모든 내용은 Redux 공식문서를 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
https://redux.js.org/
서론
프론트엔드 개발을 하다보면 상태관리 중요성을 실감하게 된다. 특히 규모가 점차 커질수록 컴포넌트 간 상태 공유가 복잡해지고 유지보수가 어려워지는 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
React는 자체적으로 상태(state)라는 개념을 제공하며, 이는 단순한 값(value)이다. React의 특징 중 하나는 단방향 데이터 바인딩으로, 부모에서 자식으로만 데이터를 전달할 수 있다. 하지만, 이러한 구조는 형제 컴포넌트 간 상태 공유나 여러 단계의 중첩된 컴포넌트 간 데이터 전달이 필요할 때 비효율적일 수 있다.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 상태 관리 라이브러리를 도입한다. Redux는 예측 가능한 전역 상태 관리 라이브러리로, 애플리케이션의 상태를 한 곳에서 관리하며, 예측 가능한 데이터 흐름을 통해 디버깅을 용이하게 하다.
What is Redux
Redux란 action이라는 이벤트를 사용해 state를 관리하고 업데이트하는 패턴 또는 라이브러리이다. state를 예측 가능한 방식으로만 업데이트할 수 있도록 규칙을 통해 전체 애플리케이션에서 사용되는 state를 관리하는 중앙 집중식 저장소이다.
Why Should I Use Redux?
Redux를 사용하는 이유는 다음과 같다.
Redux는 상태(state)가 언제, 어디서, 왜, 그리고 어떻게 변경되었는지 쉽게 이해할 수 있도록 도와준다.
예를 들어, 상태가 바뀔 때마다 Redux에서는 변경된 시점과 이유, 그리고 변경 과정을 명확하게 추적할 수 있다. 이를 통해 개발자는 "이 상태가 왜 바뀌었지?", "어떤 코드가 실행되면서 상태가 변경된 거지?" 같은 질문에 빠르게 답할 수 있다.
또한, Redux의 패턴을 따르면 상태 관리 로직이 정해진 방식대로 동작하기 때문에, 상태 변경이 예측 가능하고 디버깅이 쉬워진다. 이를 통해 애플리케이션의 동작을 더 체계적으로 이해하고 유지보수할 수 있다. Redux를 사용하면 코드를 체계적으로 관리할 수 있고, 테스트도 쉽게할 수 있어 애플리케이션이 의도한대로 잘 동작할 것이라 확신을 가질 수 있을 것이다.
When Should I Use Redux
모든 기술에는 장단점이 있듯이 Redux 또한 장단점이 있다. Redux는 store, action, reducer, dispatch 등 여러 개념을 이해해야 한다. 또한 상태를 업데이트할 때 반드시 action을 정의하고 reducer를 통해 변경해야 하는 구조이기 때문에 코드량이 늘어난다. 또한, Redux를 사용하면 상태를 직접 변경하는 것이 아니라, Action을 통해 Reducer가 상태를 변경하는 방식을 따르게 된다. 즉, 상태를 변경하는 과정이 더 복잡해지고, 중간 단계가 추가된다. 이러한 간접적인 방식(indirection)은 유지보수성과 예측 가능성을 높여주지만, 코드가 길어지고 직관성이 떨어질 수 있다.
그럼에도 불구하고 Redux를 사용하면 다음과 같은 장점이 있다.
- 상태가 크고 여러 컴포넌트에서 필요할 때
- 상태가 자주 변경될 때
- 상태 변경 로직이 복잡할 때
- 대규모 프로젝트에서 여러 명이 협업할 때
Redux는 반드시 사용하는 기술이 아니며, 적절한 상황에서 사용해야한다.
Redux Libraries and Tools
- React-Redux(React-Redux) : redux는 어떤 프레임워크와 함께 사용할 수 있지만, react가 상태기반 컴포넌트 구조를 갖고 있어서 react와 어울리는 라이브러리이다. React-Redux를 사용하면 react와 redux 연결이 쉬워지며,
useSelector를 이용하여 store에 있는 특정 state를 get할 수 있으며,useDispatch를 action과 함께 사용하면 state를 업데이트할 수 있다.
- Redux Toolkit(Redux ToolKit) : RTK는 redux를 좀 더 쉽게 사용할 수 있도록 도와주는 라이브러리이다. Redux 애플리케이션을 작성할 때 자주 사용하는 코드를 간소화할 수 있다.
createSlice는 상태 관리와 리듀서 및 액션을 한 번에 정의할 수 있는 간편한 방법이며,configureStore는 Redux store를 쉽게 설정할 수 있는 방법이다. RTK을 사용하면 Redux의 복잡한 설정과 반복적인 코드 작성을 줄일 수 있다. 또한, Redux를 처음 사용할 때 자주 겪는 실수를 미연에 방지할 수 있도록 돕는다.
- Redux DevTools Extension(Redux DevTools Extension) : Redux DevTools Extension은 redux의 상태 변화를 디버깅해주는 브라우저 확장 프로그램이다. state의 변화를 감지해 Redux DevTools Extension에 기록하고 타임에 따라 변화를 확인할 수 있다.
Redux Terms and Concepts
State Management
function Counter() {
// State: a counter value
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0)
// Action: code that causes an update to the state when something happens
const increment = () => {
setCounter(prevCounter => prevCounter + 1)
}
// View: the UI definition
return (
<div>
Value: {counter} <button onClick={increment}>Increment</button>
</div>
)
}
- State : application에서의 데이터
- View : state를 기반으로 그리는 역할
- Action : 사용자 입력을 감지하고 상태를 변경하는 역할
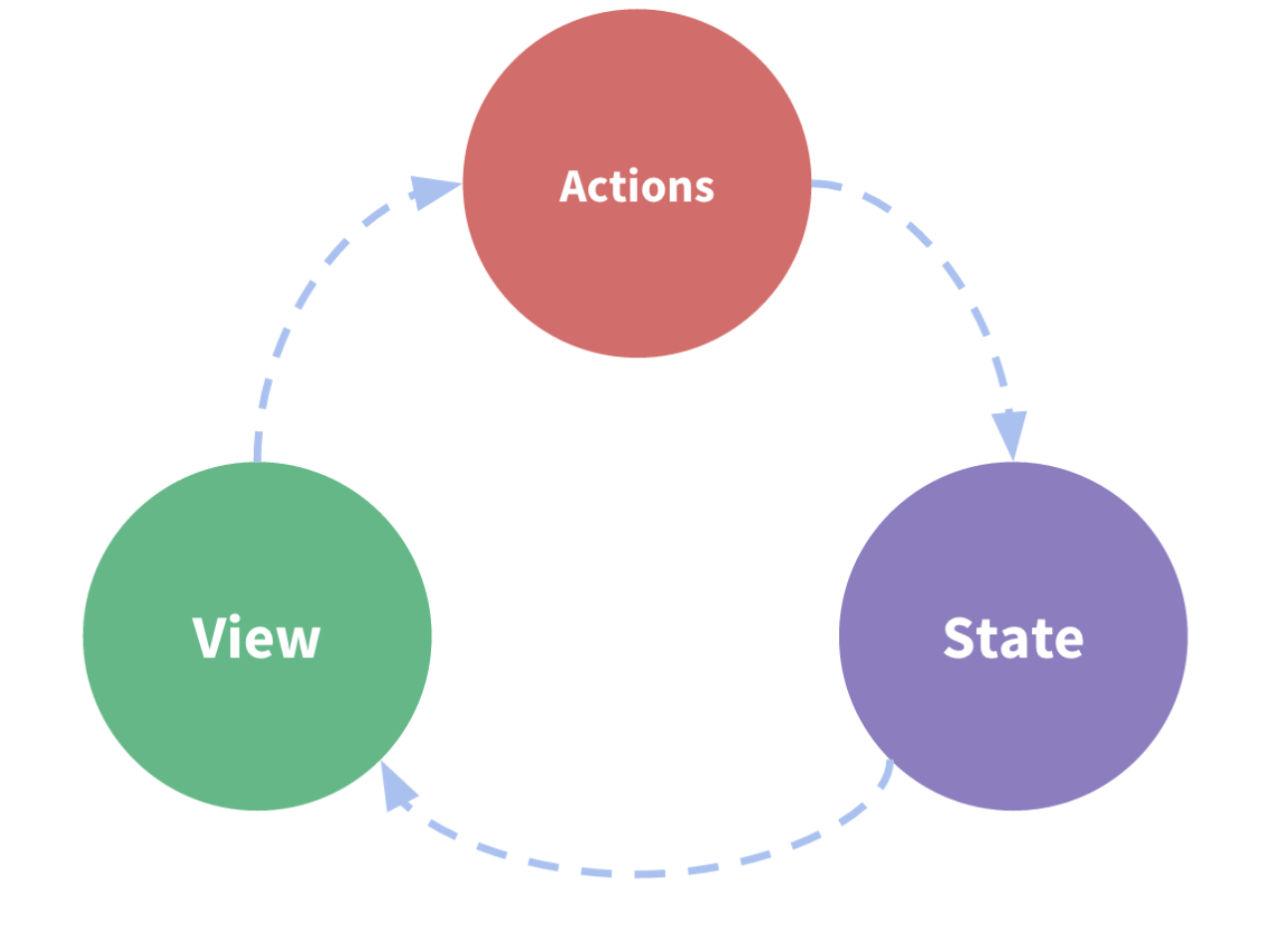
state는 특정 시점에서의 데이터를 의미하며 State를 기반으로 View가 UI를 그린다. 사용자가 어떤 행동을 하면 Action이 실행되며, Action에 따라 state가 변경된다. 이후 변경된 state에 따라 UI는 업데이트 되며 view는 리렌더링이 된다.
단순한 로직 & 컴포넌트인 경우에 문제 없겠지만 규모가 커지면서 한 state가 여러개의 view를 동작해야한다고 가정해보자. 이런 경우 해당 state를 사용하는 컴포넌트들의 공통 컴포넌트 부모까지 올라가 props drilling을 처리해야한다. 이는 많은 props로 인해 컴포넌트가 복잡해지며 가독성이 떨어진다.
이를 해결하기 위해 Redux가 탄생하였다. Redux는 컴포넌트 내부에서 state를 관리하는 것이 아닌, 외부 저장소(중앙 집중식)에서 state를 저장하고 관리한다. 이는 state가 view에 있지 않기 때문에 복잡성이 감소하며 필요할 때만 갖고와 사용하면 되기 때문에 가독성이 증가한다. 또한 구독한 컴포넌트만 state 변경시 리렌더가 진행되기 때문에 효율적이다.
Redux의 핵심 철학은 전역 상태를 한 곳에서 관리(Store)하고, 상태 변경 과정(Dispatch → Reducer → Store)을 명확한 규칙(Action 및 Reducer)으로 통제하는 것이다.
Immutability
Javascript에서의 Object & Array는 불변성이 아닌 가변성이다. 즉, 객체(Object)와 배열(Array)은 한 번 생성된 후에도 내부 값을 변경할 수 있다.
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 }
// still the same object outside, but the contents have changed
obj.b = 3
const arr = ['a', 'b']
// In the same way, we can change the contents of this array
arr.push('c')
arr[1] = 'd'Javascript에서의 object 및 array는 값을 저장할 때 직접적으로 값을 할당 하는 게 아닌 메모리를 참조하여 값을 저장하기 때문에 object 또는 array를 복사할 때 조심해야한다.
const obj = { name: "Alice" };
const newObj = obj; // 같은 메모리 참조를 가짐
newObj.name = "Bob"; // 원본 객체도 변경됨 (mutation)
console.log(obj); // { name: "Bob" } (원본이 변경됨)Javascript에서의 가변적인 Object & Array 값을 불변성(immutability)을 유지하면서 업데이트하려면, 기존 객체/배열의 복사본을 만들고 그 복사본을 수정해야 한다. JavaScript의 배열/객체 스프레드 연산자(spread operator)를 사용하거나, 기존 배열을 변경하지 않고 새로운 배열을 반환하는 메서드(map / filter / slice)를 사용하여 직접 이를 수행할 수 있다.
const obj = {
a: {
// To safely update obj.a.c, we have to copy each piece
c: 3
},
b: 2
}
const obj2 = {
// copy obj
...obj,
// overwrite a
a: {
// copy obj.a
...obj.a,
// overwrite c
c: 42
}
}
const arr = ['a', 'b']
// Create a new copy of arr, with "c" appended to the end
const arr2 = arr.concat('c')
// or, we can make a copy of the original array:
const arr3 = arr.slice()
// and mutate the copy:
arr3.push('c')불변성을 유지하면서 배열을 복사하는 방법
- Spread Opeartor : 배열의 얕은 복사(...)를 통해 배열 또는 객체를 복사함.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; const newArr = [...arr, 4]; // 원본 배열을 유지하면서 새로운 요소 추가 console.log(newArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3] (원본 유지)
- map() : 각 요소를 변환하여 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; const doubled = arr.map(num => num * 2); console.log(doubled); // [2, 4, 6] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3] (원본 유지)
- filter() : 조건에 맞는 요소만 걸러서 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const evens = arr.filter(num => num % 2 === 0); console.log(evens); // [2, 4] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4] (원본 유지)
- slice() : 배열의 특정 부분을 복사하여 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; const newArr = arr.slice(1, 4); // index 1~3 복사 console.log(newArr); // [2, 3, 4] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] (원본 유지)
- concat() : 두 개 이상의 배열을 합쳐서 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3]; const arr2 = [4, 5]; const newArr = arr1.concat(arr2); console.log(newArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] console.log(arr1); // [1, 2, 3] (원본 유지) console.log(arr2); // [4, 5] (원본 유지)
- reduce() : 배열을 순회하면서 새로운 배열을 만들어 반환할 수 있음.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const newArr = arr.reduce((acc, num) => { acc.push(num * 2); return acc; }, []); console.log(newArr); // [2, 4, 6, 8] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4] (원본 유지)
- toSorted() ES2023+ : 원본 배열을 변경하지 않고 정렬된 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr = [3, 1, 4, 2]; const sortedArr = arr.toSorted(); console.log(sortedArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4] console.log(arr); // [3, 1, 4, 2] (원본 유지)
- toSpliced() ES2023+ : 기존 splice()와 다르게 원본 배열을 변경하지 않고 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const newArr = arr.toSpliced(1, 2); // index 1부터 2개 삭제한 새로운 배열 반환 console.log(newArr); // [1, 4] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4] (원본 유지)
- flatMap() ES2019+ : 배열의 각 요소를 변환하고, 중첩된 배열을 펼쳐서 새로운 배열을 반환함.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; const newArr = arr.flatMap(num => [num, num * 2]); console.log(newArr); // [1, 2, 2, 4, 3, 6] console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3] (원본 유지)
Terminology
Actions
action이란 type 필드를 갖는 javascript의 객체이다. 액션은 애플리케이션 내에서 발생한 이벤트를 처리할 때 사용된다. type 필드는 액션이 어떤 event인 지 알려주는 역할을 하며, 필히 string으로 기입되어야 한다. 주로 type은 domain/eventName 형식으로 작성되고, 첫 번째는 기능 / 두 번째는 이벤트명을 명시한다. ex) "todos/todoAdded". 또한 이벤트가 아닌 해당 이벤트에서 발생한 추가정보를 dispatch로 전달하고 싶으면 주로 payload를 통해 전달한다.
const addTodoAction = {
type: 'todos/todoAdded',
payload: 'Buy milk'
}Action Creators
Redux는 매번 직접 action을 생성하는 것보단 action creators(액션 생성자 함수)를 통해 action을 생성한다.
const addTodo = text => {
return {
type: 'todos/todoAdded',
payload: text
}
}Reducers
reducer는 현재 state와 action을 받는 함수로써, 필요하다면 state를 업데이트하는 방법을 결정하고, 새로운 state를 반환하는 역할을 한다. reducer는 받은 action type에 따라 동작하는 event를 처리하는 event listener이다.
Reducer rules
- They should only calculate the new state value based on the
stateandactionarguments : 값을 수정할 때 기존 state와 action argument를 통해 값을 수정한다.- They are not allowed to modify the existing
state. Instead, they must make immutable updates, by copying the existingstateand making changes to the copied values. : state를 수정하려면 직접 수정하기 보단 불변성 업데이트를 위해 state를 복사한 후 복사된 값을 state를 변화시킨다.- They must not do any asynchronous logic, calculate random values, or cause other "side effects" : reducer는 오직 순수함수이며 비동기 / 랜덤 함수 / 부수 효과를 일으켜서는 안된다.
reducer는 action이 자신과 관련되었는 지 먼저 파악한 후 관련되어있으면, state를 복사한 뒤 값을 반환시키고, 자신과 관련이 없으면, 그대로 반환한다. reducer는 주로 로직을 결정할 때, if/else, switch를 통해 action을 처리한다.
const initialState = { value: 0 }
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
// Check to see if the reducer cares about this action
if (action.type === 'counter/increment') {
// If so, make a copy of `state`
return {
...state,
// and update the copy with the new value
value: state.value + 1
}
}
// otherwise return the existing state unchanged
return state
}Store
redux에서의 state는 store라고 불리는 곳에 저장되어 있다. store는 reducer를 사용해 선언되며, getState()를 통해 현재 State를 불러온다.
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit'
const store = configureStore({ reducer: counterReducer })
console.log(store.getState())
// {value: 0}Dispatch
store는 dispatch라는 메서드를 갖고 있는데, state를 업데이트하는 방법은 오직 action 함수를 dispatch에 넣어 호출하는 방법밖에 없다. dispatch를 통해 reducer는 action을 확인하고 state를 업데이트 한다.
const increment = () => {
return {
type: 'counter/increment'
}
}
store.dispatch(increment())
console.log(store.getState())
// {value: 2}Selectors
selector는 store에 state에서 특정 정보를 갖고오는 데 사용하는 함수이다. 애플리케이션이 점차 커지면서 이 selector 함수는 동일한 데이터를 여러 번 읽어야 하는 상황에서 로직 중복을 피하는 데 도움이 된다.
const selectCounterValue = state => state.value
const currentValue = selectCounterValue(store.getState())
console.log(currentValue)
// 2selectCounterValue(store.getState()) vs store.getState().value
직접 접근 store.getState().value
store.getState().value는 상태에서 value 값을 직접 접근하는 방식이다. 이렇게 할 경우, 상태 구조가 변경되면 그 값을 접근하는 코드들에서 모두 수정이 필요하다. 예를 들어,store.getState()의 상태 구조가{ value: 2 }에서 { counter: { value: 2 } }로 변경되면, 이 값을 참조하는 코드들은 모두store.getState().counter.value로 바꿔야 한다.셀렉터 사용 (selectCounterValue(store.getState()))
selectCounterValue는 상태 구조가 변경되더라도 그 구조 변경에 대응하기 위해 쉽게 수정할 수 있는 방법을 제공한다. selectCounterValue는 상태에서 value 값을 추출하는 방식만 알고 있기 때문에, 상태 구조가 변경되더라도 selectCounterValue 함수만 수정하면 다른 코드들에서는 그대로 사용할 수 있다.
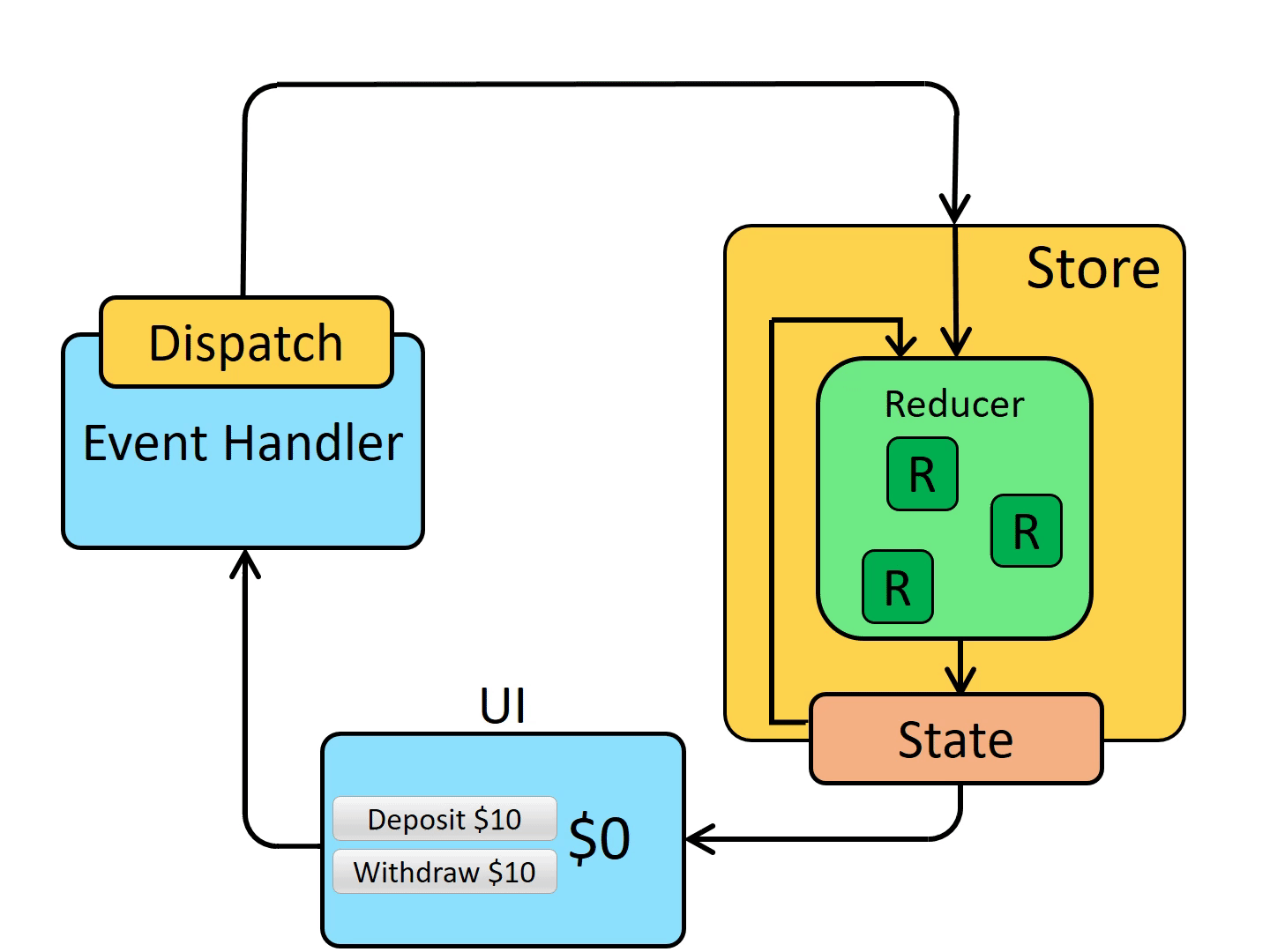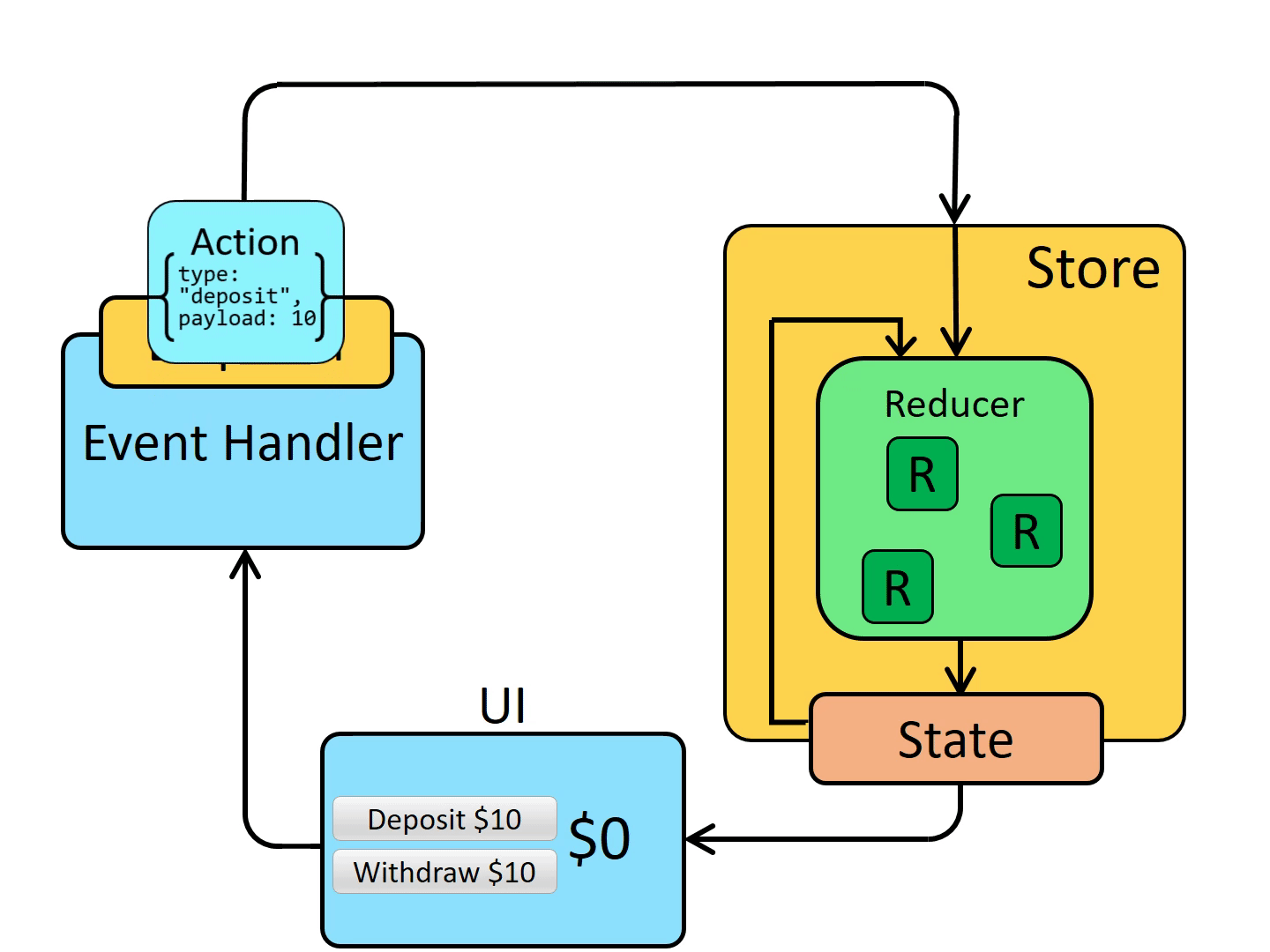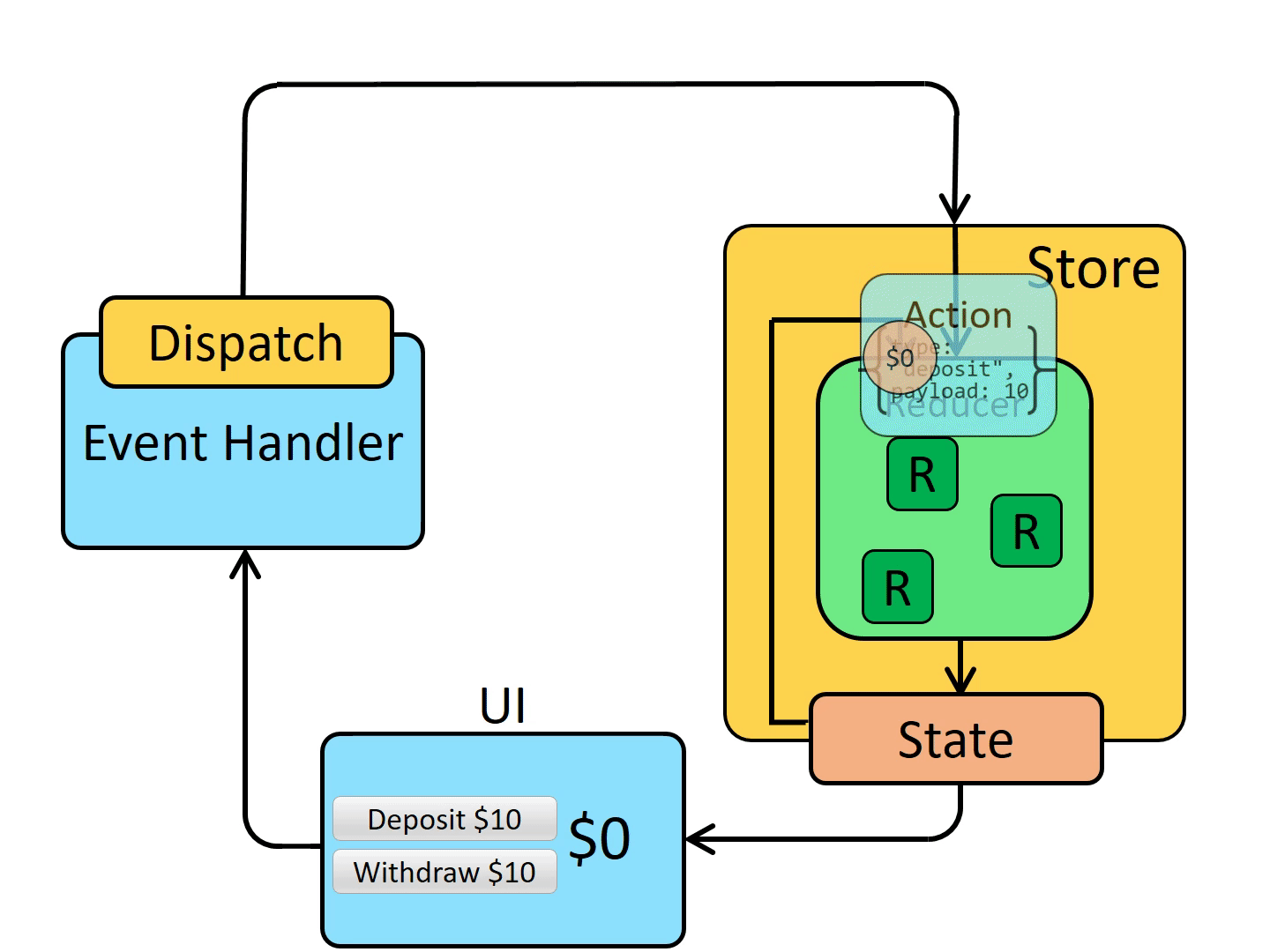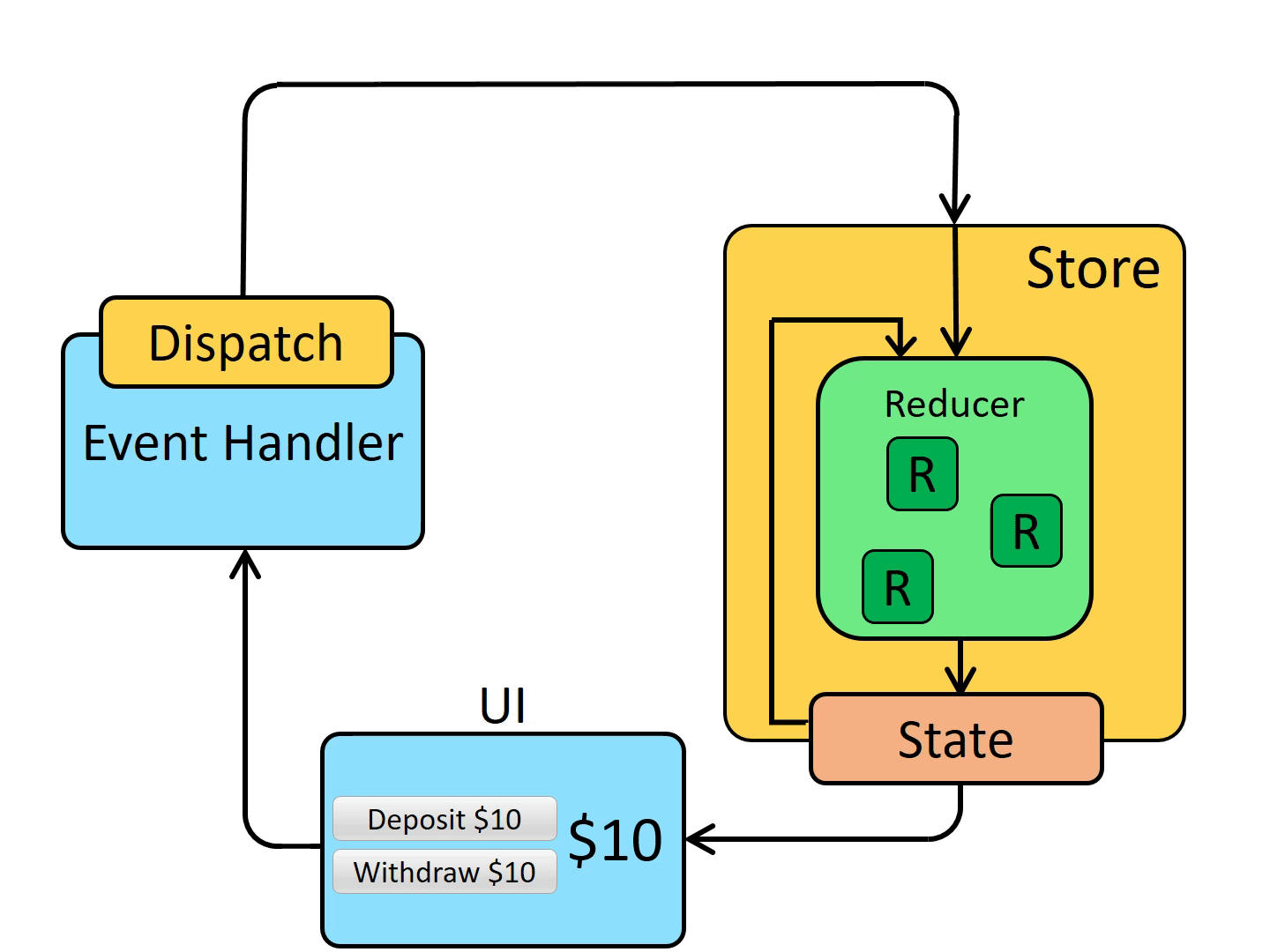
Redux Application Data Flow
Initial setup
A Redux store is created using a root reducer function
-> redux store는 root reducer를 통해 생성된다.
여기서 root reducer는 여러가지의 reducer를 하나의 합친 최종 reducer를 의미한다.
The store calls the root reducer once, and saves the return value as its initial state
-> store는 root reducer를 한번 호출하고 이후 최초 state를 값으로 받아 저장한다.
When the UI is first rendered, UI components access the current state of the Redux store, and use that data to decide what to render.
-> UI가 최초 렌더될 때, UI 컴포넌트는 store에서 현재 state를 갖고오고 현재 state를 기준으로 render할 데이터를 보여준다.
They also subscribe to any future store updates so they can know if the state has changed.
-> 또한, 컴포넌트들은 스토어 업데이트를 구독(subscribe)하여 상태가 변경되었는지 감지할 수 있도록 한다.
Updates:
Something happens in the app, such as a user clicking a button
-> 버튼 클릭과 같은 이벤트가 어플리케이션에서 발생한다면
The app code dispatches an action to the Redux store, like dispatch({type: 'counter/increment'})
-> 어플리케이션은 dispatch({type: 'counter/increment'}) 와 같이 action을 dispatch를 통해 redux store에 전달한다.
The store runs the reducer function again with the previous state and the current action, and saves the return value as the new state
-> store는 이전 state와 현재 action을 가지고 reducer 함수를 다시 실행시키고, 새로운 state를 값으로 반환하여 저장한다.
The store notifies all parts of the UI that are subscribed that the store has been updated
-> store는 구독한 UI 컴포넌트에 state가 update되었음을 알린다.
Each UI component that needs data from the store checks to see if the parts of the state they need have changed.
-> Redux store state를 사용하는 각 UI 컴포넌트는 자신이 필요로 하는 state parts가 변경되었는지 확인한다.
Each component that sees its data has changed forces a re-render with the new data, so it can update what's shown on the screen
-> 변경된 데이터를 감지한 컴포넌트는 강제로 리렌더링하여 화면을 업데이트한다.

