[코드트리 조별과제 1주차 코딩테스트 연습] 값을 반환하는 함수 / 그 계절, 그 날 (윤년) 문제 풀이 with 자바스크립트(Javascript) & 자바(Java)
0
코딩테스트연습
목록 보기
101/106

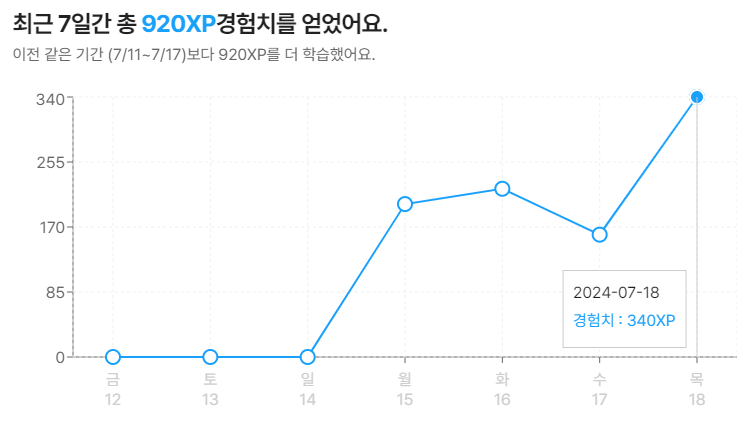
1. 첫번째 문제 풀이(2024-07-18)
해당 문제는 코테 문제 중에 유명한 윤년과 계절 맞추기를 혼합한 문제인데요. 나름 함수에 좀 익숙해진 감이 없잖아 있어서 메인 하나에 다 쓰기보다 함수를 여럿 만들어서 해당 문제를 풀어보기로 했습니다. 그럼 제가 만들어본 함수를 대략적으로 소개해 드리도록 하겠습니다.
- 주어진 월에 대한 계절을 유추하는 메서드
- 해당 연도가 윤년인지 아닌지에 따른 각각의 실행 메서드를 호출하는 메서드
- 윤년, 평년 각각의 진위 여부를 판단하는 메서드
그럼 해당 코드들을 토대로 문제를 풀어본 JS 코드를 소개해 드리겠습니다.
- 자바스크립트 버전
const fs = require('fs'); // 유효한 날짜인지 판단하는 함수 function checkNormalYear(month, day) { let flag = true; // 유효한 달인지 판단 if (month < 1 || month > 12) { return "-1"; } // 유효한 날짜인지 판단 switch (month) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: if (day < 1 || day > 31) flag = false; break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: if (day < 1 || day > 30) flag = false; break; case 2: if (day < 1 || day > 28) flag = false; break; } // 계절 반환 if (flag) return SeasonSelector(month); return "-1"; } // 윤년일 때 유효한 날짜인지 판단하는 함수 function checkLeapYear(month, day) { let flag = true; // 유효한 달인지 판단 if (month < 1 || month > 12) { return "-1"; } // 유효한 날짜인지 판단 switch (month) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: if (day < 1 || day > 31) flag = false; break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: if (day < 1 || day > 30) flag = false; break; case 2: if (day < 1 || day > 29) flag = false; break; } // 계절 반환 if (flag) return SeasonSelector(month); return "-1"; } // 주어진 연도를 기준으로 윤년, 평년 메서드 중 조건에 따라 메서드를 하나 실행하는 함수 function checkYearIs(year, month, day) { if (year % 400 === 0) { return checkLeapYear(month, day); } else if (year % 100 === 0) { return checkNormalYear(month, day); } else if (year % 4 === 0 && year % 100 !== 0 || year % 400 === 0) { return checkLeapYear(month, day); } else { return checkNormalYear(month, day); } } // 주어진 달이 속한 계절을 반환하는 함수 function SeasonSelector(month) { if (month >= 3 && month <= 5) return "Spring"; if (month >= 6 && month <= 8) return "Summer"; if (month >= 9 && month <= 11) return "Fall"; if (month === 12 || month >= 1 && month <= 2) return "Winter"; return "-1"; } // main 함수 function main() { const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim().split(" "); const Y = parseInt(input[0]); const M = parseInt(input[1]); const D = parseInt(input[2]); console.log(checkYearIs(Y, M, D)); } main();
그리고 자바 버전으로 구현한 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
- 자바 버전
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Main { static int month = 0; static int year = 0; static boolean flag = true; public static String checkNormalYear(int month, int day) { flag = true; Main.month = 0; // 유효한 달인지 판단 if (month >= 1 && month <= 12) { Main.month = month; } else { return "-1"; } // 유효한 날짜인지 판단 switch (Main.month) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: if (day < 1 || day > 31) flag = false; break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: if (day < 1 || day > 30) flag = false; break; case 2: if (day < 1 || day > 28) flag = false; break; } // 계절 서칭 if(flag) return SeasonSelector(month); return "-1"; } // 윤년일 때 체킹 (이하 유효) public static String checkLeapYear(int month, int day) { flag = true; Main.month = 0; if (month >= 1 && month <= 12) { Main.month = month; } else { return "-1"; } switch (Main.month) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: if (day < 1 || day > 31) flag = false; break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: if (day < 1 || day > 30) flag = false; break; case 2: if (day < 1 || day > 29) flag = false; break; } if(flag) return SeasonSelector(month); return "-1"; } // 주어진 연도를 기준으로 윤년, 평년 메서드 중 조건에 따라 메서드를 하나 실행하는 코드 public static String checkYearIs(int year, int month, int day) { // 400배수면 윤년 메서드 실행 if (year % 400 == 0) { return checkLeapYear(month, day); // 100 배수면 평년 메서드 실행 } else if (year % 100 == 0) { return checkNormalYear(month, day); // 4의 배수면서 100의 배수가 아니거나, 400의 배수면 윤년 메서드 실행 } else if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) { return checkLeapYear(month, day); } else { return checkNormalYear(month, day); } } // 평년일 때 체크하는 메서드 public static String SeasonSelector(int month){ if(month >= 3 && month <= 5) return "Spring"; else if(month >= 6 && month <= 8) return "Summer"; else if(month >= 9 && month <= 11) return "Fall"; else if(month == 12 || month >= 1 && month <= 2) return "Winter"; return "-1"; }; public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String[] arr = br.readLine().split(" "); int Y = Integer.parseInt(arr[0]); int M = Integer.parseInt(arr[1]); int D = Integer.parseInt(arr[2]); System.out.println(checkYearIs(Y, M, D)); } }
2. 자바와 자바스크립트 풀이 차이점
- 자바의 경우 클래스 지향이라 여러 함수를 정의할 때 static으로 정의했는데요. 물론 매개변수를 사용하면 되긴 하지만 그래도 static 필드도 몇개 만들어서 사용을 해봤습니다. 반면 JS는 함수 지향형이므로 그냥 편하게 전역으로 선언하면 되는지라... 뭐 그런거 빼면 자바에서 반환 타입 신경쓴거? 빼고는 그렇게 큰 어려움이 없었습니다.
챌린지 4일차, 프로그래머스를 해왔던 덕인지 어느정도는 버틸만 합니다 ㅎ...