기존에 있던 간단한 Service를 Repository를 사용하게 리펙토링 해보면서
직접 만든 스프링부트가 잘 작동하는지 확인하면서 이번 시리즈를 마무리를 하겠습니다!
Service
서비스가 구현해야하 메소드들을 정의해 두었습니다.
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
default int countOf(String name){
return 0;
};
}SimpleHelloService
SimpleHelloService는 HelloReposity를 주입받아 의존합니다.
@Service
public class SimpleHelloService implements HelloService {
private final HelloRepository helloRepository;
public SimpleHelloService(HelloRepository helloRepository) {
this.helloRepository = helloRepository;
}
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
this.helloRepository.increaseCount(name);
return "Hello " + name;
}
@Override
public int countOf(String name) {
return helloRepository.countOf(name);
}
}
Controller
@RestController
public class HelloController {
// final은 처음 생성할때 꼭 필요하므로 생성자가 꼭! 있어야 합니다.
private final HelloService helloService;
public HelloController(HelloService helloService) {
this.helloService = helloService;
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(String name){
// 컨트롤러의 중요한 역할인 유저의 요청사항을 검증하기
if (name == null || name.trim().length() == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return helloService.sayHello(name);
}
@GetMapping("/count")
public String count(String name) {
return name + ": " + helloService.countOf(name);
}
}
Test table @PostConstruct로 설정
매번 Test를 할때마다 @BeforeEach로 테이블을 생성하는게 불편하니
스프링부트가 시작하고 빈 설정이 끝나면 시작되는 메소드를 설정하는 어노테이션인
@PostConstruct를 사용하여 스프링부트가 시작하면 테이블을 생성하게 설정하겠습니다.
@MySpringBootApplication
public class HellobootApplication {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public HellobootApplication(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@PostConstruct // 라이프사이클 인터페이스 간편하게 사용 할 수 있게하는 어노테이션입니다.
void init() {
// 테이블 생성
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table if not exists hello(name varchar(50) primary key, count int)");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HellobootApplication.class, args);
}
}
HelloServiceConutTest
애플리케이션을 시작할때 @PostConstruct로 설정한 Table이 생성되어 테스트가 잘 통과될것입니다.
@HellobootTest
public class HelloServiceCountTest {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
@Autowired
HelloRepository helloRepository;
@Test
void sayHelloIncreaseCount(){
IntStream.rangeClosed(1,10).forEach(count -> {
helloService.sayHello("Toby");
Assertions.assertThat(helloRepository.countOf("Toby")).isEqualTo(count);
});
}
}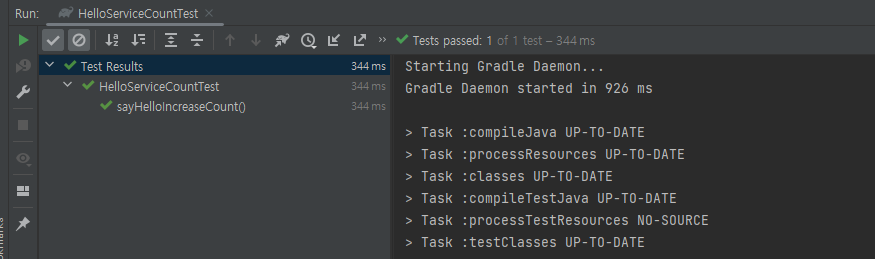
직접 만든 스프링 부트가 잘 작동하는 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다!
마무리
처음부터 스프링부트를 직접 만들어보았습니다.
스프링 부트를 직접 만들면서 스프링 부트가 어떻게 개발자에게 도움을 주는지 더 잘알게되었고
스프링 부트가 서블릿 컨테이너, 스프링컨테이너, DI, 어노테이션, 자동구성 설정, DB 연결을 어떻게 하는지 더 잘 알게되었습니다.
앞으로 스프링부트를 사용하다 오류를 만나거나 구조를 변경해야 할 때 더 깊이 생각 할수 있을것 같습니다.
다음에는 여태까지 만든 것을 스프링부트로 다시 돌려놓으면서 느낀점을 포스팅하겠습니다.