1. Stack
한쪽 끝으로만 자료를 넣고 뺄 수 있는 자료 구조 (LIFO)
//import java.util.Stack;
Stack<Integer> intStack = new Stack<Integer>(); // 선언 및 생성
intStack.push(1);
intStack.push(2);
intStack.push(3);
// peek()
System.out.println(intStack.peek()); // 맨 위값을 조회
System.out.println(intStack.size()); // 3 출력 (peek() 할때 삭제 안됬음)
while (!intStack.isEmpty()) { // 다 지워질때까지 출력
System.out.println(intStack.pop()); // 3,2,1 출력
}2. Queue
한쪽 끝으로 자료를 넣고, 반대쪽에서는 자료를 뺄 수 있는 선형구조 (FIFO)
// import java.util.LinkedList;
// import java.util.Queue;
// Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
Queue<Integer> intQueue = new LinkedList<>(); // 선언 및 생성
intQueue.add(1);
intQueue.add(2);
intQueue.add(3);
System.out.println(intQueue.peek()); // 1 출력 (맨먼저 들어간값이 1 이라서)
System.out.println(intQueue.size()); // 3 출력 (peek() 할때 삭제 안됬음)
while (!intQueue.isEmpty()) { // 다 지워질때까지 출력
System.out.println(intQueue.poll()); // 1,2,3 출력
}3. Array & Linked List
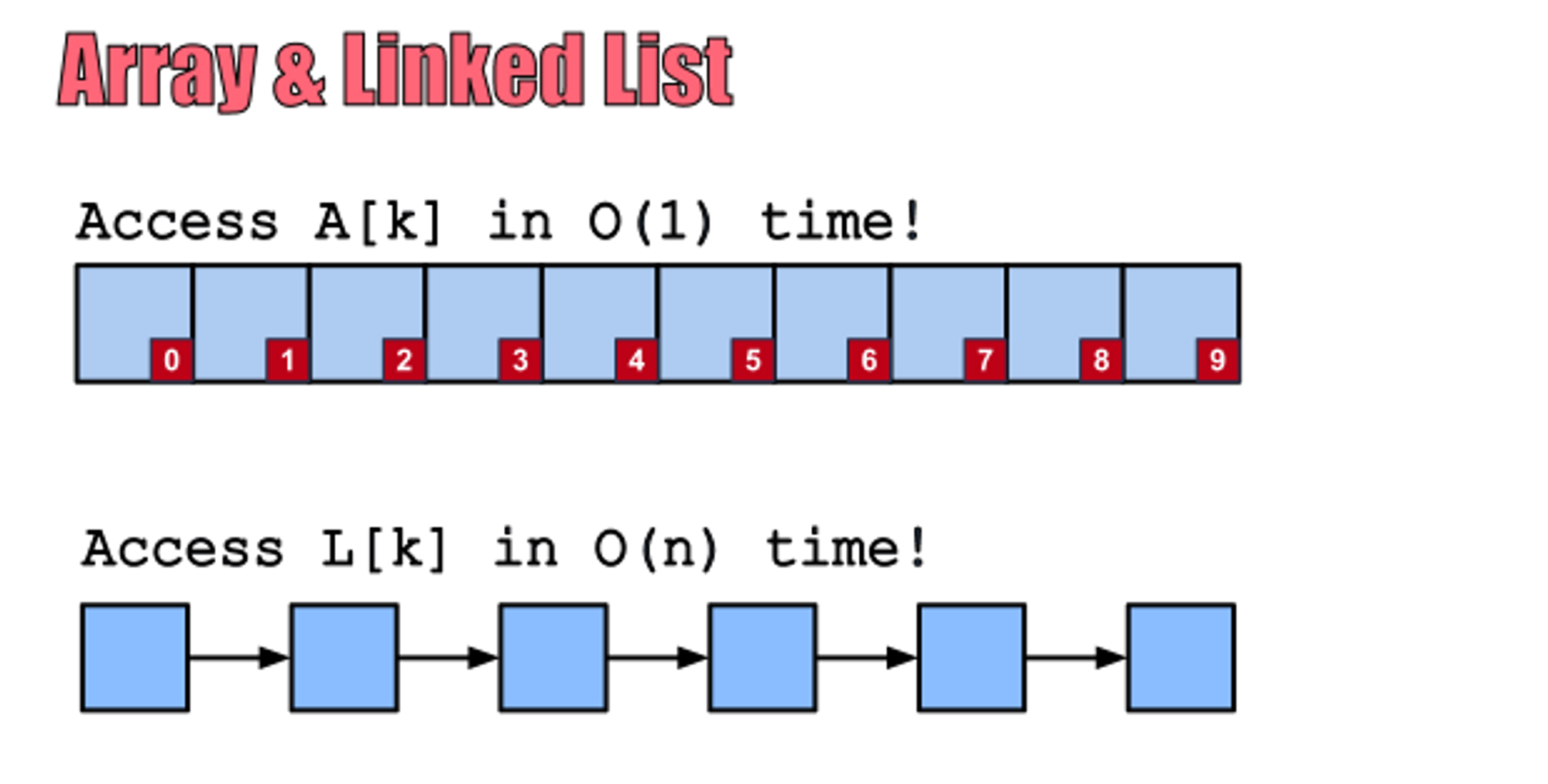
ArrayList는 내부적으로 데이터를 배열에서 관리하며
데이터의 추가, 삭제 시 임시 배열을 생성해 데이터를 복사 하는 방법을 사용
LinkedList는 각 노드가 이전 노드와 다음 노드의 상태를 알고 있다
데이터의 추가, 삭제시에 해당 부분에 추가만 하면 됨. 따라서 속도가 빠름
검색 시에는 처음부터 노드를 순회해야 하기 때문에 성능상 불리
