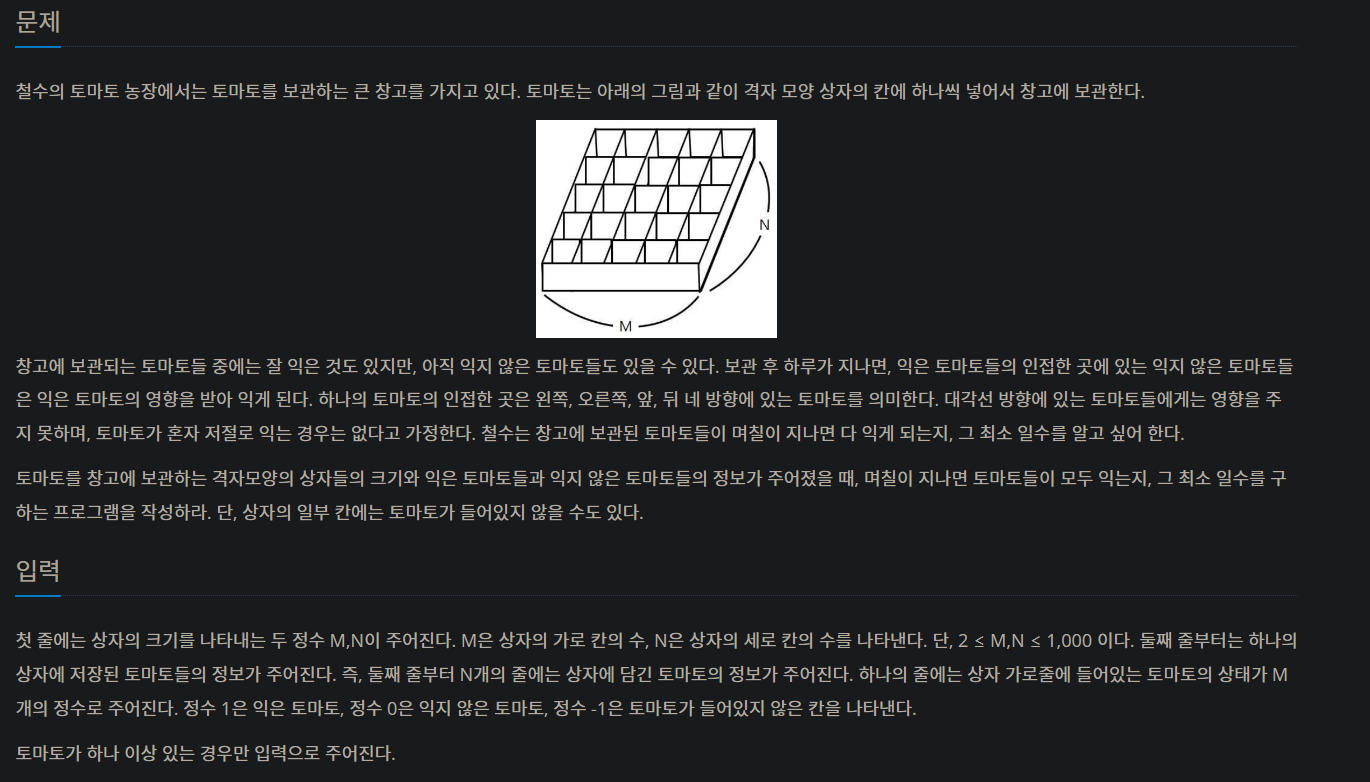
풀이 코드
from collections import deque
m, n = map(int, input().split()) # n은 행, m은 열
graph = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0] # 상 하 좌 우 이동했을때
dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
q = deque([]) # 좌표를 넣을거기 때문에 []로
result = 0 # 정답을 담을 변수
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 1:
q.append([i, j])
def bfs():
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
for d in range(4):
nx = dx[d] + x
ny = dy[d] + y
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m:
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
graph[nx][ny] = graph[x][y] + 1
q.append([nx, ny])
bfs()
for i in graph:
for j in i:
if j == 0: # 익히지 못한 토마토가 있다면
print(-1)
exit()
result = max(result, max(i))
print(result - 1)
bfs를 이용해서 문제를 풀어봤다! 공식?느낌으로 queue를 사용할려고 하였고 deque를 안쓰면 시간복잡도 때문에 문제를 해결하지 못할 거 같았다.
2차원 배열에 입력값들을 전부 넣어주고 익힌 토마토가 있는 좌표를 queue에 넣고 popleft로 graph에 값들을 움직인 값만큼 바꿔주었다.
마지막에는 전부 토마토를 익혔다면 -1해주어서 출력했다.
회고
bfs 문제에서는 우선 deque모듈을 사용해서 popleft로 하나씩 꺼내면서 queue에 아무것도 없을 때까지 반복!!

