상태관리는 무엇인가?
component를 통해서 class의 state가 관리되는 형태의 플러터는, 자식컴포넌트들 간의 데이터를 주고 받는 과정에서 불필요한 이동을 줄이고 비즈니스 로직과 위젯을 분리하기 위해서 필요로 한다.
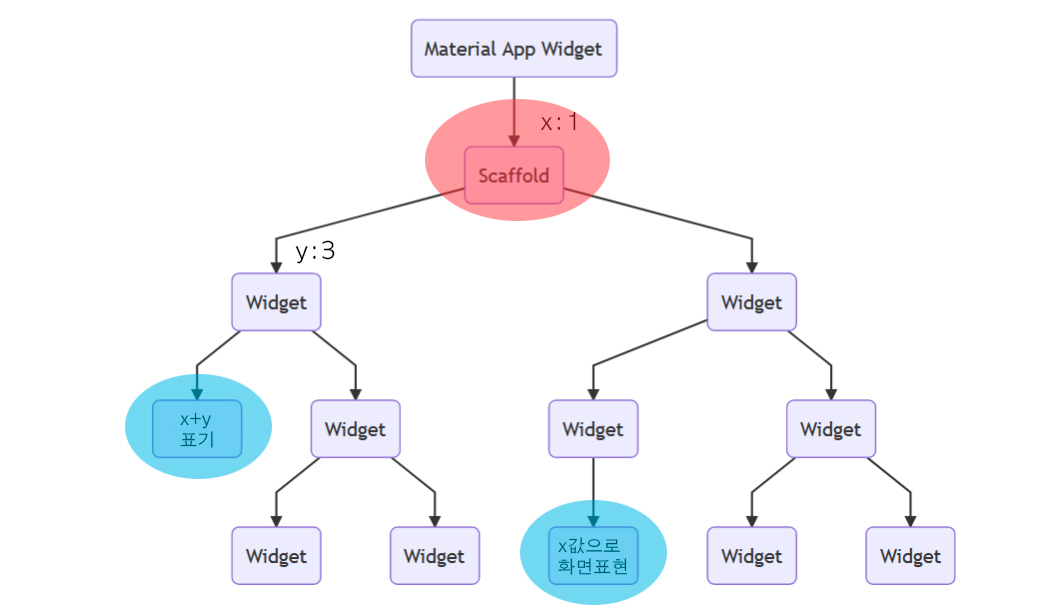
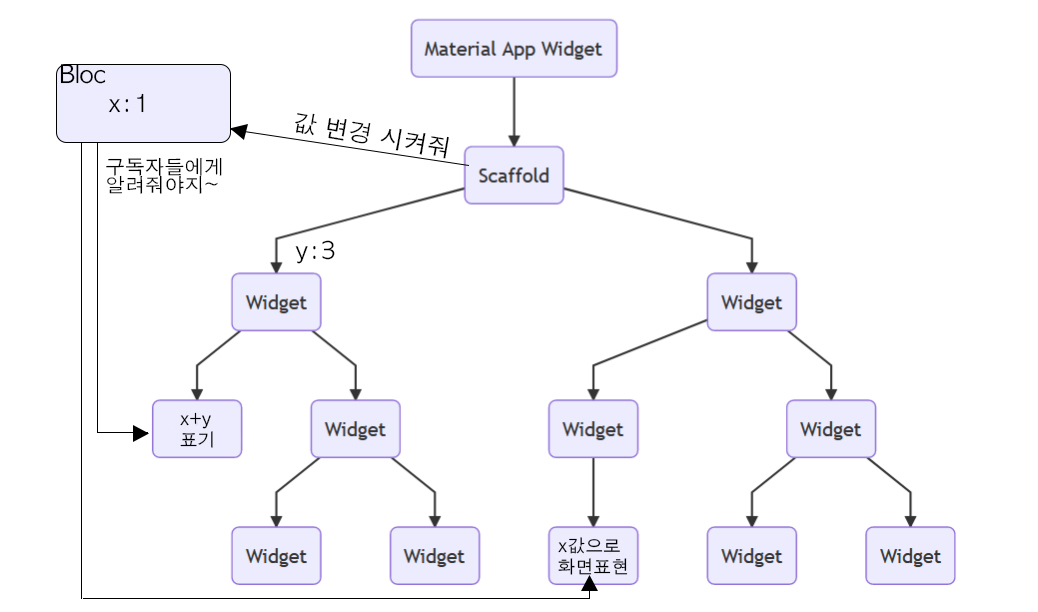
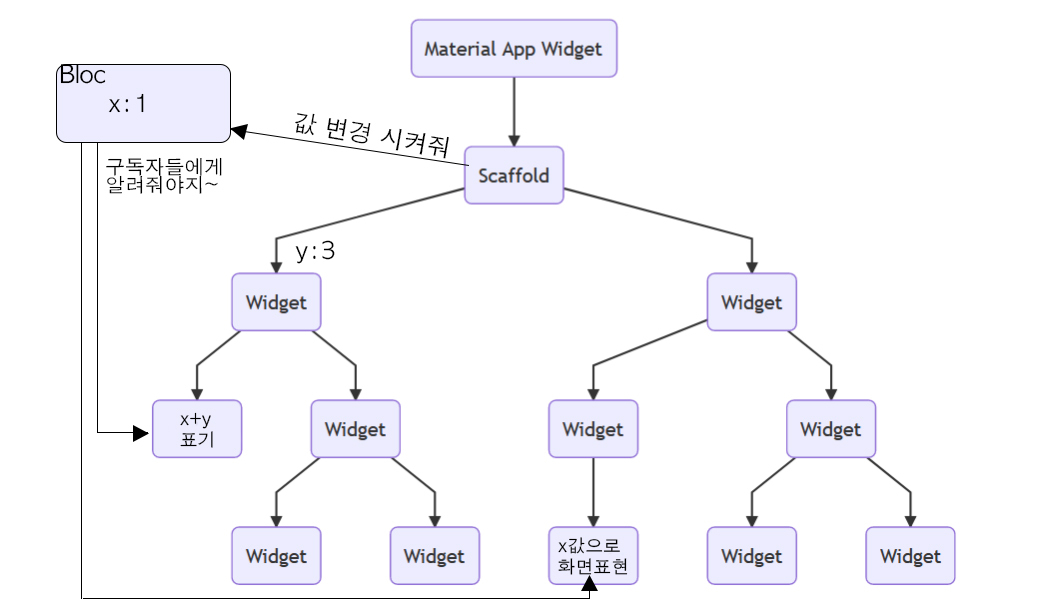
Bloc
가장 널리 쓰이는 상태관리 솔루션, Google에서 개발되었으며, UI와 Bussiness Logic을 분리하여서 의존성을 낮춘다.
장점
- 비즈니스 로직과 구현부를 나누기 쉽다.
- 예시자료가 정말 많다
- 의존성 주입
- 플러터 커뮤니티에서 폭넓게 사용중이다
단점
- 이해하기 힘들 수 있다.
- 보일러플레이트 코드가 너무 많다.
Provider
장점
- 플러터 팀이 지원한다
- 사용자가 많다.
단점
- 아래에 나올 Riverpod에서 해결된 문제가 산재해있다.
GetX
장점
- 매우 심플하다.
- 매우 짧은 코드
- 높은 사용률
- 의존성 주입
단점
- GetX 패키지에 종속된다.
- 지원이 크지 않다.
- 너무 많은 문제가 있는 너무 큰 패키지
- GetX 패키지 개발이 활발하지 않다. → fix에 너무 많은 시간이 걸린다.
States_Rebuilder
장점
- undo redo 지원
- 개발이 활발하다
단점
- 상태관리 외의 너무 많은 일을 한다.
- 지원이 크지 않다.
- 사용자가 많지 않다.
Riverpod
- 심플하며
- Provider와 유사하다.
단점
- 이용자가 많지 않다.
- 시험단계에서 막 나왔다.
- 완전히 안정적이지 않다.
MobX
장점
- 매우 심플
- 초심자에게 좋다.
- 지원을 받고 있다.
- 보일러 플레이트 코드가 없다.
단점
- 매 업데이트 마다 새로운 코드를 작성해야 한다.
- MobX 개발자의 활동이 좋지 않다.
Redux
장점
- 이미 Redux를 아는 사람에게 좋다.
단점
- 좋은 공식문서가 없다.
- 플러터 커뮤니티에서 많이 사용하지 않는다.
BLoC
공유하고자 하는 Data를 전역변수로 선언해서 사용한다.
상태 변경
class CountBloc {
int _count = 0; // 상태
final StreamController<int> _countSubject = StreamController<int>.broadcast(); // Stream 생성
Stream<int> get count => _countSubject.stream; // 구독자들에게 변경 사항 전송
add() {
_count++;
_countSubject.sink.add(_count); // 이벤트를 받아 stream에 상태 변경 추가
}
}UI 상태 받아 처리하기
return Center(
child: StreamBuilder(
stream: countBloc.count, //<--stream 들 중에서 countBloc.count 값 구독
initialData: 0,
builder: (BuildContext context, AsyncSnapshot<int> snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasData) {
return Text(snapshot.data.toString());
}
return CircularProgressIndicator();
},
),
);Provider
Provider을 선언하면서, Provider에 속한 자녀들은 전부 Provider에 접근이 가능하다.
단, 상위 Widget은 하위 위젯의 Provider에 접근이 불가능 하다.
MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
home: MultiProvider(
providers: [
ChangeNotifierProvider(
create: (BuildContext context) => CounterProvider())
],
child: Home(),
),
);- ChangeNotifier 상속받아 notifyListeners() 상태 변경 사항을 알림.
class CounterProvider extends ChangeNotifier {
int _count = 0; // 상태
add() {
_count++; //상태 변경
notifyListeners(); // 상태 변경 된 것을 알림
}
}