- 변수 범위를 잘못 설정해서 반복문 무한루프에 갇혀버림
1) 작성 문제
-1부터 20 안에서 홀수와 짝수를 구분짓어 출력하는 프로그램 작성
2) 문제 코드
for (let list = 1; 0 <=list<= 20; list++) {
if (list%2==0) {
console.log(`${list}는 짝수입니다`)
} else {
console.log(`${list}는 홀수입니다`)
}
}-0<=list<=20; ) list 변수 리스트 설정 오류로 발생
3) 해결 코드
for (let list = 1; list<= 20; list++) {
if (list%2==0) {
console.log(`${list}는 짝수입니다`)
} else {
console.log(`${list}는 홀수입니다`)
}
}- 물건의 평균값을 구할 때, 소수점이 신경쓰여서 소수점 해결코드
1) 작성 문제
세 개의 물건가격을 매개변수로 전달받아 평균값을 함수로 정의하고 해당 값 출력
2) 문제코드
function calculate (priceA,priceB,priceC) {
const avg = (priceA+priceB+priceC)/3
return avg
}
const priceA = 15000
const priceB = 24000
const priceC = 17500
const avg1 = calculate (priceA, priceB, priceC)
console.log (`평균 가격 : ${avg2}`)
3) 해결코드
function calculate (priceA,priceB,priceC) {
const avg = (priceA+priceB+priceC)/3
return avg
}
const priceA = 15000
const priceB = 24000
const priceC = 17500
const avg1 = calculate (priceA, priceB, priceC)
// 나머지를 버리고 싶어서 math()함수 사용
const avg2 = Math.floor(avg1)
console.log (`평균 가격 : ${avg2}`)4) math() method 설명
(1) 형식
const 새로운 변수 = Math.floor(적용하고 싶은 기존변수)
(2) 개념
-다른 전역 객체와 달리 생성자(constructor)가 존재하지 않음
-따로 인스턴스를 생성하지 않아도 Math 객체의 모든 메소드나 프로퍼티를 바로 사용할 수 있음
(3) 종류 [활용메소드]
① Math.ceil() : 소수점 올림, 정수 반환
② Math.floor() : 소수점 버림, 정수 반환
③ Math.round() : 소수점 반올림, 정수 반환
(3-1) 자주 사용하는 코드
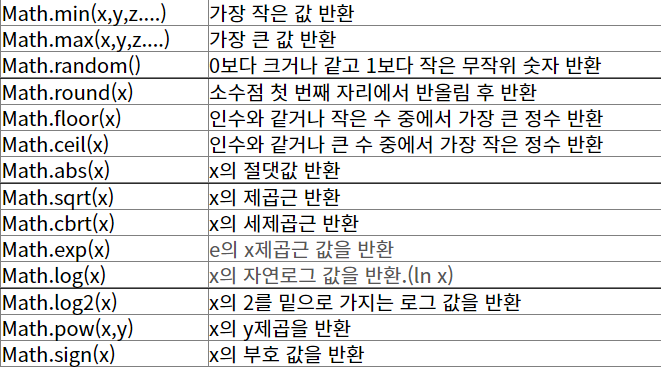
- class 개념 이해 부족으로 출력에 undefined가 뜸
1) 작성문제
-기본적으로 색깔, 사이즈, 속성이 동일한 의류 쇼핑몰 & 이 옷들의 세 속성을 바로 확인할 수 있도록 출력 필요
2) 문제코드
class shirt {
constructor (color, size, property) {
this.color = 'white',
this.size = 95,
this.property = 'loose'
}
Print1() {
console.log(`shirt 정보는 다음과 같습니다. [color : ${this.color}, size : ${this.size}, property : ${this.property}]`)
}
}
const shirt1 = new shirt()
console.log(shirt1)
console.log(shirt1.Print1())3) 문제코드 출력값
shirt { color: 'white', size: 95, property: 'loose' }
//console.log(shirt1) 출력값
shirt 정보는 다음과 같습니다. [color : white, size : 95, property : loose]
//shirt1.print1() 출력값
undefined
//console.log(shirt1.Print1())4) 해결코드
class shirt {
constructor (color, size, property) {
this.color = 'white',
this.size = 95,
this.property = 'loose'
}
Print1() {
console.log(`shirt 정보는 다음과 같습니다. [color : ${this.color}, size : ${this.size}, property : ${this.property}]`)
}
}
const shirt1 = new shirt()
console.log(shirt1)
shirt1.Print1()
5) 오류코드 발생원인
console.log(shirt1.Print1())
-shirt1.Print1() : Print1() 출력
-console.log(shirt1.Print1()) : undefined
- 문자열 반복 생성
1) 해당코드가 궁금해진 이유
-결과값이 동일한 출력을 console창에서 진행할 때, 해당 출력값이 겹쳐보여 분리할 수 있는 방법을 고민하다 궁금증이 생김
-'문자열'*100 : 해결할 수가 없음
2) 해결코드
(1) String.prototype.repeat(n)
: 문자열.repeat(n) => 문자열을 n번 반복 연결한 문자열 반환
'-'.repeat(3) // ---(참고) ES6부터 String 타입에 추가된 메서드
(2) Array.prototype.join() 활용
: Array(n+1).join('문자열') => '문자열'을 n번 반복 연결한 문자열 반환
*n은 반복할 횟수(반복할 횟수보다 1 크게 넣어줘야 함)
Array(3).join('-') // --+join('구분자') 메서드는
배열 모든 요소들을 '구분자'로 연결한 문자열을 반환하는 메서드
[1,2,3].join('-') => '1-2-3'- 배열의 합계, 평균 구하기
1) 작성문제
-6개의 상품 가격 데이터를 갖고 상품들의 가격 합계와 평균 구하기
2) 해당코드가 궁금해진 이유
-간결하게 작성할 수 있는 방법을 찾아보다 해당 함수를 찾게 됨
3) 해결함수
(1) reduce()
-배열의 합계와 평균을 구하는 방법
const (변수) = [(숫자), (숫자), (숫자) ...]
const (변수1) = (변수).reduce(function add(sum,value) {
return sum + value
},0)
console.log(변수1)(2) reduceRight()
-배열의 역순으로 연산을 원할 때
const (변수) = [(숫자), (숫자), (숫자) ...]
const (변수1) = (변수).reduceRight(function add(str,value) {
return str + value
},'')
console.log(변수1)4) 해당 함수 활용코드
const shoe = [10000, 39500, 75000, 46730, 28500, 74100]
//reduce() 함수 활용, 합계
//reduce()의 callback 함수는 누적 값과 현재 처리 중인 배열의 element(=Value)를 파라미터로 받음
//누적 값과 Value의 합을 리턴하면 리턴된 값이 callback 함수의 sum에 전달됨
//reduce() 초기값을 0으로 설정하지 않으면 shoe[0]으로 설정되기에 미리 설정하는 것이 좋다
const result = shoe.reduce(function add(sum, Value) {
return sum + Value
}, 0)
//평균값 계산
const result2 = result / shoe.length
//소수점을 버리기 위해 math() 사용
const result3 = Math.floor(result2)
console.log(result3)
