execution context (실행 컨텍스트)
function a(){
let youAreIn = 'A Scope';
b();
}
function b(){
let youAreIn = 'B Scope';
c();
}
function c(){
let youAreIn = 'C Scope';
debugger;
}
a();
// execution context 4개(A, B, C, 글로벌영역)생긴다.
// b는 a에서 호출됐고, c는 b에서 호출됐고, a는 전역에서 호출됐다. -
쉽게 말해서 '메모리 테이블'
-
execution context는 함수 단위로 생기고 block에서는 생기지 않는다.
-
function scope마다 메모리테이블이 생긴다.
-
실행시에 생긴다(어떤 함수가 호출되면, execution context가 만들어진다).
- call stack에 순서대로 push
- 함수를 벗어나면 call stack에서 pop
-
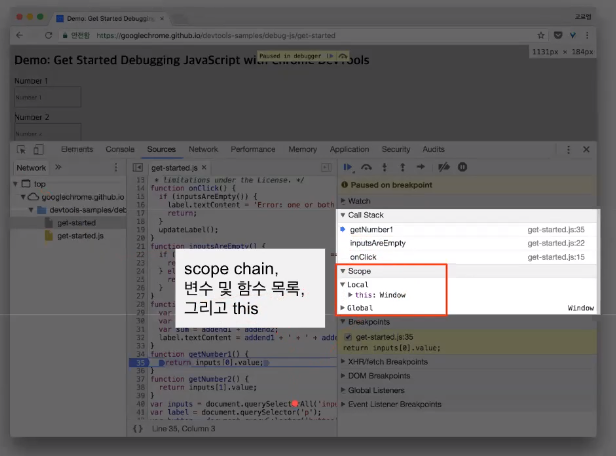
여기에 담긴 것
- scope 내 변수 및 함수(local, global)
- 전달 인자(arguments)
- 호출된 근원(caller)
- this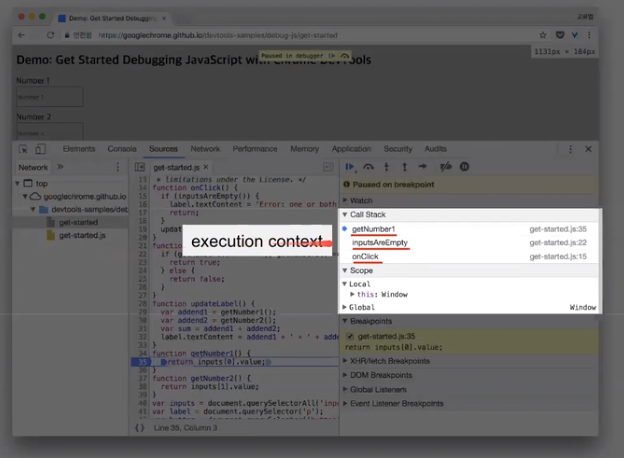
'this' keyword
모든 함수 scope 내에서 자동으로 설정되는 특수한 식별자
execution context의 구성 요소 중 하나로, 함수가 실행되는 동안 이용할 수 있다.

5 patterns of binding 'this'
(암기하기이!)
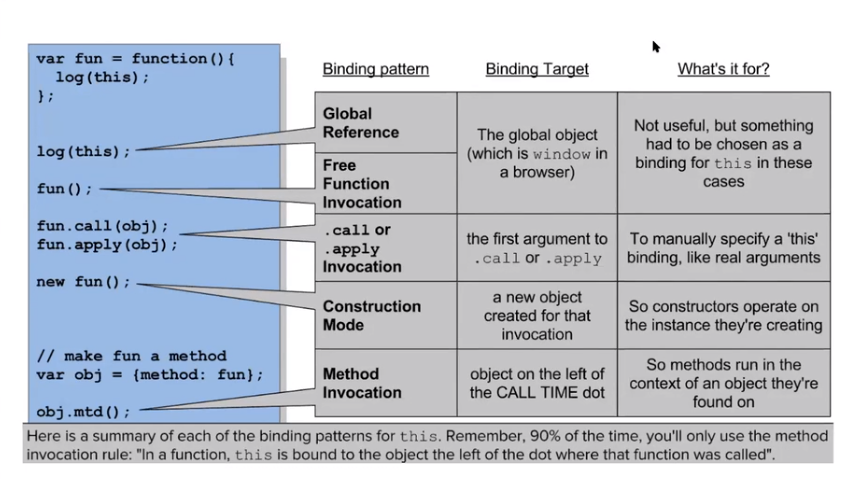
1 & 2. Global & function invocation
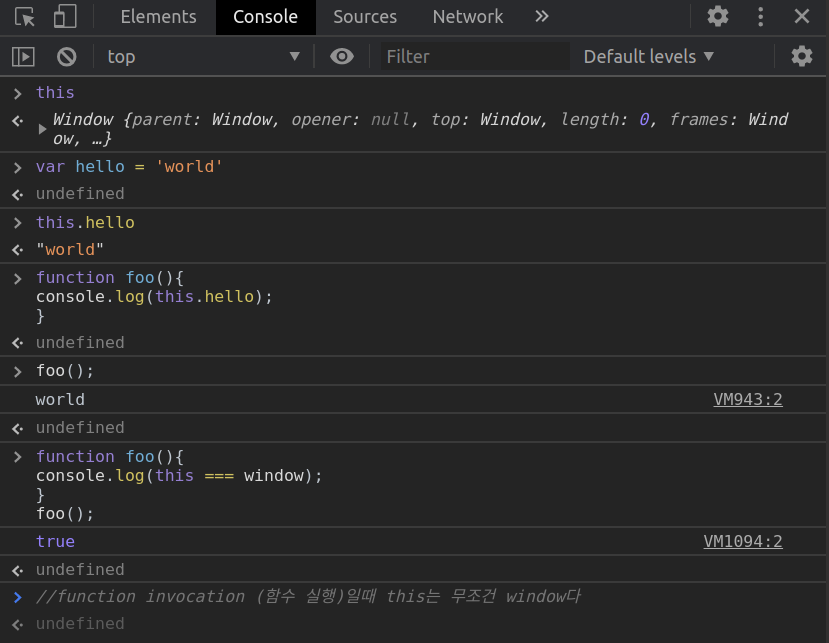
3. method 호출할 때 this는 부모 object다.
function호출과 method호출의 차이: method는 객체에 담긴 함수를 말한다.
let obj = {
foo: function(){console.log(this);}
}
obj.foo() // method 호출, {foo: f} obj
let obj2 = {
hello: {
fn: function(){console.log(this);}
}
}
obj2.hello.fn() // {fn: f}, hello만 나온다, 딱 자기 부모만 가져온다
let obj3 = {
hello: {
fn: function(){console.log(this);}
},
foo: function(){console.log(this);}
}
obj3.foo();// ojb3다 가져온다, 바로 직계 부모만 가져온다 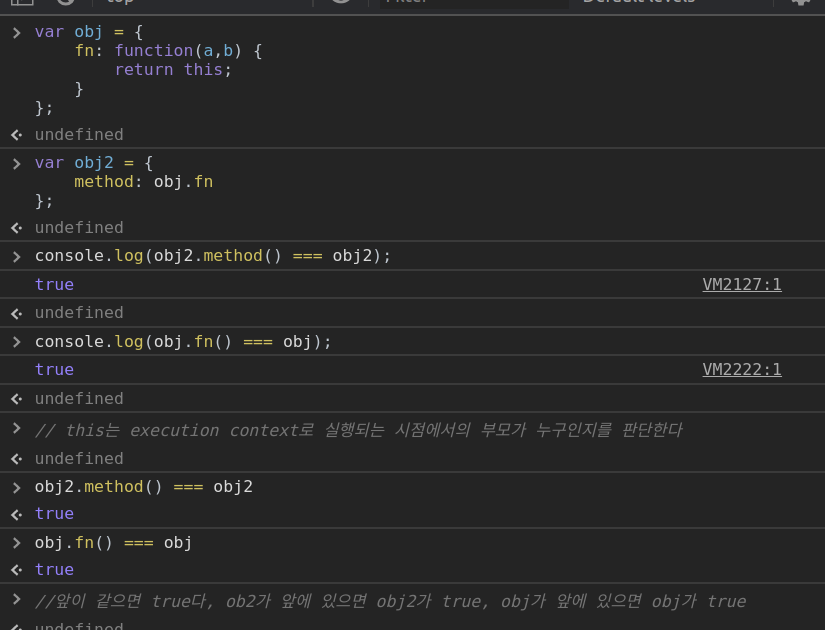
4. Construction mode (new연산자로 형성된 function 영역의 this): 새로 생성된 객체
constructor: 인스턴스가 초기화될 때 실행하는 생성자 함수

this는 instance가 된다
new키워드를 써서 만드는 것을 우리가 보통 construction mode라고 이야기하기도 한다.
이때 instance가 생기는데, 그때의 this는 avante, instance가 된다.
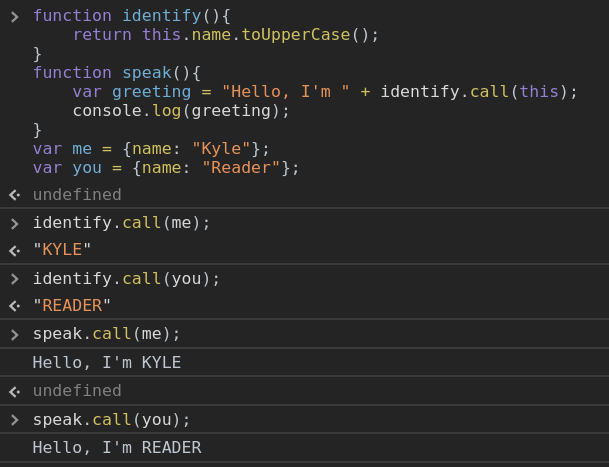
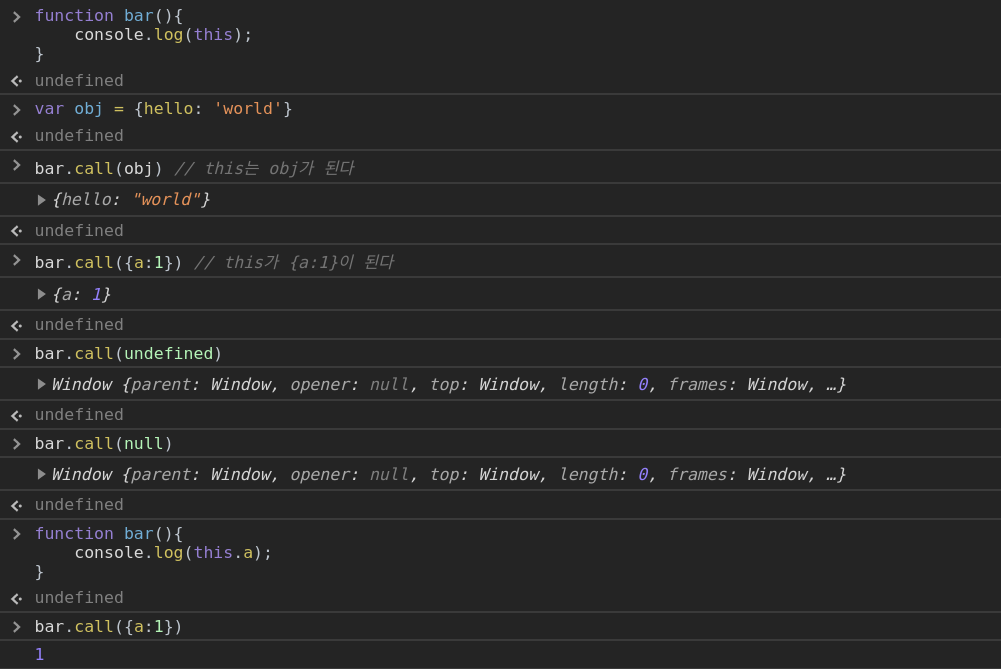
5. .call or .apply 호출: call, apply의 첫번째 인자로 명시 된 객체
함수를 실행하는 방법
1. foo() // function invocation
2. window.foo() // method invocation
3. new foo() // construction mode
4. foo.call()
5. foo.apply() .call
.apply
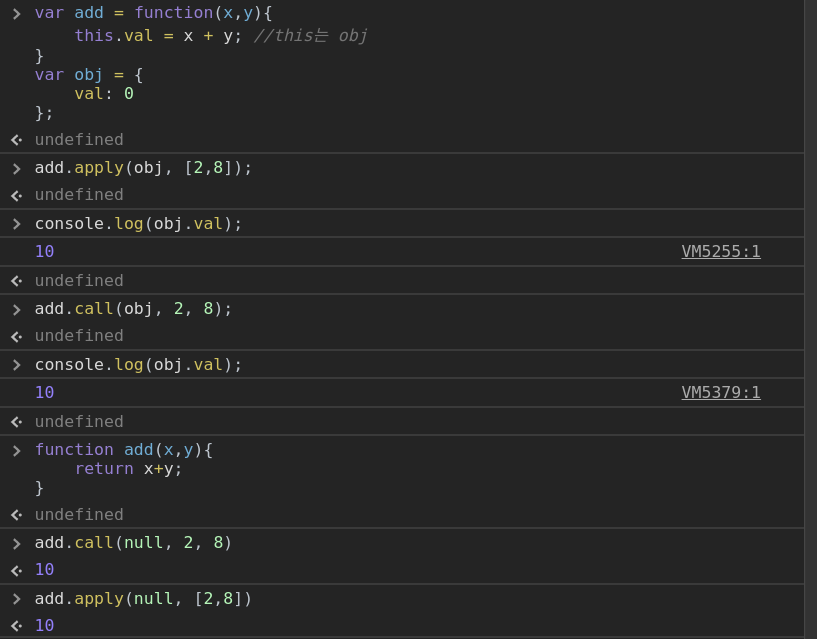
Math.max(2,3,5,1,10,14) // 14
let arr = [10, 3,5,7,1,23]
Math.max.apply(null, arr) //23 
