- ROS2로 시작하는 로봇 프로그래밍 - CH.6
- 10.15 doosan rookey boot camp
Goal: 신규 RQt 플러그인 제작 실습
6.1 RQt
- 플러그인 형태로 다양한 도구 및 인터페이스를 구현할 수 있는 ROS의 GUI
- ROS+Qt
- 토픽, 서비스, 액션 프로그래밍 가능
- 크로스 플랫폼 & 다양한 프로그래밍 언어 지원(c++, PyQt, PySide)-->(Qt의 특징)
6.2 RQt plugin
-
RQt 플러그인 스타일의 장점
- 표준화된 GUI 절차 제공
- GUI 시작 및 종료 처리 용이
- 다양한 옵션 저장 및 복원 가능 - API 제공
- 표준화된 GUI 절차 제공
-
RQt 패키지
| pkg name | explanation |
|---|---|
| rqt 패키지 | RQt의 메타 패키지 rqt_gui, rqt_gui_py, rqt_py_common 패키지 포함 |
| rqt_gui 패키지 | 여러 rqt 위젯을 단일 창에 도킹하는 위젯 패키지 |
| rqt_gui_cpp 패키지 | c++ 클라이언트 라이브러리를 사용하여 제작 가능한 api 제공 |
| rqt_gui_py 패키지 | python 클라이언트 라이브러리를 사용하여 제작 가능한 api 제공 |
| rqt_py_common 패키지 | python으로 작성된 RQt 플러그인에서 공용사용되는 기능을 모듈로 제공하는 패키지 |
| rqt_common_plugins 패키지 | rqt_action, rqt_bag 등 20여개의 RQt 플러그인을 포함하는 메타패키지 |
| qt_gui_core 패키지 | qt_gui, qt_gui_cpp, qt_gui_py_common, qt_gui_app, qt_dotgraph 등을 담은 메타패키지 |
| python_qt_binding 패키지 | Qtcore,QtGui, QtWidgets 등을 사용할 때 python 언어 기반의 Qt API를 제공하는 바인딩 패키지 |
6.2.1
-
python_qt_binding
- Qt Python API 사용
- python으로 Qt API 사용시 Qt C++ API 대신, Python으로 바인딩된 API 사용
- python으로 Qt API 사용시 Qt C++ API 대신, Python으로 바인딩된 API 사용
- 장점
- PyQt, PySide 구분없이 사용 가능
- 필요 시 두 바인딩 API 간 전환 가능
- 사용 순서
- rqt_gui_py.plugin 모듈의 Plugin 클래스 상속
- qt_gui.plugin 모듈의 Plugin 클래스 상속
- python_qt_binding.QtCore 모듈의 Qobject 클래스 상속
- 상속 관계
1) python_qt_binding.QtCore 모듈의 Qobject 클래스
2) qt_qui.plugin 모듈의 Plugin 클래스는 1)을 상속
3) rqt_gui_py.plugin 모듈의 Plugin 클래스가 2)를 상속
- Qt Python API 사용
-
RQt 플러그인 개발 환경
- `ros-humble- desktop'설치 시 추가 설치 필요 x
sudo apt install qtcreator로 설치 가능
6.3 RQt plugin 구성
(1)
패키지 생성
- RQt 플러그인의 기본 기능 관련 및 gui 관련 패키지는 의존성 패키지로 포함
- python 언어로 작성하지만 RQt 플러그인의 일부로 작성하기에 ament_cmake로 설정# 플러그인 패키지 생성 $ cd ~/workspace/src $ ros2 pkg create rqt_example --build-type ament_cmake --dependencies rclpy rqt_gui_py python_qt_binding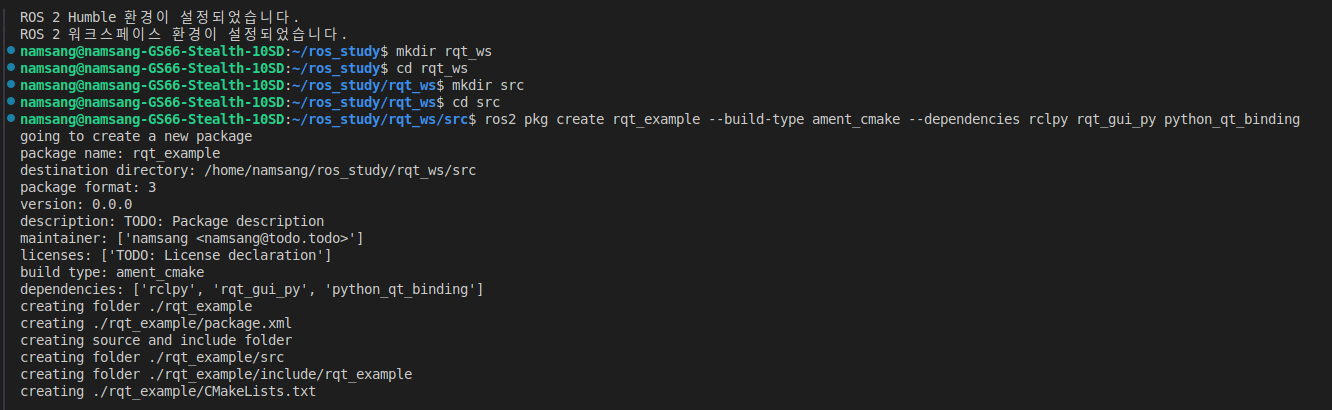
(1-1) 폴더 및 파일 생성

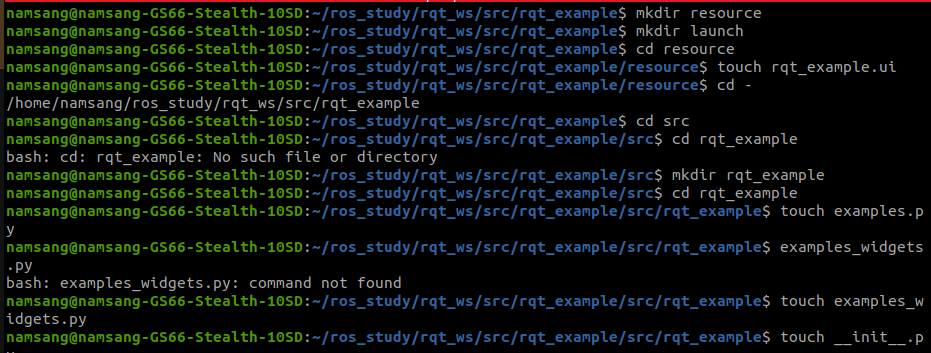
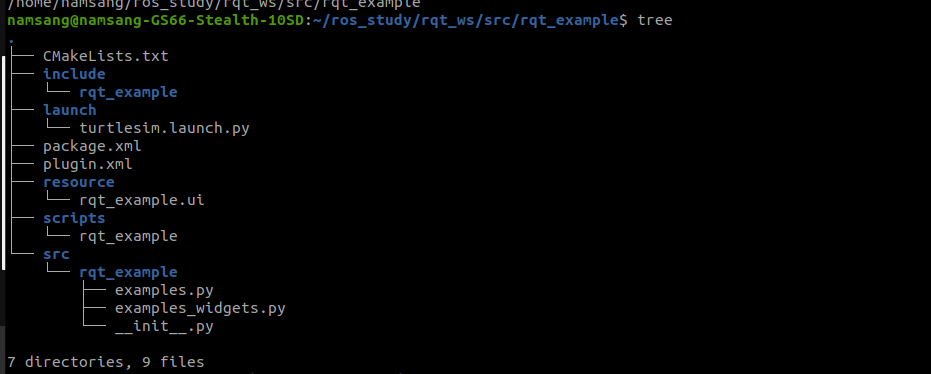
(2) packagae.xml 수정 (패키지, 빌드 설정 파일)
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>rqt_example</name>
<version>0.6.0</version>
<description>ROS 2 example for RQt plugin</description>
<maintainer email="user@email.com">Juwan</maintainer>
<license>Apache 2.0</license>
<author email="user@email.com">Juwan</author>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<exec_depend>geometry_msgs</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>python_qt_binding</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>python3-catkin-pkg-modules</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>qt_gui_py_common</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>rclpy</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>rqt_gui</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>rqt_gui_py</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>rqt_py_common</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>std_srvs</exec_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
<rqt_gui plugin="${prefix}/plugin.xml"/>
</export>
</package>-
pakcage.xml 파일은 패키지의 메타데이터와 의존성을 정의한다. 위 코드에서 주요 의존성에 대하여 설명하겠다
-
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>- ROS2 패키지 빌드 도구, cmake 기반의 build tool
- 패키지 빌드시에만 cmake 의존
-
<exec_depend> ... </exec_depend>geometry_msgs
: ROS에서 사용하는 기본적인 메시지 타입 패키지(point, qauternion, pose) 정의python_qt_binding
:python과 Qt GUI 연결 라이브러리, RQt 플러그인 작성 시 필수python3-catkin-pkg-modules
: ROS1의 catkin을 Python3에서 사용하기 위한 라이브러리(패키지 관리)qt_gui_py_common
: Qt 기반 GUI 요소를 위한 Python 모듈rclpy
: ROS2에서 python을 사용하기 위한 기본 라이브러리rqt_gui
: RQt 툴을 지원하는 패키지,rqt_gui_py
: Python으로 작성된 RQt 플러그인을 지원하는 패키지, RQt 플러그인을 Python으로 작성할 때 필요한 라이브러리 및 기능을 제공rqt_py_common
:Python으로 작성된 RQt 플러그인에서 공통적으로 사용하는 기능을 제공하는 라이브러리, 플러그인의 로딩, 관리 등의 기능을 포함std_srvs
: ROS에서 정의된 표준 서비스 타입들을 포함하는 패키지
-
<rqt_gui plugin="${prefix}/plugin.xml"/>- plugin: 플러그인에 대한 경로 지정
- ${prefix} : 패키지가 설치될 디렉토리를 나타내는 변수 --> 실제로는 install/<package_name>
: 해당 경로에 위치한 XML 파일을 통해 플러그인의 메타데이터를 로드하고 사용하도록 지시
(3) plugin.xml 생성 (플러그인 파일 생성)
<library path="src">
<class name="Examples" type="rqt_example.examples.Examples" base_class_type="rqt_gui_py::Plugin">
<description>
A plugin visualizing messages and services values
</description>
<qtgui>
<group>
<label>Visualization</label>
<icon type="theme">folder</icon>
<statustip>Plugins related to visualization</statustip>
</group>
<label>Viewer</label>
<icon type="theme">utilities-system-monitor</icon>
<statustip>A plugin visualizing messages and services values</statustip>
</qtgui>
</class>
</library>-
plugin.xml 파일은 RQt 플러그인의 클래스 경로, 설명, GUI상에서의 그룹과 아이콘을 정의합니다.
-
library: 플러그인의 파일경로
-path="src": 플러그인 코드가 위치한 경로 정의
-
class: 플러그인으로 사용될 클래스와 타입 정의 --> examples.py 정의
-name: 플러그인의 이름 지정
-type: 클래스의 모듈 경로와 클래스 이름 지정
-
qtgui: 플러그인이 RQt GUI의 표시 설정, 사용자 인터페이스에서의 레이블,아이콘, 그룹 정보를 담고 있음group: 메뉴의 세부 항목이 됨
| 항목 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| label | 그룹 이름 |
| icon | 플러그인의 레이블(이름) 정의 |
| statustip | 그룹에 대한 간단한 설명 |
(4) script/rqt_example 생성 (스크립트 폴더 및 파일 생성)
- scripts : 실행 가능한 스크립트를 포함하는 폴더
rqt_example: 플러그인의 실행 스크립트
-> 이 파일의 확장자명을 기입하지 않은 이유:- 실행 가능한 스크립트로 명령어로 실행가능하도록 하기 위함
- RQt, ROS2 환경에서 플러그인과 관련된 실행 파일이 경로 기반으로 관리되어 확장자는 중요성이 떨어짐
# !/usr/bin/env python3
# 실행환경을 지정하는 shebang, python3 인터프리터 지정
import sys
from rqt_gui.main import Main # Main 클래스는 RQt API의 실행기능 제공
from rqt_example.examples import Examples # plugin.xml에 정의된 플러그인 클래스, 구현 클래스
plugin = 'rqt_example.examples.Examples' # 경로 문자열
main = Main(filename=plugin) # Main 객체 생성, 플러그인 경로 지정
sys.exit(main.main(standalone=plugin)) # 프로그램 종료시 반환값 전달
(5) resource/req_example.ui (리소스 폴더 및 UI 파일 생성)
- Qt의 ui파일은 XML 태그를 이용
ui
(6) 런치 폴더 및 런치 파일 생성,
(6.1) turtlesim.launch.py
- turtlesim 패키지의 turtlesim_node와 함께 연동하여 테스트 가능
- namespace = turtle1 --> turtlesim_node의 토픽과 맞추기 위함
from launch import LaunchDescription # 여러 노드와 액션을 조합하여 실행하도록 설명하는 객체 from launch.actions import LogInfo # 로그 메시지 출력을 위한 msg_type from launch_ros.actions import Node # 노드 정의를 위한 호출
def generate_launch_description():
# LaunchDescription 객체를 생성하여 여러 노드를 포함할 수 있도록 합니다.
return LaunchDescription([
# 런치가 시작될 때 출력될 로그 메시지 정의
LogInfo(msg=['Execute the rqt_example with turtlesim node.']),
# rqt_example 노드를 정의
Node(
namespace='turtle1', # 노드가 속할 네임스페이스
package='rqt_example', # 실행할 노드가 포함된 패키지
executable='rqt_example', # 실행할 노드의 실행 파일 이름
name='rqt_example', # 이 노드에 부여할 이름
output='screen' # 이 노드의 출력을 터미널에 표시
),
# turtlesim 노드를 정의
Node(
package='turtlesim', # 실행할 노드가 포함된 패키지
executable='turtlesim_node', # 실행할 노드의 실행 파일 이름
name='turtlesim', # 이 노드에 부여할 이름
output='screen' # 이 노드의 출력을 터미널에 표시
)
])
(7) 메인 소스 코드
(7-1) examples.py
```python
from rqt_example.examples_widget import ExamplesWidget # 사용자 정의 위젯 임포트
from rqt_gui_py.plugin import Plugin # RQt 플러그인 기반 클래스 임포트
class Examples(Plugin):
# RQt 플러그인의 초기화 메서드
def __init__(self, context):
# 부모 클래스 초기화
super(Examples, self).__init__(context)
# 플러그인 이름 설정
self.setObjectName('RQt example')
# ExamplesWidget 객체 생성, 현재 노드를 전달
self.widget = ExamplesWidget(context.node)
# 플러그인 인스턴스의 고유 번호 가져오기
serial_number = context.serial_number()
# 고유 번호가 1보다 클 경우, 창 제목에 고유 번호 추가
if serial_number > 1:
self.widget.setWindowTitle(self.widget.windowTitle() + ' ({0})'.format(serial_number))
# 위젯을 RQt 컨텍스트에 추가
context.add_widget(self.widget)
# 플러그인 종료 시 호출되는 메서드
def shutdown_plugin(self):
print('Shutdown the RQt example.') # 종료 메시지 출력
self.widget.shutdown_widget() # 위젯 종료 메서드 호출-
Examples클래스 : 'rqut_gui_py.plugin'의 Plugin 클래스 상속- RQt 플러그인 기본 기능 제공
- 플러그인 관리, 초기화 및 종료와 같은 기능 처리
-
self.setObjectName()함수는 QObject 계열일 경우 지정하는 이름 -
ExamlplsWidget: 작성하고자 하는 UI를 포함한 실제 코드가 담긴 클래스, 사용자 정의 위젯 -
Plugin: RQt의 기본 플러그인 클래스 해당 클래스를 상속받아 RQt 플러그인을 구현- 인자로 context.node 사용
- context 매개변수는 플러그인의 실행 환경에 대한 정보를 포함하며, 이를 통해 노드, 고유번호 등의 정보를 얻을 수 있음
- 해당 노드가 클래스 내에서 rclpy의 노드역할을 수행
-
생성된 widget은 마지막 contex의 add_widget() 함수를 통해 RQt 위젯으로 추가
- serial_number는 context 생성 시 현재 사용하지 않는 첫번째 양의 정수
--> 복수의 RQt 플러그인을 구별하기 위해 사용하는 ID 개념, 동일한 플러그인 인스턴스의 개수를 확인하기 위해 고유 번호를 가져옴, 이는 여러 인스턴스가 동시에 실행될 수 있는 경우에 유용 -
shutdown_plugin: rqt_example 노드를 실행한 터미널 창에서 ctrl+c 명령어 등으로 SIGINT 신호를 받을 때, 또는 UI 화면에서 X 버튼을 눌러 종료시 호출되는 함수
(7-2) examples_widget.py
import os
from ament_index_python.resources import get_resource
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from python_qt_binding import loadUi
from python_qt_binding.QtCore import Qt
from python_qt_binding.QtCore import QTimer
from python_qt_binding.QtGui import QKeySequence
from python_qt_binding.QtWidgets import QShortcut
from python_qt_binding.QtWidgets import QWidget
import rclpy
from rclpy.qos import QoSProfile
from std_srvs.srv import SetBool
class ExamplesWidget(QWidget):
# ExamplesWidget 클래스 정의: QWidget을 상속받아 RQt 위젯을 생성함
def __init__(self, node):
super(ExamplesWidget, self).__init__()
self.setObjectName('ExamplesWidget') # 위젯 이름 설정
self.node = node # RCLPY 노드 저장
# 타이머 간격 및 속도 조정 상수
self.REDRAW_INTERVAL = 30 # UI 업데이트 간격 (ms)
self.PUBLISH_INTERVAL = 100 # 토픽 발행 간격 (ms)
self.CMD_VEL_X_FACTOR = 1000.0 # x축 속도 조정 비율
self.CMD_VEL_YAW_FACTOR = -10.0 # yaw 각도 조정 비율
pkg_name = 'rqt_example' # 패키지 이름
ui_filename = 'rqt_example.ui' # UI 파일 이름
topic_name = 'cmd_vel' # 토픽 이름
service_name = 'led_control' # 서비스 이름
# UI 파일 경로 가져오기
_, package_path = get_resource('packages', pkg_name)
ui_file = os.path.join(package_path, 'share', pkg_name, 'resource', ui_filename)
loadUi(ui_file, self) # UI 파일 로드
# 속도 초기화
self.pub_velocity = Twist() # 발행할 속도 메시지
self.pub_velocity.linear.x = 0.0 # 초기 x축 속도
self.pub_velocity.angular.z = 0.0 # 초기 각속도
self.sub_velocity = Twist() # 수신할 속도 메시지
self.sub_velocity.linear.x = 0.0
self.sub_velocity.angular.z = 0.0
# UI 요소 초기화
self.slider_x.setValue(0) # 슬라이더 초기값 설정
self.lcd_number_x.display(0.0) # x축 LCD 디스플레이 초기값
self.lcd_number_yaw.display(0.0) # yaw LCD 디스플레이 초기값
# QoS 설정
qos = QoSProfile(depth=10)
self.publisher = self.node.create_publisher(Twist, topic_name, qos) # 속도 발행자 생성
self.subscriber = self.node.create_subscription(Twist, topic_name, self.get_velocity, qos) # 속도 구독자 생성
self.service_server = self.node.create_service(SetBool, service_name, self.set_led_status) # 서비스 서버 생성
self.service_client = self.node.create_client(SetBool, service_name) # 서비스 클라이언트 생성
# 타이머 설정
self.publish_timer = QTimer(self) # 발행 타이머
self.publish_timer.timeout.connect(self.send_velocity) # 타이머가 만료되면 send_velocity 호출
self.publish_timer.start(self.PUBLISH_INTERVAL) # 타이머 시작
self.update_timer = QTimer(self) # UI 업데이트 타이머
self.update_timer.timeout.connect(self.update_indicators) # 타이머가 만료되면 update_indicators 호출
self.update_timer.start(self.REDRAW_INTERVAL) # 타이머 시작
# 버튼 및 단축키 연결
self.push_button_w.pressed.connect(self.increase_linear_x) # 'W' 버튼: x축 속도 증가
self.push_button_x.pressed.connect(self.decrease_linear_x) # 'X' 버튼: x축 속도 감소
self.push_button_a.pressed.connect(self.increase_angular_z) # 'A' 버튼: yaw 각속도 증가
self.push_button_d.pressed.connect(self.decrease_angular_z) # 'D' 버튼: yaw 각속도 감소
self.push_button_s.pressed.connect(self.set_stop) # 'S' 버튼: 정지
# 버튼에 단축키 설정
self.push_button_w.setShortcut('w')
self.push_button_x.setShortcut('x')
self.push_button_a.setShortcut('a')
self.push_button_d.setShortcut('d')
self.push_button_s.setShortcut('s')
# 스페이스바 단축키 설정
self.shortcut_space = QShortcut(QKeySequence(Qt.Key_Space), self)
self.shortcut_space.setContext(Qt.ApplicationShortcut)
self.shortcut_space.activated.connect(self.push_button_s.pressed) # 스페이스바로 정지
# LED 서비스 버튼 연결
self.radio_button_led_on.clicked.connect(self.call_led_service) # LED 켜기
self.radio_button_led_off.clicked.connect(self.call_led_service) # LED 끄기
# LED 버튼에 단축키 설정
self.radio_button_led_on.setShortcut('o')
self.radio_button_led_off.setShortcut('f')
def get_velocity(self, msg):
self.sub_velocity = msg # 수신된 속도 메시지 저장
def set_led_status(self, request, response):
# LED 상태 설정 서비스 콜백
if request.data:
self.push_button_led_status.setText('ON') # LED가 켜짐
self.push_button_led_status.setStyleSheet('color: rgb(255, 170, 0);') # 색상 변경
response.success = True
response.message = 'LED ON'
elif not request.data:
self.push_button_led_status.setText('OFF') # LED가 꺼짐
self.push_button_led_status.setStyleSheet('') # 기본 색상으로 되돌림
response.success = True
response.message = 'LED OFF'
else:
response.success = False
return response # 서비스 응답 반환
def increase_linear_x(self):
self.pub_velocity.linear.x += 0.1 # x축 속도 증가
def decrease_linear_x(self):
self.pub_velocity.linear.x -= 0.1 # x축 속도 감소
def increase_angular_z(self):
self.pub_velocity.angular.z += 0.1 # yaw 각속도 증가
def decrease_angular_z(self):
self.pub_velocity.angular.z -= 0.1 # yaw 각속도 감소
def set_stop(self):
self.pub_velocity.linear.x = 0.0 # 속도 정지
self.pub_velocity.angular.z = 0.0
def call_led_service(self):
request = SetBool.Request() # 서비스 요청 생성
# 선택된 LED 상태에 따라 요청 데이터 설정
if self.radio_button_led_on.isChecked():
request.data = True
elif self.radio_button_led_off.isChecked():
request.data = False
wait_count = 1
while not self.service_client.wait_for_service(timeout_sec=0.5): # 서비스가 준비될 때까지 대기
if wait_count > 5: # 5회 이상 대기 시 중단
return
self.node.get_logger().error('Service not available #{0}'.format(wait_count)) # 서비스 미준비 에러 로그
wait_count += 1
future = self.service_client.call_async(request) # 비동기적으로 서비스 호출
while rclpy.ok(): # ROS가 정상적으로 작동 중인 동안
if future.done(): # 서비스 호출 완료 시
if future.result() is not None: # 결과가 정상적으로 반환되었을 경우
response = future.result()
self.node.get_logger().info(
'Result of service call: {0}'.format(response.message)) # 서비스 호출 결과 로그
else:
self.node.get_logger().error('Error calling service') # 서비스 호출 에러 로그
break
def send_velocity(self):
# 현재 속도를 Twist 메시지로 발행
twist = Twist()
twist.linear.x = self.pub_velocity.linear.x
twist.linear.y = 0.0
twist.linear.z = 0.0
twist.angular.x = 0.0
twist.angular.y = 0.0
twist.angular.z = self.pub_velocity.angular.z
self.publisher.publish(twist) # Twist 메시지 발행
def update_indicators(self):
# UI 요소 업데이트
self.slider_x.setValue(int(self.sub_velocity.linear.x * self.CMD_VEL_X_FACTOR)) # 슬라이더 값 업데이트
self.dial_yaw.setValue(int(self.sub_velocity.angular.z * self.CMD_VEL_YAW_FACTOR)) # 다이얼 값 업데이트
self.lcd_number_x.display(self.sub_velocity.linear.x) # LCD 디스플레이 업데이트
self.lcd_number_yaw.display(self.sub_velocity.angular.z) # LCD 디스플레이 업데이트
def shutdown_widget(self):
# 위젯 종료 시 자원 해제
self.update_timer.stop() # 업데이트 타이머 중지
self.publish_timer.stop() # 발행 타이머 중지
self.node.destroy_client(self.service_client) # 서비스 클라이언트 파괴
self.node.destroy_service(self.service_server) # 서비스 서버 파괴
self.node.destroy_subscription(self.subscriber) # 구독자 파괴
self.node.destroy_publisher(self.publisher) # 발행자 파괴ExamplesWidget클래스는 앞서 설명한 GUI 화면 구성을 담당하는 rqt_example.ui 파일을 호출 및 화면에 출력- topic publisher/subscriber, service server/client, timer, push button, radio button 등 포함
