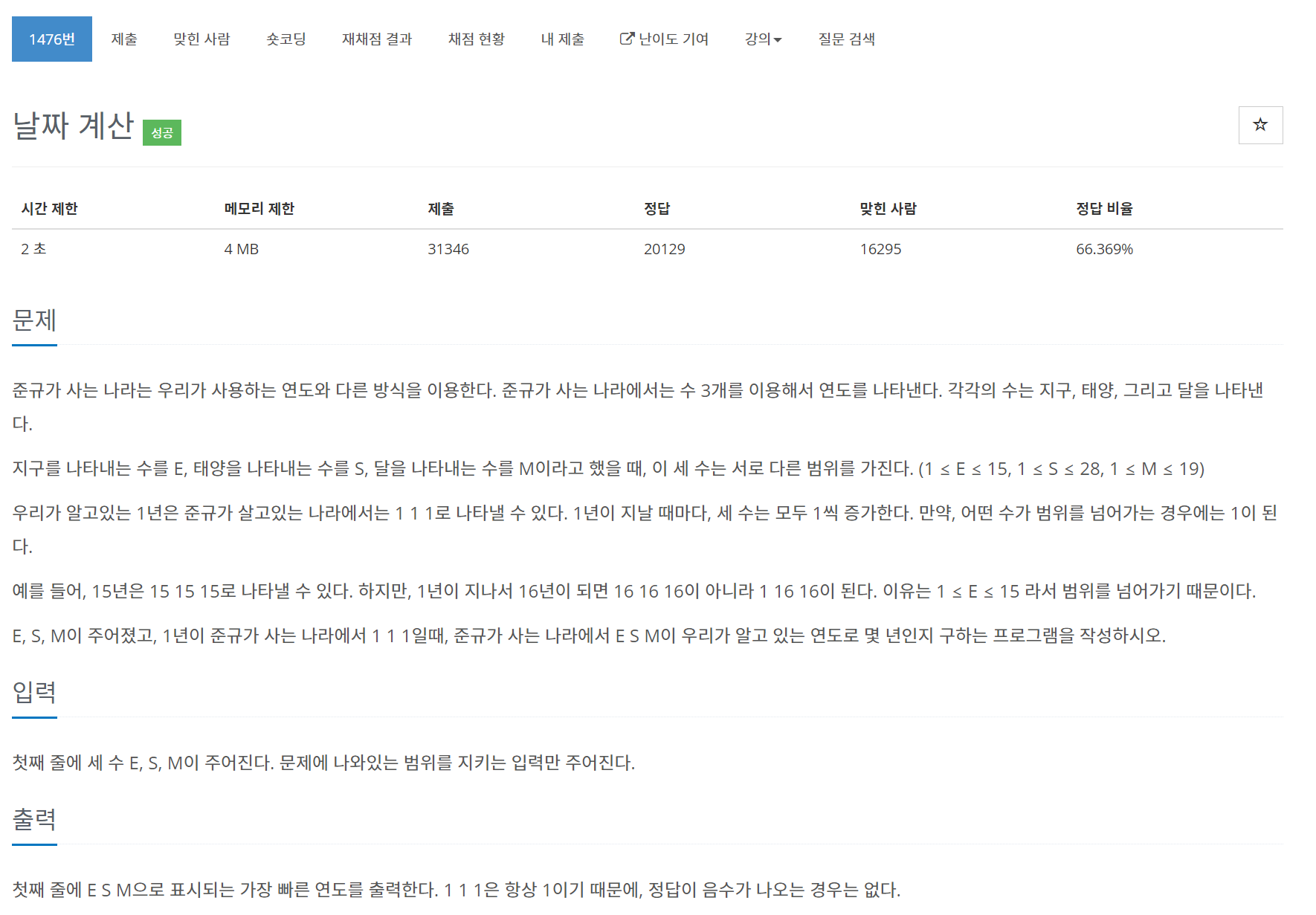
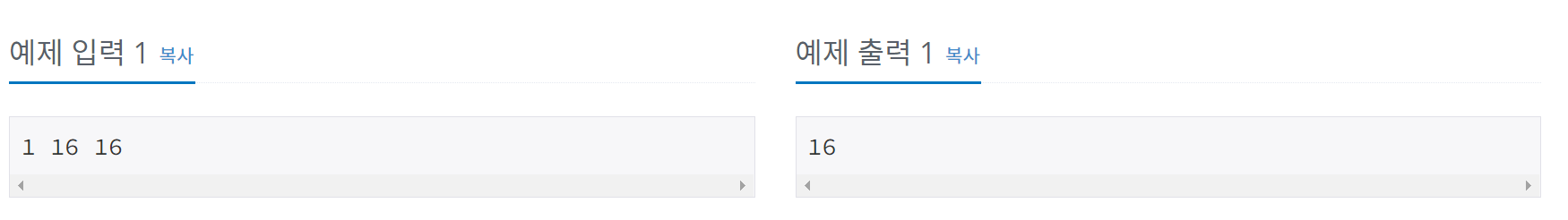
문제
풀이
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int e = sc.nextInt();
int s = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int answer = 0;
while(true) {
answer++;
if((answer - e) % 15 == 0 && (answer - s) % 28 == 0 && (answer - m) % 19 == 0) {
break;
}
}
System.out.print(answer);
sc.close();
}
}
6064번 카잉 달력
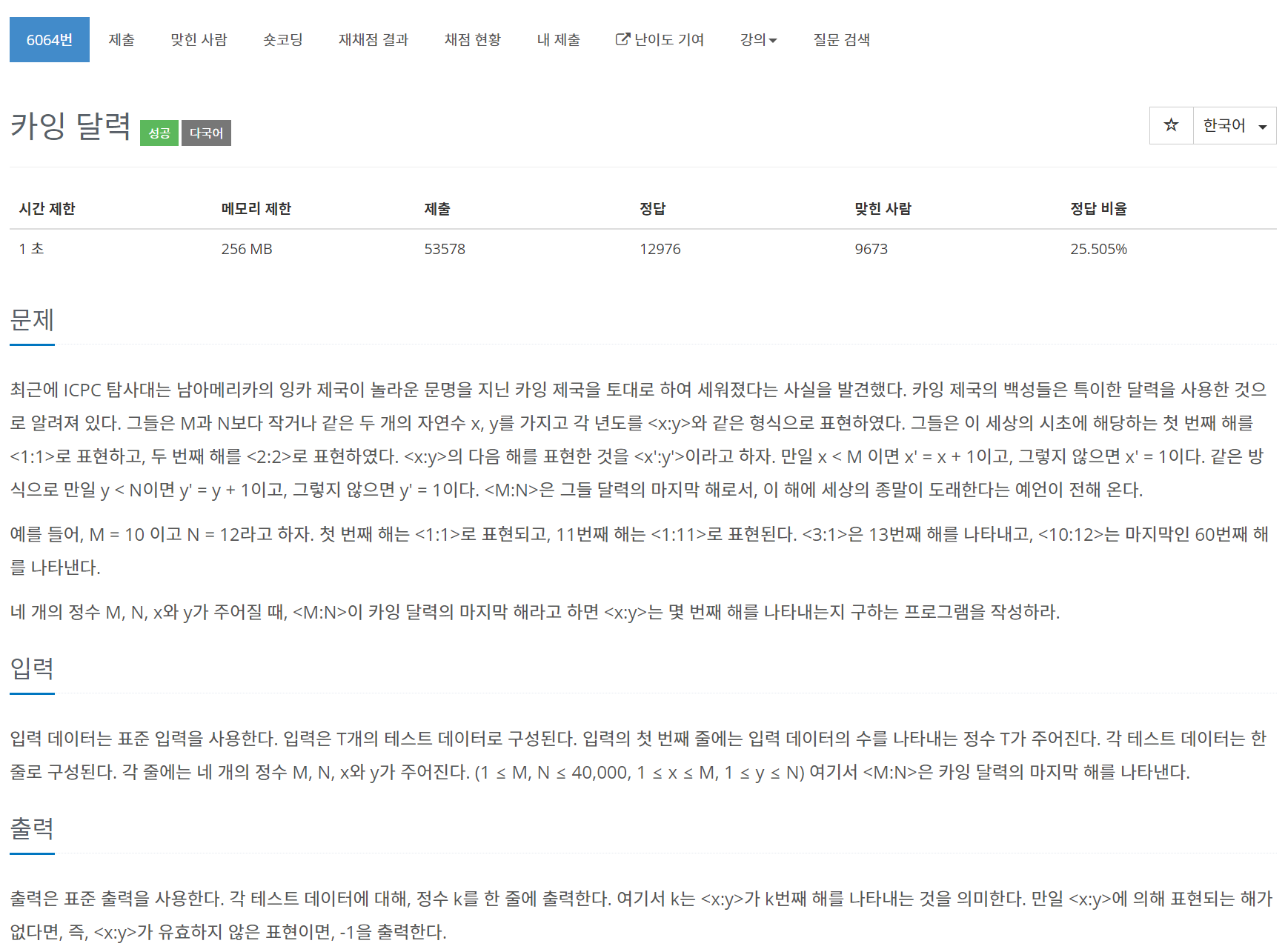
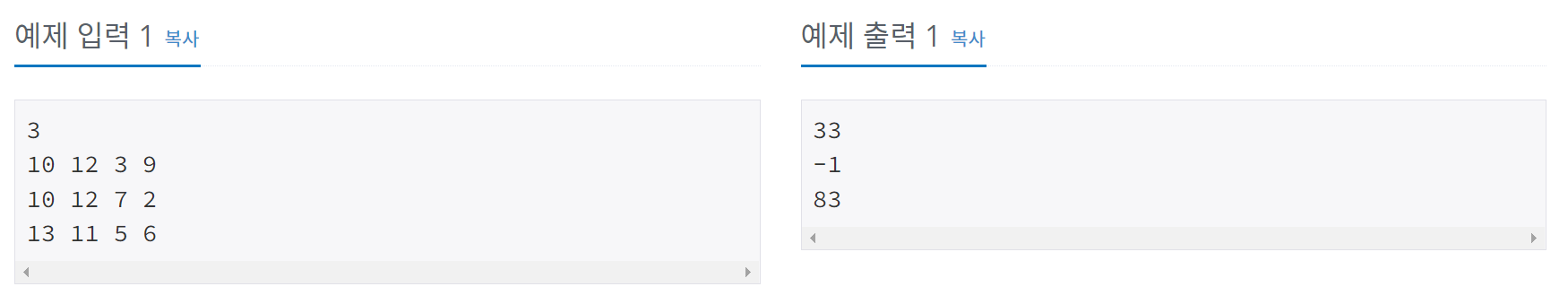
문제
풀이
x가 m만큼 증가할 때 마다 -> x의 값은 동일하지만 y의 값은 변함
y가 n만큼 증가할 때 마다 -> y의 값은 동일하지만 x의 값은 변함
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
for (int s = 0; s < t; s++) {
boolean answer = false;
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int x = sc.nextInt() - 1; // 나머지 값이 0이 나오는 것을 미리 방지
int y = sc.nextInt() - 1;
for (int i = x; i < (n * m); i += m) {
if (i % n == y) {
System.out.println(i + 1);
answer = true;
break;
}
}
if (!answer) {
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
sc.close();
}
}