wait()/notify()
- 리소스가 어떤 조건에서 더 이상 유효하지 않은 경우, 리소스를 기다리기 위해 Thread가 wait() 상태가 된다.
- wait() 상태가 된 Thread는 notify()가 호출 될 때까지 기다린다.
- 유효한 자원이 생기면 notify()가 호출되고 wait()하고 있는 Thread중 무작위로 하나의 Thread를 재시작 하도록 한다.(어떤 Thread가 가장 먼저 재시작 할지는 모른다.)
- notifyAll()이 호출되는 경우 wait()하고 있는 모든 Thread가 재시작 된다.
- 이 경우, 유효한 리소스만큼의 Thread만이 수행될 수 있고 자원을 갖지 못한 Thread의 경우는 다시 wait() 상태로 만든다.(끝까지 재시작 하지 못하는 Thread가 있을 가능성도 있다.)
- 자바에서는
notifyAll()메서드의 사용을 권장한다.
도서관에서 책을 빌리는 예제
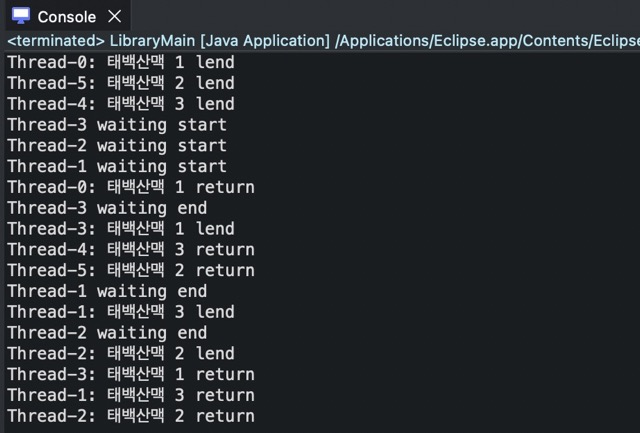
notify()를 사용한 경우
Class Library{
public ArrayList<String> shelf = new ArrayList<String>();
public Library(){
shelf.add("태백산맥 1");
shelf.add("태백산맥 2");
shelf.add("태백산맥 3");
}
public synchronized String lendBook() throws InterruptedException{
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
if(shelf.size() == 0 ) {
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting start");
wait();
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting end");
}
String book = shelf.remove(0);
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + book + " lend");
return book;
}
public synchronized void returnBook(String book){
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
shelf.add(book);
notify();
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + book + " return");
}
}
class Student extends Thread{
public void run(){
try{
String title = LibraryMain.library.lendBook();
if( title == null ) return;
sleep(5000);
LibraryMain.library.returnBook(title);
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
public class LibraryMain {
public static Library library = new Library();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student std1 = new Student();
Student std2 = new Student();
Student std3 = new Student();
Student std4 = new Student();
Student std5 = new Student();
Student std6 = new Student();
std1.start();
std2.start();
std3.start();
std4.start();
std5.start();
std6.start();
}
}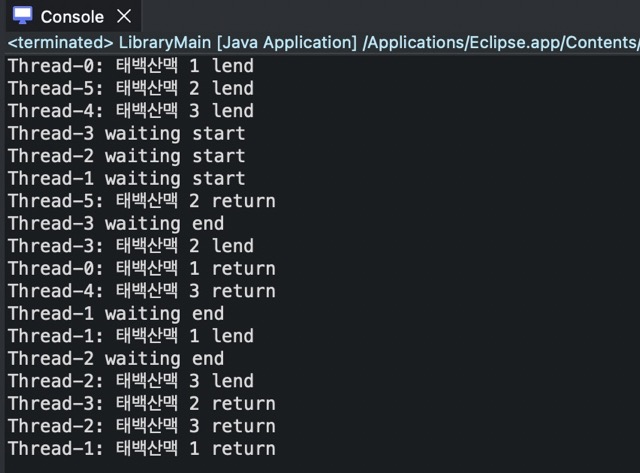
notifyAll()을 사용한 경우
lendBook()/ returnBook() 메서드 수정
public synchronized String lendBook() throws InterruptedException{
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
while( shelf.size() == 0 ){
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting start");
wait();
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting end");
}
String book = shelf.remove(0);
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + book + " lend");
return book;
}
public synchronized void returnBook(String book){
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
shelf.add(book);
notifyAll();
System.out.println(t.getName() + ": " + book + " return");
}