Introduction
- 클래스 구축, 클래스 멤버에 대한 엑세스 제어, 생성자 생성에 대해 자세히 알아보기
- 문제가 발생했음을 나타내기 위해 예외를 throw 하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
- 구성(Composition) - 클래스가 다른 클래스의 객체에 대한 참조를 멤버로 가질 수 있게 해주는 기능입니다.
- 열거형(enum) 유형에 대한 자세한 내용들
- 정적인 클래스 구성원과 최종 인스턴스 변수에 대해 자세히 논의합니다.
- 대규모 어플리케이션을 관리하고 재사용을 촉진하기 위해 패키지로 클래스를 구성하는 방법 보여주기
Time Class Case Study
- Class Time1 은 하루 중 시간을 나타냅니다.
- private int 인스턴스 변수 hour, minute, 그리고 second 는 보편적 시간의 형식을 나타냅니다. (시간은 0 ~ 23, 분 및 초는 각각 0 ~ 59의 범위인 24시간 시계 형식)
- public methods 는 시간을 toUniversalString, toString 으로 설정합니다.
- 클래스가 클라이언트에게 제공하는 공공 서비스 및 공공 인터페이스를 호출합니다.
// Fig. 8.1: Time1.java
// Time1 class declaration maintains the time in 24-hour format.
public class Time1
{
private int hour; // 0 ~ 23
private int minute; // 0 ~ 59
private int second; // 0 ~ 59
// set a new time value using universal time: throw an
// exception if the hour, minute or second is invalid
public void setTime(int hour, int minute, int second)
{
if (hour < 0 || hour >= 24 || minute < 0 || minute >= 60 || second < 0 || second >= 60)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException("hour, minute and/or second was out of range");
}
this.hour = hour;
this.minute = minute;
this.second = second;
}
// convert to String in universal-time format (HH:MM:SS)
public String toUniversalString()
{
return String.format("%02d:%02d:%02d", hour, minute, second);
}
// convert to String in standard-time format (H:MM:SS AM or PM)
public String toString()
{
return String.format("%d:%02d:%02d %s",
((hour == 0 || hour == 12) ? 12 : hour % 12),
minute, second, (hour < 12 ? "AM" : "PM"));
}
} // end class Time1위 코드의 setTime 과 같은 방법의 경우, 인스턴스 변수 값을 설정하는 데 사용하기 전에 방법의 모든 인수를 검증하여 모든 인수가 유효한 경우에만 개체의 데이터가 수정되는지 확인합니다.
Chapter 3 에서 액세스 수정자로 선언된 방법은 비공개 방법이 선언된 클래스의 다른 방법으로만 호출할 수 있다는 점을 기억하세요. 이러한 방법은 일반적으로 클래스의 다른 방법의 작동을 지원하는 데 사용되기 때문에 utility methods 또는 helper methods 이라고도 합니다.
// Fig. 8.2: TimeTest.java
// Time1 object used in an app
public class TimeTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create and initialize a Time1 object
Time1 time = new Time1(); // invokes Time1 constructor
// output string representations of the time
displayTime("After time object is created", time);
System.out.println();
// change time and output updated time
time.setTime(13, 27, 6);
displayTime("After calling setTime", time);
System.out.println();
// attempt to set time with invalid values
try
{
time.setTime(99, 99, 99); // all values out of range
}
catch(IllegalArgumentException e)
{
System.out.printf("Exception: %s%n%n", e.getMessage());
}
// display time after attempt to set invalid values
displayTime("After calling setTime with invalid values", time);
}
// displays a Time1 object in 24-hour and 12-hour formats
private static void displayTime(String header, Time1 t)
{
System.out.printf("%s%nUniversal time: %s%nStandard time: %s%n",
header, t.toUniversalString(), t.toString());
}
} // end Class TimeTest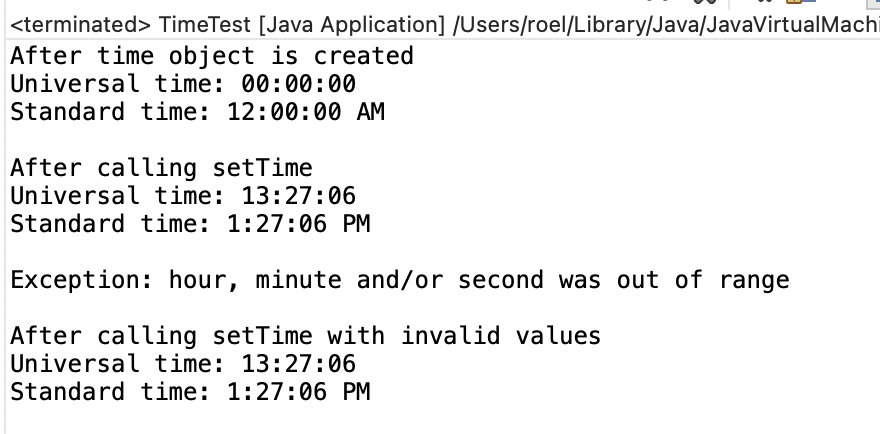
- Class Time1 는 생성자를 선언하지 않았으므로 컴파일러가 기본 생성자(default)를 제공합니다.
- 각 인스턴스 변수는 암묵적으로 기본값을 받습니다. int value.
- 인스턴스 변수는 클래스 본문에 선언될 때 로컬 변수와 동일한 초기화 구문을 사용하여 초기화할 수도 있습니다.
Method setTime 그리고 Throwing Exceptions
- Method setTime 은 시간을 설정할 때 쓰일 정수 파라미터들을 선언합니다.
- 각 인수를 테스트하여 값이 적절한 범위를 벗어나는지 확인합니다.
잘못된 값의 경우, setTime 은 IllegalArgumentException 유형의 예외를 throw 합니다.
- 잘못된 인수가 메서드에 전달되었음을 클라이언트 코드에 알립니다.
- try…catch 문을 사용하여 예외를 잡고 복구를 시도할 수 있습니다.
- throw statement 의 클래스 인스턴스 생성 표현을 IllegalArgumentException 라는 새로운 개체를 생성합니다. 이 경우 사용자가 지정 오류 메세지를 지정할 수 있는 생성자를 호출합니다.
- 예외 개체가 생성된 후 throw statement 은 setTime 을 즉시 종료하고 예외는 시간을 설정하려고 시도한 호출 메서드로 돌아갑니다.
Class Time1 선언의 소프트웨어 엔지니어링
- 인스턴수 변수 hour, minute, second 는 각각 private 로 선언됩니다.
- 클래스 내에서 사용되는 실제 데이터 표현은 클래스의 클라이언트에게 아무런 문제가 되지 않습니다.
- Time1 이 내부적으로 시간을 자정 이후의 초수 또는 자정 이후의 분 및 초수로 표현하는 것은 합리적입니다.
- 클라이언트는 이것을 인식하지 못한 채 public methods 을 사용하여 동일한 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
클래스는 프로그래밍을 단순화합니다.
클라이언트는 클래스의 public methods 만 사용할 수 있기 때문입니다.
이러한 방법은 일반적으로 구현 지향적이라기보다는 클라이언트 지향적입니다.
클라이언트는 클래스의 구현을 인식하지도, 관여하지도 않습니다.
클라이언트는 일반적으로 클래스가 하는 일에는 관심이 있지만 클래스가 하는 방식에는 관심이 없습니다.
인터페이스는 구현보다 덜 자주 변경됩니다.
구현이 변경되면 구현 종속 코드가 그에 따라 변경되어야 합니다.
구현을 숨기면 다른 프로그램 부분이 클래스 구현 세부 정보에 의존하게 될 가능성이 줄어듭니다.
Java SE 8 - 날짜/시간 API
- 일반적으로 나만의 날짜 및 시간 클래스를 구축하는 대신 Java API에서 제공하는 클래스를 재사용합니다.
- Java SE 8은 java.time 패키지의 클래스로 정의되는 새로운 날짜/시간 API를 도입했습니다.
- 는 이전 클래스의 다양한 문제를 수정하고 날짜, 시간대, 시간대, 캘린더 등을 조작할 수 있는 보다 강력하고 사용하기 쉬운 기능을 제공합니다.
- 이전 클래스의 다양한 문제를 수정하고 날짜, 시간대, 시간대, 캘린더 등을 조작할 수 있는 보다 강력하고 사용하기 쉬운 기능을 제공합니다.
Controlling Access to Members
- 엑세스 수정자를 public 및 private 로 제어하여 클래스의 변수 및 방법에 대한 엑세스 권한을 부여합니다.
- 클래스의 클라이언트에 제시되는 public methods 는 클래스가 제공하는 서비스의 한 뷰입니다.(클래스의 public 인터페이스)
- 클라이언트는 클래스가 작업을 수행하는 방식에 대해서 걱정할 필요가 없습니다.
- 이러한 이유로 클래스의 private 변수와 private methods 은 그것의 클라이언트에 액세스 할 수 없습니다.
- private 클래스 구성원은 외부 클래스에 접근할 수 없습니다.
// Fig. 8.3: MemberAccessTest.java
// Private members of class Time1 are not accessible.
public class MemberAccessTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Time1 time = new Time1(); // create and initialize Time1 object
time.hour = 7; // error: hour has private access in Time1
time.minute = 15; // error: hour has private access in Time1
time.second = 30; // error: hour has private access in Time1
}
} // and class MemberAccessTest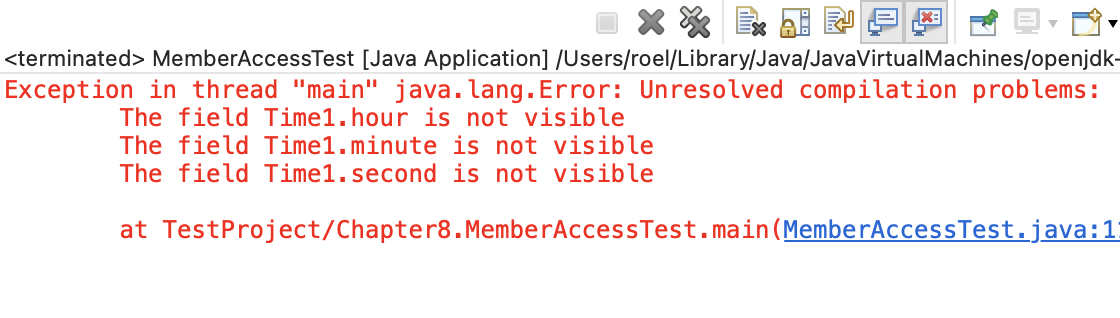
클래스의 멤버가 아닌 방법으로 해당 클래스의 private 멤버에 액세스하려고 하면 컴파일 오류가 발생합니다.

