _strdup("");
break;
default:
if (isLetter(lch)) {
tok = (Token*)malloc(sizeof(Token));
if (tok == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed for tok.\n");
exit(1); // 프로그램 종료
}
tok->literal = _strdup(readIdentifier(lexer));
tok->type = LookupIdent(tok->literal);
return tok;
}
else if (isDigit(lch)) {
tok = (Token*)malloc(sizeof(Token));
if (tok == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed for tok.\n");
exit(1); // 프로그램 종료
}
tok->type = INT;
tok->literal = readNumber(lexer);
return tok;
}
else {
tok = newToken(ILLEGAL_TOKEN, lch);
}
}
readChar(lexer);
return tok;
}
Token*newToken(TokenType token, char input)
{
Token* newToken = (Token*)malloc(sizeof(Token));
char* str = (char*)malloc(2);
str[0] = input; // 입력받은 char를 첫 번째 위치에 저장
str[1] = '\0'; // 문자열 종료 문자 추가
//토큰 받으면 input 받아서 리터럴 처리한후에 토큰 객체 돌려주기
//newToken->literal = _strdup(TokenTypeNames[token]);
//그냥 어차피 상수 포인터로 가르키기만 할건데 이렇게 해도 될듯...?
newToken->type = token;
newToken->literal = _strdup(str);
return newToken;
}
void skipWhitespace(Lexer* l)
{
while (l->ch == ' ' || l->ch == '\t' || l->ch == '\n' || l->ch == '\r')
readChar(l);
}
bool isLetter(char ch)
{
return 'a'<=ch&&ch<='z'||'A'<=ch&&ch<='Z'||ch=='_';
}
bool isDigit(char ch)
{
return '0'<=ch&&ch<='9';
}
char* readIdentifier(Lexer* l)
{
int position = l->position;
while (isLetter(l->ch)) {
readChar(l);
}
const int len = l->position - position;
char* str = (char*)malloc(len + 1);
if (str == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed\n");
return;
}
strncpy_s(str, len + 1, l->input + position, len);
return str;
}
const char* LookupIdent(const char* ident) {
if (strcmp(ident, "fn") == 0) {
return FUNCTION_TOKEN;
}
if (strcmp(ident, "let") == 0) {
return LET_TOKEN;
}
if (strcmp(ident, "true") == 0) {
return TRUE_TOKEN;
}
if (strcmp(ident, "false") == 0) {
return FALSE_TOKEN;
}
if (strcmp(ident, "if") == 0) {
return IF_TOKEN;
}
if (strcmp(ident, "else") == 0) {
return ELSE_TOKEN;
}
if (strcmp(ident, "return") == 0) {
return RETURN_TOKEN;
}
return IDENT_TOKEN; // 매칭되는 키워드가 없으면 IDENT 반환
}
추가사항으로 ==등을 확인하기 위해서 peekChar() 함수를 만들어
= 나 ! 이 나올때 다음 문자를 확인한후 !=인지 ==인지 체크후 처리하게끔 한다.
REPL
Monkey언어에는 REPL이 필요하다.
repl.c
#include "repl.h"
#include "lexer.h"
#include "token.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void start(FILE*in,FILE*out)
{
char line[MAX_LIEN_LENGTH];
while (true) {
fprintf(out, PROMPT);
if (fgets(line, MAX_LIEN_LENGTH, in) == NULL) {
break; //EOF 또는 오류
}
//개행문자 제거
size_t len = strlen(line);
if (len > 0 && line[len - 1] == '\n') {
line[len - 1] = '\0';
}
Lexer* lexer = New(line);
while (true) {
Token *tok = NextToken(lexer);
if (strcmp(tok->type, EOF_TOKEN) == 0) {
break;
}
fprintf(out, "{Type:%s, Literal:%s}\n", tok->type, tok->literal);
}
free(lexer);
}
}
main.c
#include"repl.h"
#include <windows.h>
#include <lmcons.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "lexer_test.h"
int main() {
test_start();
char username[UNLEN + 1];
DWORD username_len = UNLEN + 1;
GetUserName(username, &username_len);
printf("Hello %s! This is the Monkey programming lauguage!\n", username);
printf("Feel free to type in commands\n");
start(stdin, stdout);
return 0;
}repl 실행 결과
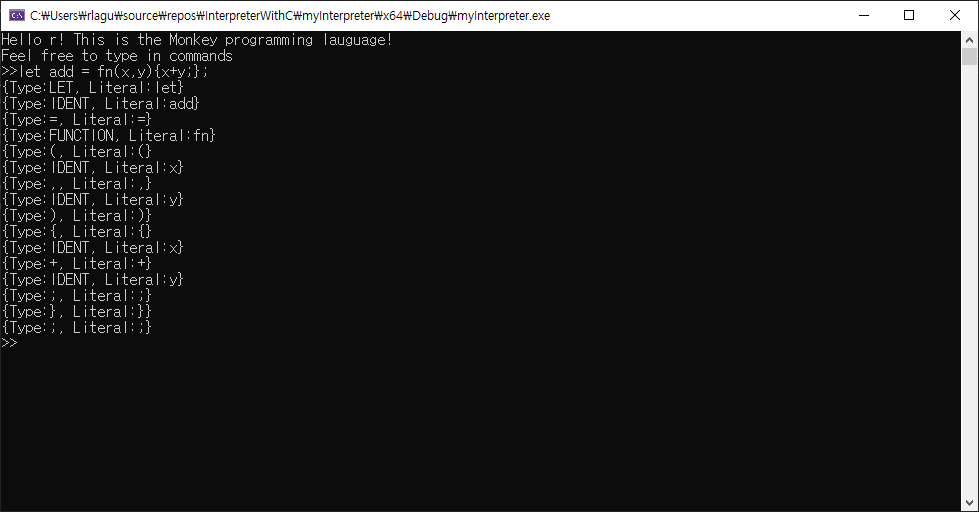
렉서 끝내고 느낀점?
go로 적힌 언어를 c로 바꾸는게 생각보다 쉬운거 같으면서 어려웠음
책 따라가면서 따라 치는거라 생각보다 막 어렵다고 느껴지지는 않았음.
나중에 내가 다 만들고 기능들 추가하거나 c++로 만들거나 해봐야겠음