SQL
- Structured Query Language -> 구조화된 Query 언어
- Query:
- 질의문
- 검색어도 Query의 일종
- 저장되어 있는 정보를 필터 하기 위한 질문
- 데이터베이스 용 프로그래밍 언어
- 데이테베이스에 query를 보내 원하는 데이터만 추출
- Why do we need this?
- In-memory
- 끄면 데이터가 없어짐
- File I/O
- 원하는 데이터만 가져올 수 없고 모든 데이터를 가져온 뒤 서버에서 필터 필요
- Database
- 필터링 외에도 FS로 구현이 힘든 관리를 위한, 여러 기능을 가지고 있는 데이터에 특화된 서버
- 엑셀과 비슷. 테이블 - 시트. Column and Row.
- 필터 기능(쿼리)
- Select * FROM employee WHERE gender = 'M'
- In-memory
마지막에 ; 가 있어야 끝낼 수 있다.
SELECT
다 가져오는 것
- used to select data from a database.
- SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name;
SELECT DISTINCT
다른 것만 가져오기
- return only distinct (different values)
- only list different values. Skip duplicate values
- SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2 FROM table_name;
WHERE
어디어디
- used to filter records
- used to extract those records that fulfill a specified condition
- SELECT column1, colum2 FROM table_name WHERE condition;
- Text values require single quotes, (most allow double quotes), but numeric fields should not be quoted
SQL AND, OR and NOT Operators
- WHERE clause can be combined with AND, OR and NOT operators
- AND Syntax
- SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition1 AND condition2;
- OR Syntax
- SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition1 OR condition2;
- NOT Syntax
- SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE NOT condition1 ;
SQL ORDER BY
순차 정렬
- used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending order
- sorts the records in ascending by default. use the DESC keyword if descending order is wanted
- SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name ORDER BY column1, column2 ASC|DESC ;
- ORDER BY Several Columns
- Two can use two factors to ORDER BY. It orders by the first and if some rows have same info, it orders by the second factor.
- SELECT * FROM Customers ORDER BY Country, CustomerName;
- Table can be sorted differently by different factors, using ASC and DESC.
- SELECT * FROM Customers ORDER BY Country ASC, CustomerName DESC;
- In this case, rows will be sorted ASC by country, and the rows with same country name will be sorted DESC.
INSERT INTO
값을 삽입
-
used to insert new records in a table. Two ways to carry this out.
-
#1
- INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3) VALUES (value1, value2, value3)
-
#2
- INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, value3)
없는 부분은 null로 들어간다.
SELECT CustomerName, ContactName, Address FROM Customers WHERE Address IS NOT NULL | IS NULL
SQL Wildcards
편하다. 그 전 이나 후 중간 내용을 몰라도 찾을 수 있다.
- used to substitute one or more characters in a string.
- %
- SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE &es&; (selects all customers with a City containing the pattern "es")
- _
- SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE '_ondon'; (with any character, followed by "ondon")
- [charlist] : if you put !, it's opposite
- SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE '[bsp]%'; (select customers with a City starting with "b", "s", or "p")
- SELECT FROM Customers WHERE City LIKE '[!bsp]%'; (select customers with a City not starting with "b", "s", or "p") or SELECT FROM Customers WHERE City NOT LIKE '[bsp]%'; (select customers with a City not starting with "b", "s", or "p")
SQL Aliases
아직 더 써봐야 알 것같다. 데이터를 가명으로 가져와 합쳐 새로운 테이블을 만든다.
- used to give a table, or a column in a table, a temporary name
- aliases make column names more readable
- exists for the duration of the query
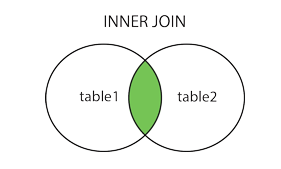
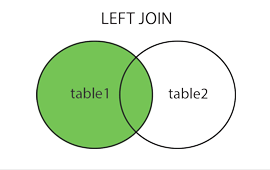
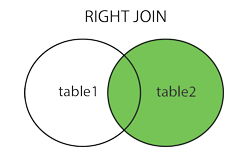
SQL Joins
데이터 합치기.
- (INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table
SQL INNER JOIN / LEFT JOIN / RIGHT JOIN
- selects records that have matching values in both tables
- SELECT column_name FROM table1 INNER JOIN / LEFT JOIN / RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
NULL Value
- a field with no value.
- It is possible to insert a new record or update a record without adding a value to this field.
Schema and Query Design
Schema: a description of the way data is organized in a database and the relationships among its different entities. "Blueprint for your database"
Entity: District units of information. Data 의 Object같은 것.
Fields: Entity Name? Group Name
Table: Data Table.
Consider the relationship between tables.
- One-to-many: 하나가 여러 (Prof to Class)
- Referencing a table's primary key in a different table, the id value is called a foreign key. 데이터가 커지면서 검색이 어려워진다. Can't store multiple values inside one column.
- 데이터가 중복되는 것도 피해야 함.
- Many-to-Many: 여러가 여러 (Class to Student)
- Make a new table in between. That table will have one-to-many relationship with both class and student table.
수강신청 Schema
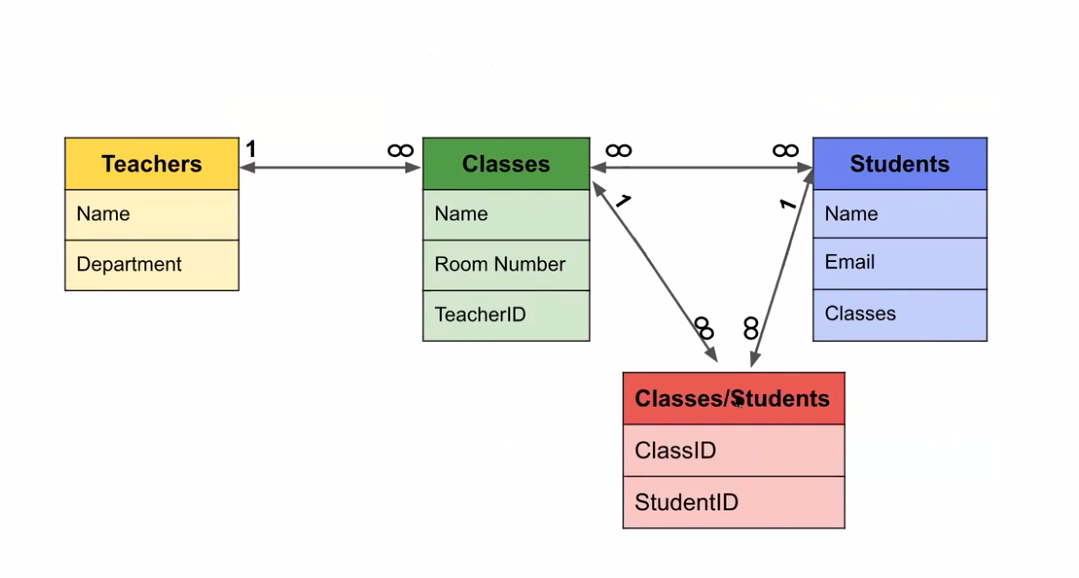
Now to Data Base Table
When would we use alias?
- When we have one table, it doesn't matter, but when we use multiple tables, we use it.
- Subquery:
- Use query inside query.
- Use join when conditions are equal.
- 연결하는 이유: 몇몇 정보를 모르기 때문이다.
느낀점
- 음 일단 SQL이란 언어를 배우기 시작하는데 기대가 된다. 데이터 베이스를 배울 때 필수인 부분을 잘 배워 잘 활용하고 싶다. 그냥 튜토리얼을 조금 따라가면 아직은 괜찮은 것 같은데 막상 실제로 해봐야 알 것 같다. 데이터 관리를 위한 언어라니. Fancy 하다. 잘만 사용한다면 매우 편리할 것 같다.
- 오늘 토이 잘 했다. 밀린 토이를 시간이 있다면 하고 싶은데, 리덕스도 정리해야하고 Article Collector도 한번 더 봐야한다.
