How browsers work
https://web.dev/howbrowserswork/
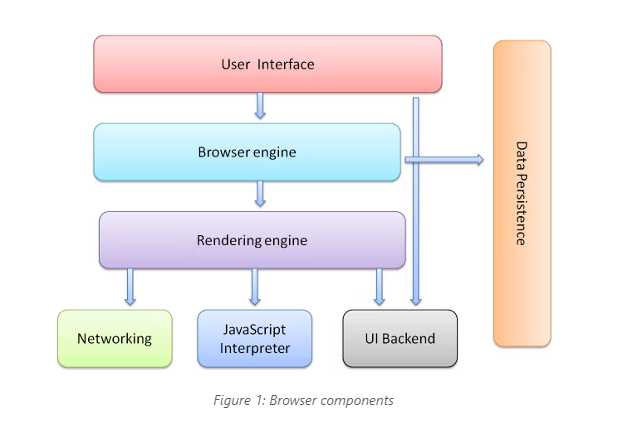
The browser's main components are:
- The user interface: this includes the address bar, back/forward button, bookmarking menu, etc. Every part of the browser display except the window where you see the requested page.
- The browser engine: marshals actions between the UI and the rendering engine.
- The rendering engine: responsible for displaying requested content. For example if the requested content is HTML, the rendering engine parses HTML and CSS, and displays the parsed content on the screen.
- Networking: for network calls such as HTTP requests, using different implementations for different platform behind a platform-independent interface.
- UI backend: used for drawing basic widgets like combo boxes and windows. This backend exposes a generic interface that is not platform specific. Underneath it uses operating system user interface methods.
- JavaScript interpreter. Used to parse and execute JavaScript code.
- Data storage. This is a persistence layer. The browser may need to save all sorts of data locally, such as cookies. Browsers also support storage mechanisms such as localStorage, IndexedDB, WebSQL and FileSystem.
마샬링(marshalling) : 한 객체의 메모리에서 표현방식을 저장 또는 전송에 적합한 다른 데이터 형식으로 변환하는 과정