🚀링크
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/49189
💻문제
n개의 노드가 있는 그래프가 있습니다. 각 노드는 1부터 n까지 번호가 적혀있습니다. 1번 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드의 갯수를 구하려고 합니다. 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드란 최단경로로 이동했을 때 간선의 개수가 가장 많은 노드들을 의미합니다.
노드의 개수 n, 간선에 대한 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열 vertex가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 1번 노드로부터 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드가 몇 개인지를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
제한사항
노드의 개수 n은 2 이상 20,000 이하입니다.
간선은 양방향이며 총 1개 이상 50,000개 이하의 간선이 있습니다.
vertex 배열 각 행 [a, b]는 a번 노드와 b번 노드 사이에 간선이 있다는 의미입니다.
입출력 예
n vertex return
6 [[3, 6], [4, 3], [3, 2], [1, 3], [1, 2], [2, 4], [5, 2]] 3
입출력 예 설명
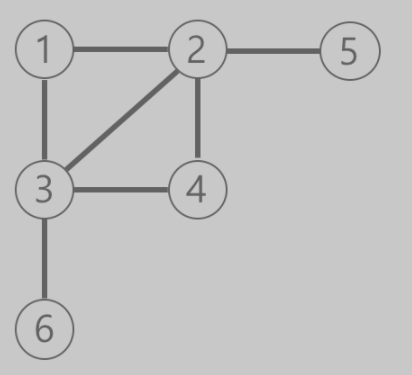
예제의 그래프를 표현하면 아래 그림과 같고, 1번 노드에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드는 4,5,6번 노드입니다.
🌏문제풀이
1) 인접행렬을 링크드리스트 그래프로 변환.
2) point
count[e] = count[tmp]+1q 가장 앞의 값을 poll() 하면서 큐에 넣는 노드들은 같은 깊이를 가지며, poll()한 노드보다 +1 만큼 깊다.
👩💻코드
import java.util.*;
class CngEdge{
int n;
boolean[] visited;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
int[] count;
int anw = 0;
public CngEdge(int n){
this.n = n;
this.visited = new boolean[n+1];
this.count = new int[n+1];
this.graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
}
public void put(int x, int y){
graph.get(x).add(y);
graph.get(y).add(x);
}
public int get(){
return anw;
}
public void print(){
for(int i=0; i<n+1; i++){
System.out.print(i + " : ");
for(int j=0; j<graph.get(i).size(); j++){
System.out.print(graph.get(i).get(j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void dfs(int x){
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.offer(x);
visited[x] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int tmp = q.poll();
for(int e : graph.get(tmp)){
if(!visited[e]){
//[0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2]
//poll()기준으로 연결된 노드를 가져왔다는 것은 poll()한 값보다 깊이가 +1
count[e] = count[tmp]+1;
q.offer(e);
visited[e] = true;
}
}
}
//가장 깊은 거리를 가진 노드를 카운트
int max = 0;
for(int i=0; i<count.length; i++){
if(max < count[i]){
max = count[i];
anw = 0;
}
if(max == count[i]){
anw++;
}
}
}
}
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list;
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
list = new ArrayList<>();
CngEdge cngEdge = new CngEdge(n);
for(int i=0; i<edge.length; i++){
cngEdge.put(edge[i][0], edge[i][1]);
}
cngEdge.dfs(1);
answer = cngEdge.get();
return answer;
}
}