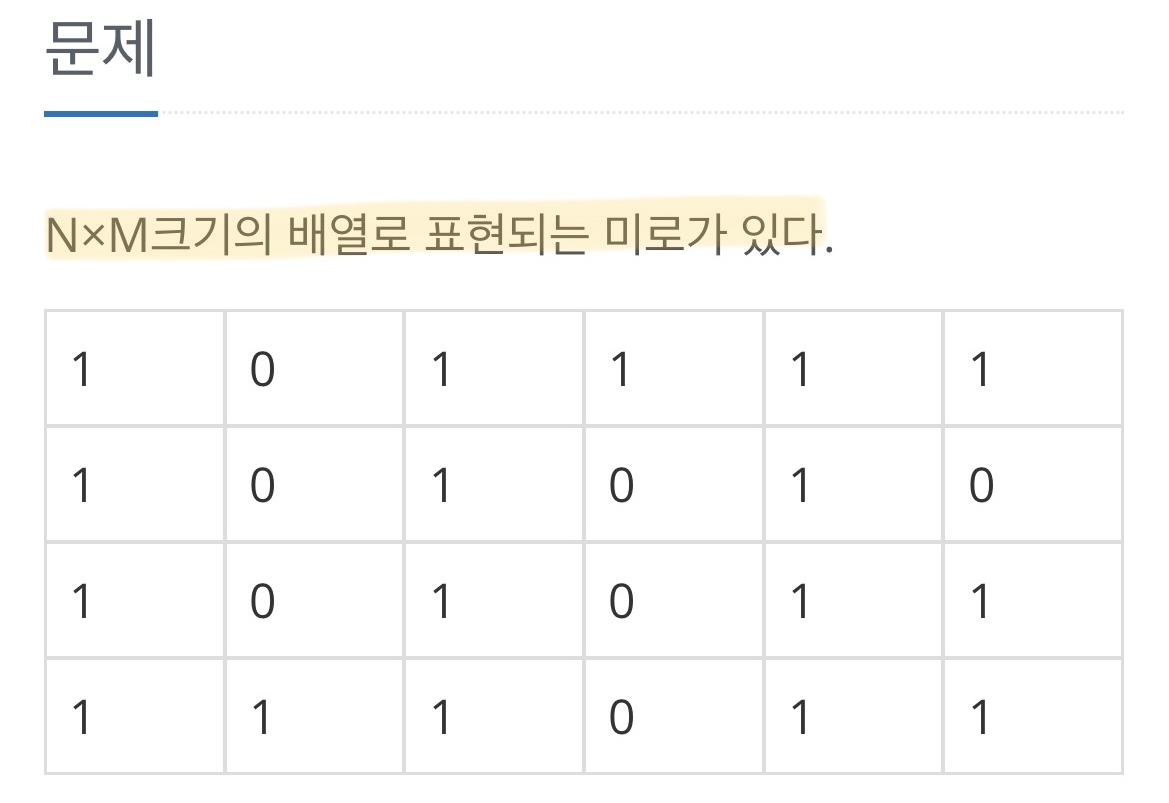
문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576

풀이
원래는 BFS 탐색을 시작하는 좌표가 있는데 이 경우에는 익은 토마토를 기준으로 전부 탐색해야 하니까 x, y좌표를 함수 인자로 전달하는 게 아니라 바로 큐에 넣어주는 방식으로 풀어야 함
전형적인 BFS 최단경로 문제인데 2차원 배열에서 M, N을 거꾸로 해야하는 걸 나중에 알아서 한참을 해맸다
-
기존에 풀었던 최단 경로 문제 : 아예 N x M 배열이라고 문제에서 주어짐
-
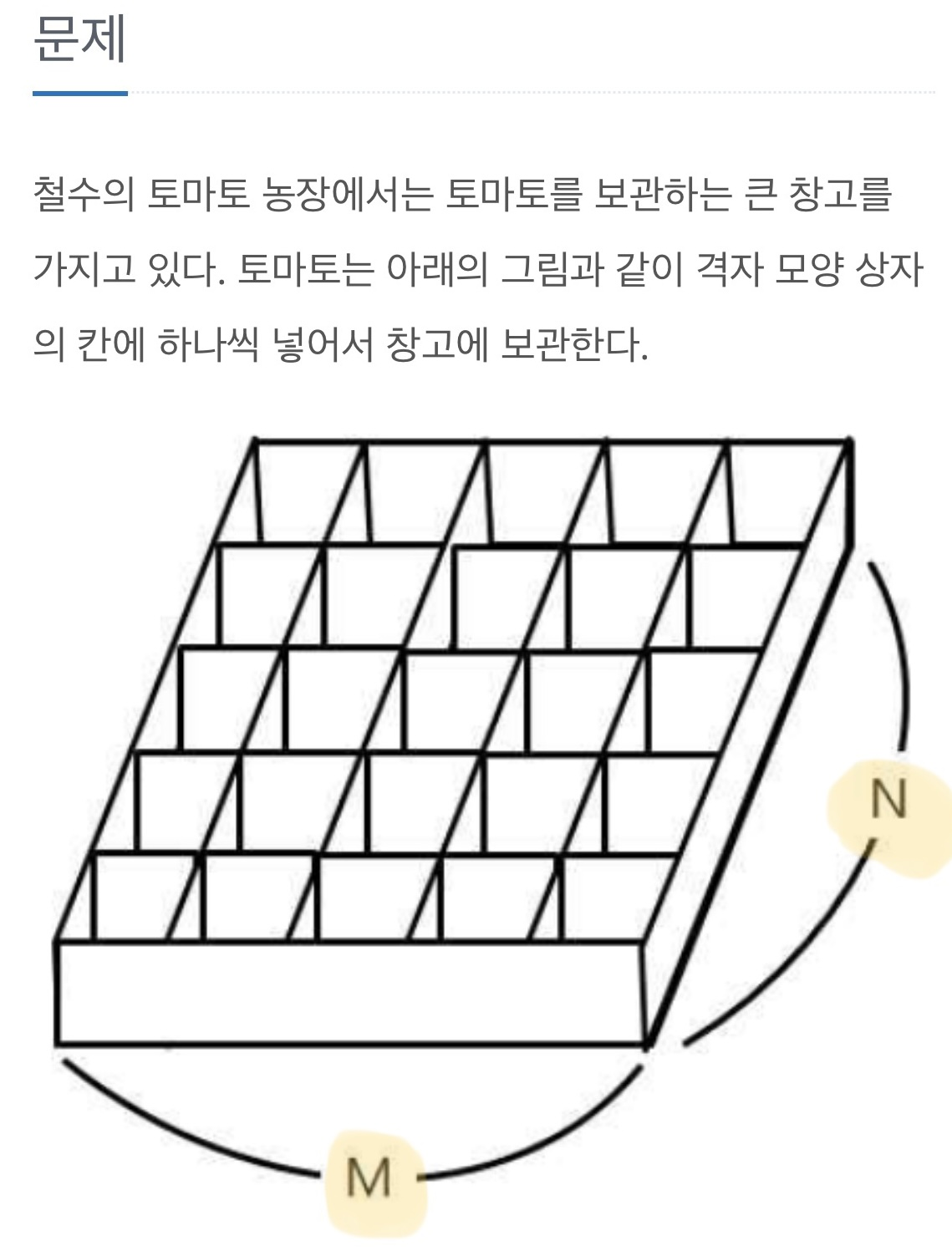
킹받는 토마토 문제 : M x N 모양의 박스
- 이중 for문으로 입력받을 때 세로부터 입력받고, map[i][j]에 넣어주면 됨
- BFS 함수에서는 모든 걸 다 y부터 하면 됨
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<M; j++) {
}
}
void BFS() {
int yy = q.front().first;
int xx = q.front().second;
int ny = yy + dy[i];
int nx = xx + dx[i];
map[ny][nx]
q.push({ ny, nx });
}
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
/*
2차원 토마토
*/
int M, N;
int map[1000][1000];
int dx[4] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
void bfs() {
while (!q.empty()) {
int yy = q.front().first;
int xx = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int ny = yy + dy[i];
int nx = xx + dx[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < M && ny >= 0 && ny < N && map[ny][nx] == 0) {
map[ny][nx] = map[yy][xx] + 1;
q.push({ ny, nx });
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int ans = 0;
cin >> M >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
if (map[i][j] == 1)
q.push({ i, j });
}
}
bfs();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
cout << -1;
return 0;
}
if (map[i][j] > ans)
ans = map[i][j];
}
}
cout << ans - 1;
return 0;
}