INNER JOIN 문제 풀이
<예제> Hackerrank: African Cities
[문제]
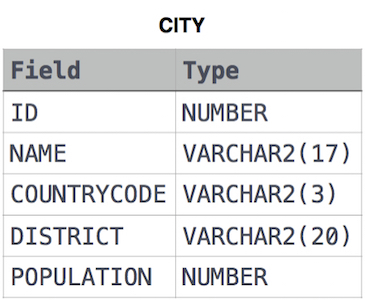
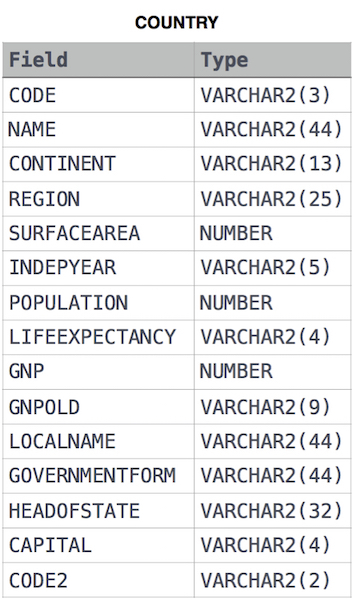
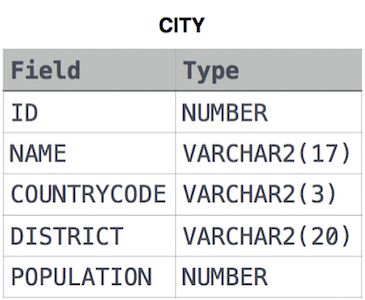
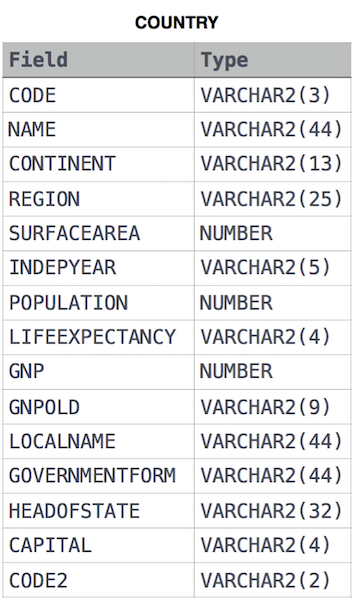
Given the CITY and COUNTRY tables, query the names of all cities where the CONTINENT is 'Africa'.
Note: CITY.CountryCode and COUNTRY.Code are matching key columns.
[풀이]
SELECT city.name
FROM city
INNER JOIN country ON city.countrycode = country.code
WHERE country.continent = 'Africa'출처: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/african-cities/problem
<예제> Hackerrank: Population Census
[문제]
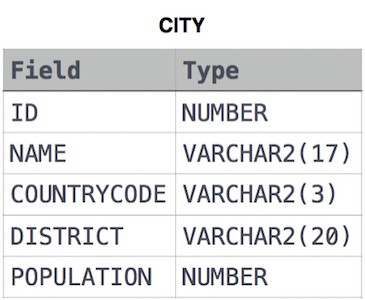
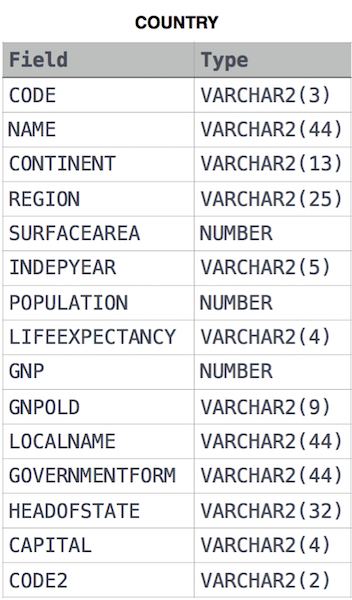
Given the CITY and COUNTRY tables, query the sum of the populations of all cities where the CONTINENT is 'Asia'.
Note: CITY.CountryCode and COUNTRY.Code are matching key columns.
[풀이]
SELECT SUM(city.population)
FROM city
INNER JOIN country ON city.countrycode = country.code
WHERE country.continent = 'Asia'출처: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/asian-population/problem?h_r=internal-search
<예제> Hackerrank: Average Population of Each Continent
[문제]
Given the CITY and COUNTRY tables, query the names of all the continents (COUNTRY.Continent) and their respective average city populations (CITY.Population) rounded down to the nearest integer.
Note: CITY.CountryCode and COUNTRY.Code are matching key columns.
[풀이]
SELECT country.continent
, FLOOR(AVG(city.population))
FROM city
INNER JOIN country ON city.countrycode = country.code
GROUP BY country.continent<예제> HackerRank: Placements
[문제]
You are given three tables: Students, Friends and Packages. Students contains two columns: ID and Name. Friends contains two columns: ID and Friend_ID (ID of the ONLY best friend). Packages contains two columns: ID and Salary (offered salary in $ thousands per month).
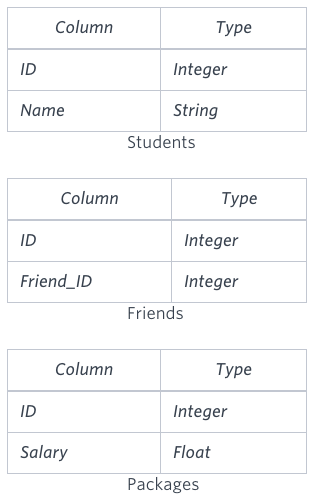
Write a query to output the names of those students whose best friends got offered a higher salary than them. Names must be ordered by the salary amount offered to the best friends. It is guaranteed that no two students got same salary offer.
[풀이]
SELECT s.name
FROM students AS s
INNER JOIN friends AS f ON s.id = f.id
INNER JOIN packages AS ss ON s.id = ss.id
INNER JOIN packages AS fs ON f.friend_id = fs.id
WHERE ss.salary < fs.salary
ORDER BY fs.salary 출처: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/placements/problem
참고: https://www.sqlshack.com/learn-sql-join-multiple-tables/
SELF JOIN 문제 풀이
<예제> LeetCode: 181. Employees Earning More Than Their Managers
[문제]
The Employee table holds all employees including their managers. Every employee has an Id, and there is also a column for the manager Id.
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| Id | Name | Salary | ManagerId |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 3 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 4 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | NULL |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | NULL |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
Given the Employee table, write a SQL query that finds out employees who earn more than their managers. For the above table, Joe is the only employee who earns more than his manager.
+----------+
| Employee |
+----------+
| Joe |
+----------+
[풀이]
SELECT e.name AS Employee
FROM employee AS e
INNER JOIN employee AS m ON e.managerid = m.id
WHERE e.salary > m.salary 출처: https://leetcode.com/problems/employees-earning-more-than-their-managers/submissions/
<예제> LeetCode: 197. Rising Temperature
[문제]
Table: Weather
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| recordDate | date |
| temperature | int |
+---------------+---------+
id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information about the temperature in a certain day.
Write an SQL query to find all dates' id with higher temperature compared to its previous dates (yesterday).
Return the result table in any order.
The query result format is in the following example:
Weather
+----+------------+-------------+
| id | recordDate | Temperature |
+----+------------+-------------+
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |
+----+------------+-------------+
Result table:
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 2 |
| 4 |
+----+
In 2015-01-02, temperature was higher than the previous day (10 -> 25).
In 2015-01-04, temperature was higher than the previous day (20 -> 30).
[풀이]
SELECT today.id
FROM Weather AS yesterday
INNER JOIN Weather AS today ON DATE_ADD(yesterday.recorddate, INTERVAL 1 DAY) = today.recorddate
WHERE today.temperature > yesterday.temperature출처: https://leetcode.com/problems/rising-temperature/solution/
참고: MySQL 시간 더하기, 빼기
DATE_ADD (기준날짜, INTERVAL)
: 날짜에 시간/날짜 간격을 더해서 리턴함.
<예시>
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 SECOND)
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 MINUTE)
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 HOUR)
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 DAY)
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 MONTH)
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 YEAR)
- SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL -1 YEAR)
DATE_SUB (기준날짜, INTERVAL)
: 날짜에 시간/날짜 간격을 빼서 리턴함.
<예시>
- SELECT DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 SECOND)
<예제> Hackerrank: Symmetric Pairs
[문제]
You are given a table, Functions, containing two columns: X and Y.
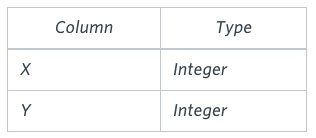
Two pairs (X1, Y1) and (X2, Y2) are said to be symmetric pairs if X1 = Y2 and X2 = Y1.
Write a query to output all such symmetric pairs in ascending order by the value of X. List the rows such that X1 ≤ Y1.
Sample Input
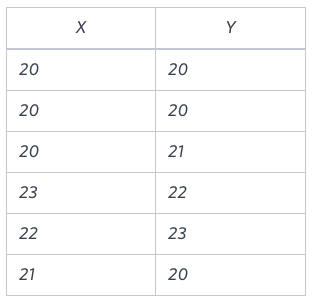
Sample Output
20 20
20 21
22 23[풀이1]
-- x와 y가 다른 경우
(SELECT f1.x
, f1.y
FROM functions AS f1
INNER JOIN functions AS f2 ON f1.x = f2.y AND f1.y = f2.x
WHERE f1.x < f1.y)
UNION
-- x와 y가 같은 경우
(SELECT x
, y
FROM functions
GROUP BY x, y
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1)
ORDER BY x[풀이2]
SELECT f1.x
, f1.y
FROM Functions AS f1
INNER JOIN Functions AS f2 ON f1.x = f2.y AND f1.y = f2.x
GROUP BY f1.x, f1.y
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1 OR f1.x < f1.y
ORDER BY f1.x출처: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/symmetric-pairs/problem
** 참고 (INNER JOIN vs. LEFT JOIN)
Functions 테이블
| id | x | y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 |
| 3 | 20 | 21 |
| 4 | 23 | 22 |
| 5 | 22 | 23 |
(1) LEFT JOIN
SELECT f1.id, f1.x, f1.y, f2.id, f2.x, f2.y
FROM Functions f1
LEFT JOIN Functions f2 ON f1.x = f2.y AND f2.x = f1.y| f1.id | f1.x | f1.y | f2.id | f2.x | f2.y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 20 | 20 |
| 1 | 20 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 20 |
| 3 | 20 | 21 | null | null | null |
| 4 | 23 | 22 | 5 | 22 | 23 |
| 5 | 22 | 23 | 4 | 23 | 22 |
➡️ LEFT JOIN을 사용하면 f1의 x = 20, y = 21에 대응하는 x = 21, y = 20인 row가 f2에 존재하지 않아도, null 값으로 채워져서 row를 리턴하게 됨. 이와 같은 대응이 되지 않는 rows를 제거하고, 대응되는 rows만 리턴하기 위해 INNER JOIN을 사용함.
(2) INNER JOIN
SELECT f1.id, f1.x, f1.y, f2.id, f2.x, f2.y
FROM Functions f1
INNER JOIN Functions f2 ON f1.x = f2.y AND f2.x = f1.y| f1.id | f1.x | f1.y | f2.id | f2.x | f2.y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 20 | 20 |
| 1 | 20 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 | 1 | 20 | 20 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 | 2 | 20 | 20 |
| 4 | 23 | 22 | 5 | 22 | 23 |
LEFT JOIN 문제 풀이
<예제> LeetCode: 183. Customers Who Never Order
[문제]
Suppose that a website contains two tables, the Customers table and the Orders table. Write a SQL query to find all customers who never order anything.
Table: Customers.
+----+-------+
| Id | Name |
+----+-------+
| 1 | Joe |
| 2 | Henry |
| 3 | Sam |
| 4 | Max |
+----+-------+
Table: Orders.
+----+------------+
| Id | CustomerId |
+----+------------+
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
+----+------------+
Using the above tables as example, return the following:
+-----------+
| Customers |
+-----------+
| Henry |
| Max |
+-----------+
[풀이]
SELECT name AS Customers
FROM customers AS c
LEFT JOIN orders AS o ON c.id = o.customerid
WHERE o.id IS NULL출처: https://leetcode.com/problems/customers-who-never-order/
<예제> LeetCode: 175. Combine Two Tables
[문제]
Table: Person
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| PersonId | int |
| FirstName | varchar |
| LastName | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
PersonId is the primary key column for this table.
Table: Address
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| AddressId | int |
| PersonId | int |
| City | varchar |
| State | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
AddressId is the primary key column for this table.
Write a SQL query for a report that provides the following information for each person in the Person table, regardless if there is an address for each of those people:
FirstName, LastName, City, State
[풀이]
SELECT firstname
, lastname
, city
, state
FROM person AS p
LEFT JOIN address AS a ON p.personid = a.personid
.jpg)