Database I/O Architecture
(1)에서 살펴본것과 같이 데이터베이스의 I/O 구조는 다음과 같다.
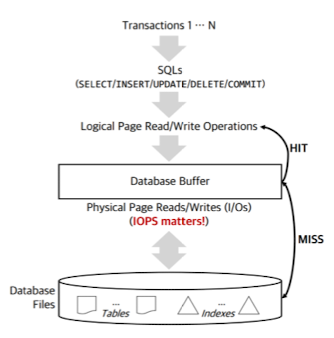
Overview of Buffer Manager in DBMS
 Disk의 data block을 가지고 있는 buffer manager caches가 frequently access data하기 때문에, 성능의 향상을 위해선 빠른 DRAM에 접근해야만 한다.
Disk의 data block을 가지고 있는 buffer manager caches가 frequently access data하기 때문에, 성능의 향상을 위해선 빠른 DRAM에 접근해야만 한다.
- Buffer HIT -> Pin the page and return its address
- Buffer MISS
- Replacement하기 위한 victim buffer frame을 고른다.
먼저 clean page는 write후 버퍼풀에서 디스크로 반영이 된것이고,
dirty page는 write 됐지만 디스크로 반영이 되지 않은 page이다.- If the chosen victim is clean : simply discard the data of the frame
- If the chosen victim is dirty : First write it to storage, then read the requested page from stroage into the victim buffer frame. 그 후 pin the page and return its address.
- Replacement하기 위한 victim buffer frame을 고른다.
Hit Ratio = # of hits / # of page requests to buffer cache
one MISS는 one(or two) disk I/O를 해야함을 의미한다.
Disk I/O는 DRAM에 비해 1000배 성능이 저하되기 때문에 MISS를 꼭 낮춰야하는 것이다.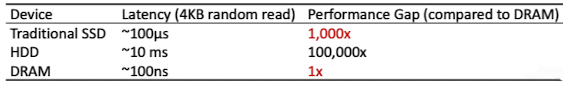
InnoDB Architecture
InnoDB는 MySQL의 스토리지 엔진이다. 자체적으로 메인 메모리 안에 데이터 캐싱과 인덱싱을 위한 버퍼 풀(pool)을 관리한다. 구조는 다음과 같다.
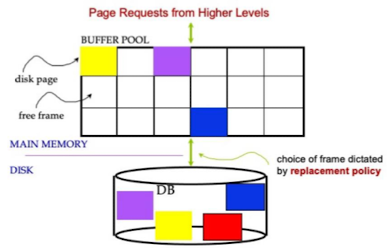
MYSQL Buffer Pool and Replacement Policy
-
Buffer Replacement Policy
- replacement policy에 의해 교체될 buffer frame이 선택된다.
- ex) Random, FIFO, LRU, MRU, LFU, Clock, etc..
- num of I/O에 큰 영향을 미친다.
- 좋은 replacement policy는 higher buffer hit ratio.
-
Buffer Pool
- InnoDB가 액세스 할 때 테이블 및 인덱스 데이터를 캐시하는 메인 메모리 영역이다.
- LRU를 사용한다. -> 잘 쓰이지 않는 데이터가 cache에서 aged out된다.
Buffer Pool LRU Algorithm
MySQL은 LRU의 변형으로 two sub-lists로 버퍼 풀을 관리한다. 다음 그림은 buffer pool list다.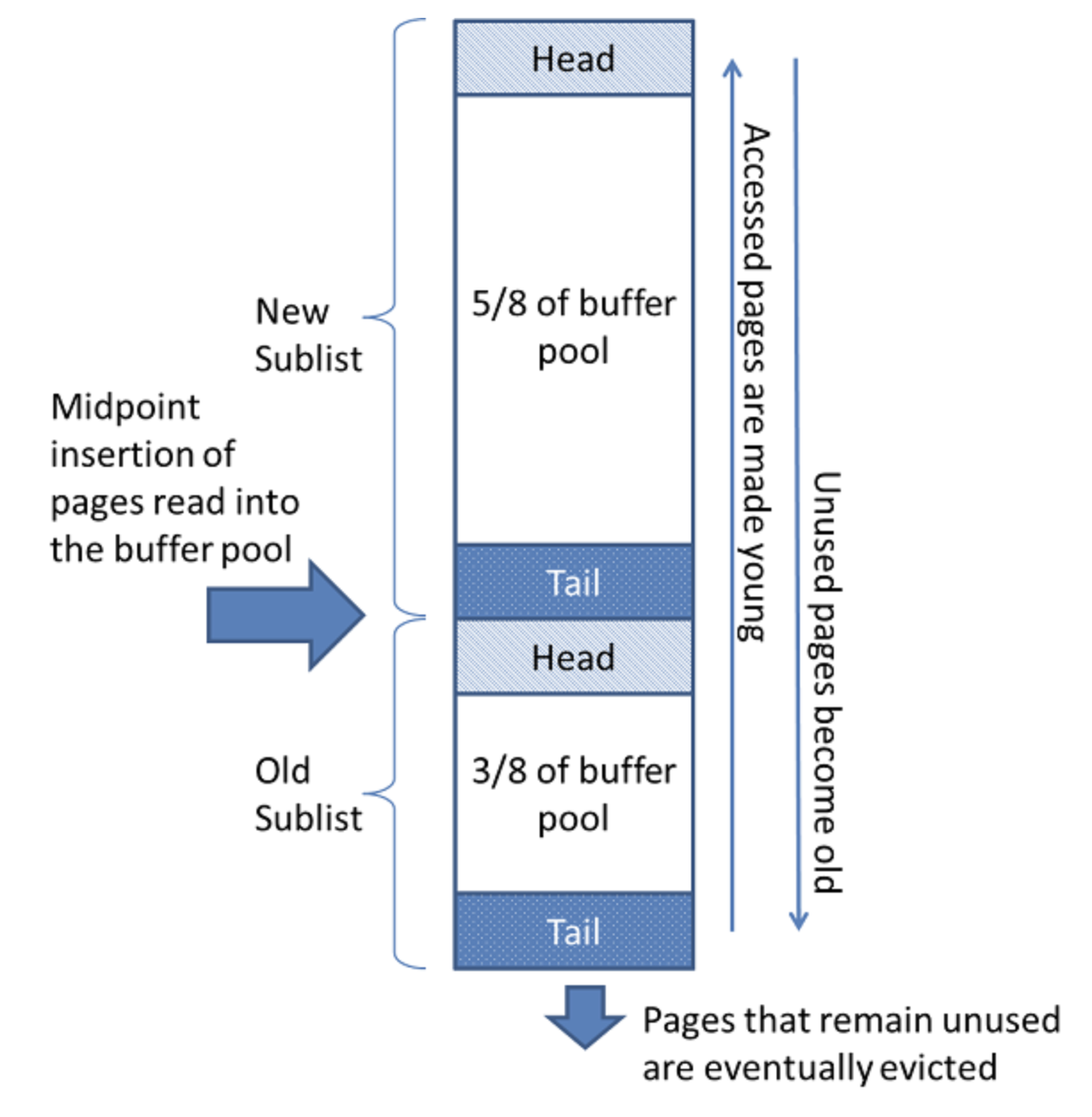 이 알고리즘은 New Sublist에 많은 페이지를 유지한다. Old sublist에는 덜 사용된 페이지들이 있어서 곧 제거될 페이지들이라고 보면 된다. 기본적으로 알고리즘은 다음과 같이 작동한다.
이 알고리즘은 New Sublist에 많은 페이지를 유지한다. Old sublist에는 덜 사용된 페이지들이 있어서 곧 제거될 페이지들이라고 보면 된다. 기본적으로 알고리즘은 다음과 같이 작동한다.
- MySQL이 buffer pool에 있는 page를 읽으면, 제일 먼저 midpoint에 삽입된다.
- Page HITs in the:
Old Sub-list : make the page young (페이지를 new sublist의 head로 옮긴다.)
New Sub-list : 페이지가 new sublist head에서 특정 거리만큼 떨어져있다면 head로 옮긴다. - Least recently used pages는 리스트의 tail로 가게되고 쫓겨난다.
그렇다면 왜 LRU list를 two sub-list로 나눠서 관리할까?
- 자주 접근되는 hot page가 buffer pool에 계속 남겨지는걸 보장하기 위해서
- never accessed again의 특성을 가지는 read-ahead 또는 scan같은 버퍼 풀 스캔이 buffer pool에 저장되는 양을 최소화하기 위해서
- read-ahead 또는 full table index scans에 의해서 buffer pool이 변동되지 않도록 하기위해서
왜 midpoint에 insertion하는걸까?
- Read-ahead 또는 large scans는 스캔동안 한 번만 스캔하고 다시 access하지 않는다는 특성을 가지고있기 때문에 midpoint에 insertion시켜 곧 쫓겨나게 하는것이다. midpoint insertion을 하지 않으면 head에 들어올것이고 나가는데 시간이 오래걸리기 때문이다.