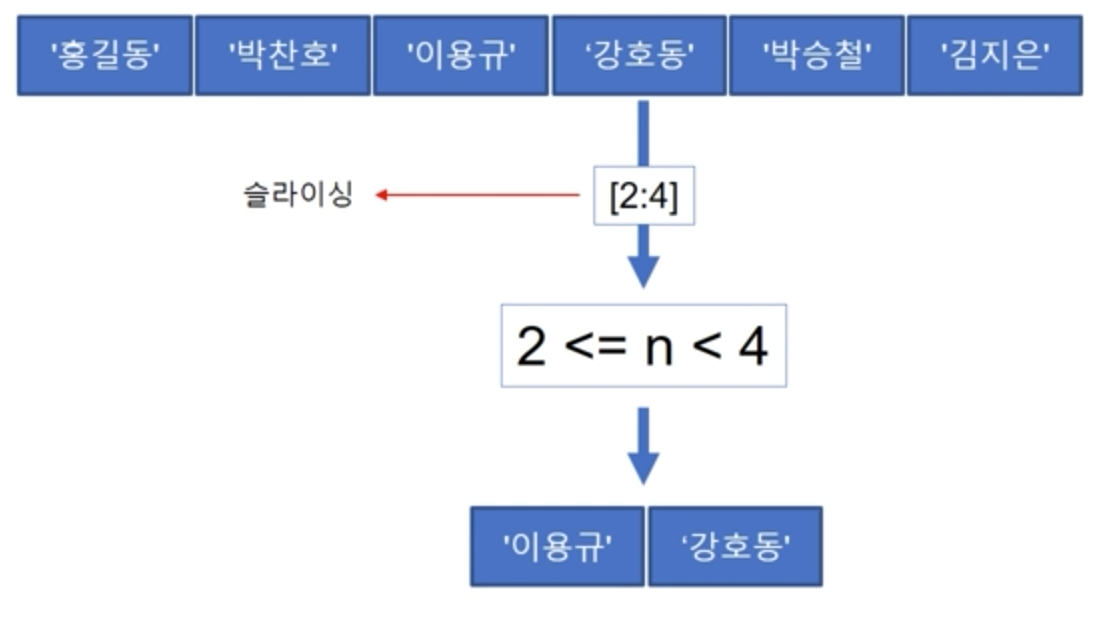
Tuple slicing
List와 마찬가지로 [n:m]을 이용하면 List에서 원하는 아이템만 뽑아낼 수 있다.
- slicing할 때 단계를 설정할 수 있다.
numbers = (2, 50, 0.12, 1, 9, 7, 17, 35, 100, 3.14) print('numbers: {}'.format[2:-2])) print('numbers: {}'.format[2:-2:2])) print('numbers: {}'.format[-2:2])) print('numbers: {}'.format[::2]))
- slicing을 이용해서 아이템을 변경할 수 있다.
- Tuple은 slicing을 이용해서 아이템을 변경할 수 없다.
- List는 Tuple 아이템으로 변경 가능하다.
slice() 함수
slice()함수를 이용해서 아이템을 slicing할 수 있다.
myItem = ('laptop', 'mouse', 'keyboard', 'cup', 'pen', 'note') print('myItem: {}'.format(myItem)) print('myItem: {}'.format(myItem[slice(2, 4)])) print('myItem: {}'.format(myItem[slice(4)])) print('myItem: {}'.format(myItem[slice(2, len(myItem))])) print('myItem: {}'.format(myItem[slice(2, len(myItem) - 2)])) print('myItem: {}'.format(myItem[slice(len(myItem) - 5, len(myItem) - 2)]))
* 이 글은 제로베이스 데이터 스쿨의 강의 자료 일부를 발췌하여 작성되었습니다.