데이터 타입
let integer = 8; // 정수
let double = 8.8; // 실수
let negative = -8 // 음의 정수console.log(1 === 1.0) // true // 숫자 타입은 모두 실수로 처리된다.
console.log(10/0) // Infinity
console.log(10/-0) // -Infinity
console.log(1 * "string") // NaN문자열 타입
=> 작은,큰 따옴표, 백틱let string = word; // 따옴표로 감싸지 않은 word를 식별자로 인식 let str = "hello
world" // 문법 에러let fee;
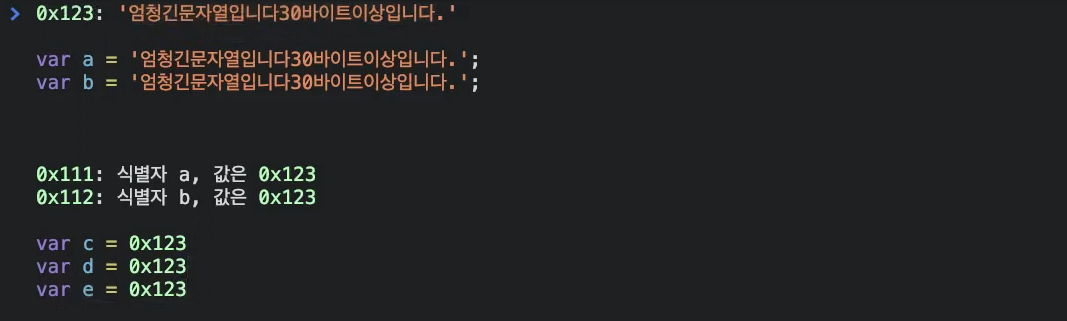
console.log(fee) // undifinedvar foo = 'Lee';
// 이전에 할당되어 있던 값에 대한 참조를 제거. foo 변수는 더 이상 'Lee'를 참조하지 않는다.
// 유용해 보이지는 않는다. 변수의 스코프를 좁게 만들어 변수 자체를 재빨리 소멸시키는 편이 낫다.
foo = null;불변값의 개념
// c 변수에는 1바이트 정수 타입의 값(-128 ~ 127)만을 할당할 수 있다.
char c;
// num 변수에는 4바이트 정수 타입의 값(-2,124,483,648 ~ 2,124,483,647)만을 할당할 수 있다.
int num;var foo;
console.log(typeof foo); // undefined
foo = 3;
console.log(typeof foo); // number
foo = 'Hello';
console.log(typeof foo); // string
foo = true;
console.log(typeof foo); // boolean
foo = null;
console.log(typeof foo); // object
foo = Symbol(); // 심벌
console.log(typeof foo); // symbol
foo = {}; // 객체
console.log(typeof foo); // object
foo = []; // 배열
console.log(typeof foo); // object
foo = function () {}; // 함수
console.log(typeof foo); // function연산자
// 산술 연산자
5 * 4 // -> 20
// 문자열 연결 연산자
'My name is ' + 'Lee' // -> 'My name is Lee'
// 할당 연산자
color = 'red' // -> 'red'
// 비교 연산자
3 > 5 // -> false
// 논리 연산자
true && false // -> false
// 타입 연산자
typeof 'Hi' // -> stringvar x = '1';
// 문자열을 숫자로 타입 변환한다.
console.log(+x); // 1
// 부수 효과는 없다.
console.log(x); // "1"
// 불리언 값을 숫자로 타입 변환한다.
x = true;
console.log(+x); // 1
// 부수 효과는 없다.
console.log(x); // true
// 불리언 값을 숫자로 타입 변환한다.
x = false;
console.log(+x); // 0
// 부수 효과는 없다.
console.log(x); // false
// 문자열을 숫자로 타입 변환할 수 없으므로 NaN을 반환한다.
x = 'Hello';
console.log(+x); // NaN
// 부수 효과는 없다.
console.log(x); // "Hello"// 부호를 반전한다.
-(-10); // -> 10
// 문자열을 숫자로 타입 변환한다.
-'10'; // -> -10
// 불리언 값을 숫자로 타입 변환한다.
-true; // -> -1
// 문자열은 숫자로 타입 변환할 수 없으므로 NaN을 반환한다.
-'Hello'; // -> NaN// 문자열 연결 연산자
'1' + 2; // -> '12'
1 + '2'; // -> '12'
// 산술 연산자
1 + 2; // -> 3
// true는 1로 타입 변환된다.
1 + true; // -> 2
// false는 0으로 타입 변환된다.
1 + false; // -> 1
// null은 0으로 타입 변환된다.
1 + null; // -> 1
// undefined는 숫자로 타입 변환되지 않는다.
+undefined; // -> NaN
1 + undefined; // -> NaNvar x;
// 할당문은 표현식인 문이다.
console.log(x = 10); // 10// 동등 비교. 결과를 예측하기 어렵다.
'0' == ''; // -> false
0 == ''; // -> true
0 == '0'; // -> true
false == 'false'; // -> false
false == '0'; // -> true
false == null; // -> false
false == undefined; // -> false// NaN은 자신과 일치하지 않는 유일한 값이다.
NaN === NaN; // -> false// 양의 0과 음의 0의 비교. 일치 비교/동등 비교 모두 결과는 true이다.
0 === -0; // -> true
0 == -0; // -> truevar x = 2;
// 2 % 2는 0이고 0은 false로 암묵적 타입 변환된다.
var result = x % 2 ? '홀수' : '짝수';
console.log(result); // 짝수var x = 2, result;
// 2 % 2는 0이고 0은 false로 암묵적 타입 변환된다.
if (x % 2) result = '홀수';
else result = '짝수';
console.log(result); // 짝수// 암묵적 타입 변환
!0; // -> true
!'Hello'; // -> false'Cat' && 'Dog'; // -> 'Dog'!(x || y) === (!x && !y)
!(x && y) === (!x || !y)typeof '' // -> "string"
typeof 1 // -> "number"
typeof NaN // -> "number"
typeof true // -> "boolean"
typeof undefined // -> "undefined"
typeof Symbol() // -> "symbol"
typeof null // -> "object"
typeof [] // -> "object"
typeof {} // -> "object"
typeof new Date() // -> "object"
typeof /test/gi // -> "object"
typeof function () {} // -> "function"Math.pow(2, 2); // -> 4
Math.pow(2, 2.5); // -> 5.65685424949238
Math.pow(2, 0); // -> 1
Math.pow(2, -2); // -> 0.25// 지수 연산자의 결합 순서는 우항에서 좌항이다. 즉, 우결합성을 갖는다.
2 ** (3 ** 2); // -> 512
Math.pow(2, Math.pow(3, 2)); // -> 512var num = 5;
num **= 2; // -> 25var x;
// 할당 연산자는 변수 값이 변하는 부수 효과가 있다.
// 이는 x 변수를 사용하는 다른 코드에 영향을 준다.
x = 1;
console.log(x); // 1
// 증가/감소 연산자(++/--)는 피연산자의 값을 변경하는 부수 효과가 있다.
// 피연산자 x의 값이 재할당되어 변경된다. 이는 x 변수를 사용하는 다른 코드에 영향을 준다.
x++;
console.log(x); // 2
var o = { a: 1 };
// delete 연산자는 객체의 프로퍼티를 삭제하는 부수 효과가 있다.
// 이는 o 객체를 사용하는 다른 코드에 영향을 준다.
delete o.a;
console.log(o); // {}