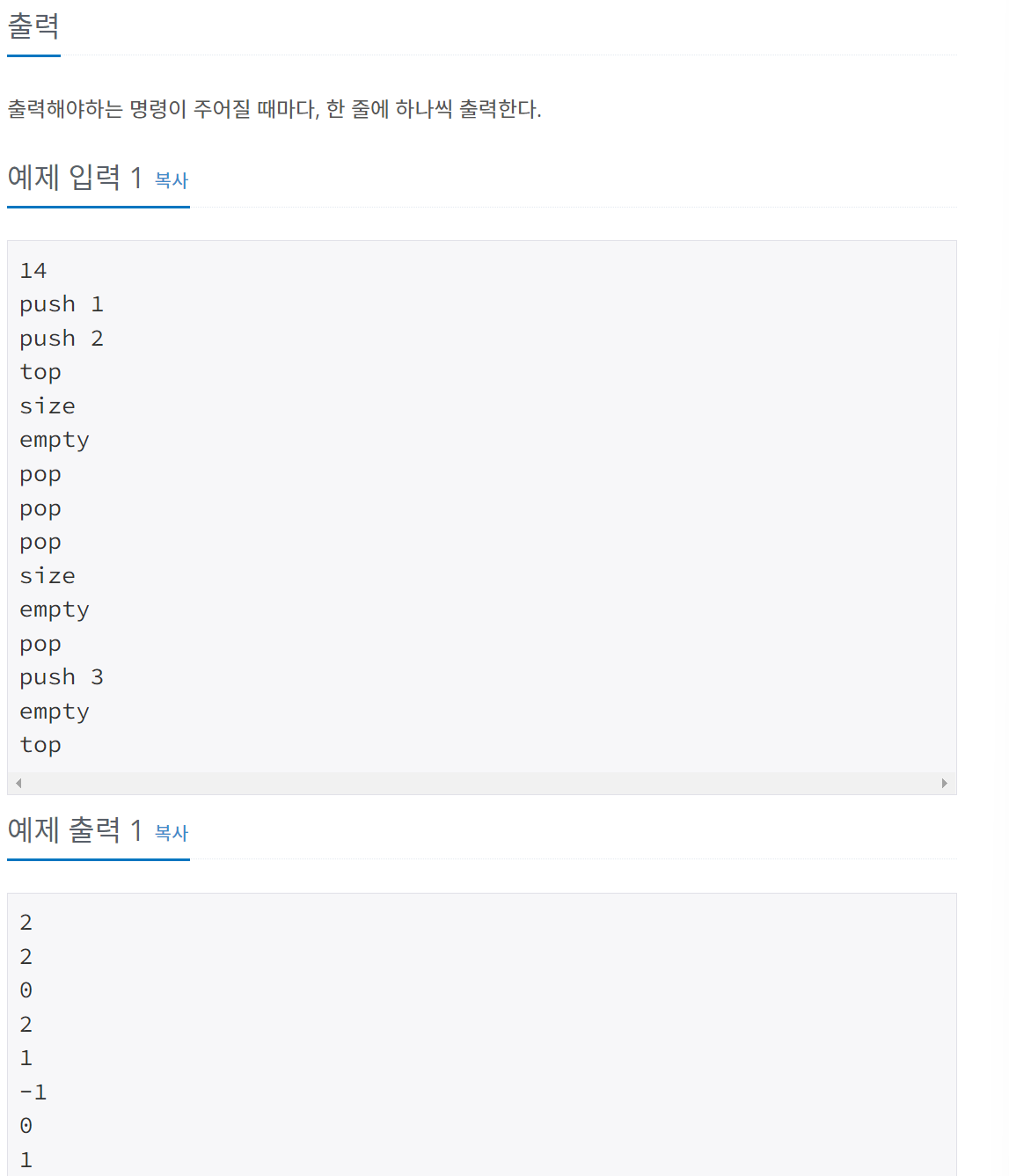
10828번 스택
문제

풀이
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = sc.next();
if(str.equals("push")) {
stack.push(sc.nextInt());
break;
} else if(str.equals("pop")) {
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(-1);
sb.append("\n");
} else {
sb.append(stack.pop()).append("\n");
}
break;
} else if(str.equals("top")) {
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(-1);
sb.append("\n");
} else {
sb.append(stack.peek()).append("\n");
}
break;
} else if(str.equals("empty")) {
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(1);
sb.append("\n");
} else {
sb.append(0).append("\n");
}
break;
} else if(str.equals("size")) {
sb.append(stack.size()).append("\n");
break;
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
}그러나... 오답처리 되었다.
생각해보니 push인 경우에는 equals가 아니라 contains로 해줘야 뒤에 숫자가 붙어도 if문 처리가 될 수 있다는 걸 깨닫고 이렇게 수정했다. 그리고, if문이 너무 중첩되는것 같아서 삼항연산자도 이용했다.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = sc.next();
if(str.contains("push")) {
stack.push(sc.nextInt());
} else if(str.equals("pop")) {
sb.append(stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.pop()).append("\n");
} else if(str.equals("top")) {
sb.append(stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek()).append("\n");
} else if(str.equals("empty")) {
sb.append(stack.isEmpty() ? 1 : 0).append("\n");
} else if(str.equals("size")) {
sb.append(stack.size()).append("\n");
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
}그랬더니 성공함!
9093번 단어 뒤집기
문제


풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String arr[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(arr[j]);
System.out.print(sb.reverse() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}n줄을 입력받고, 한줄당 공백을 기준으로 쪼갠뒤에 StringBuilder의 reverse 메소드로 뒤집어서 출력되게 했다.
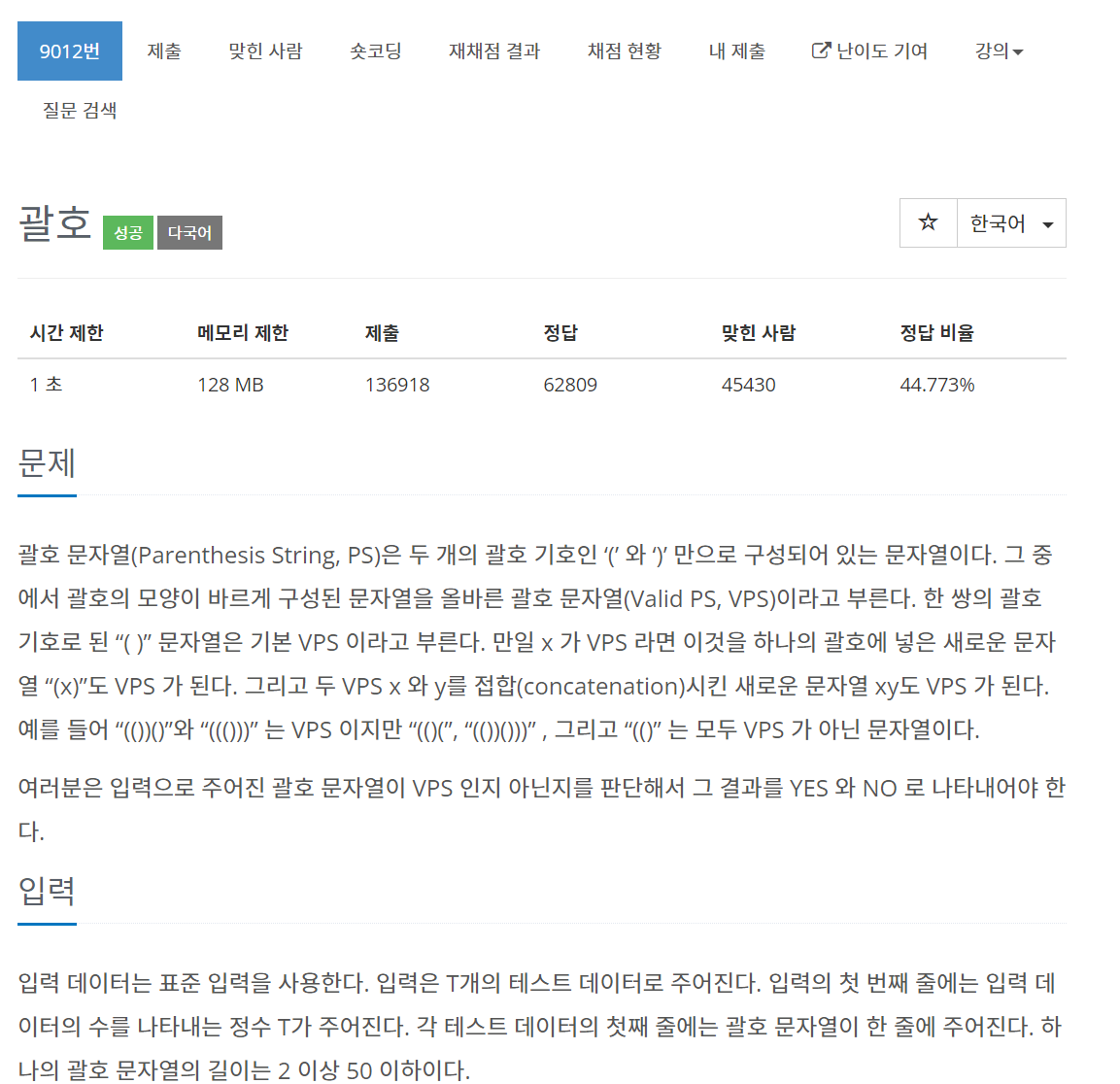
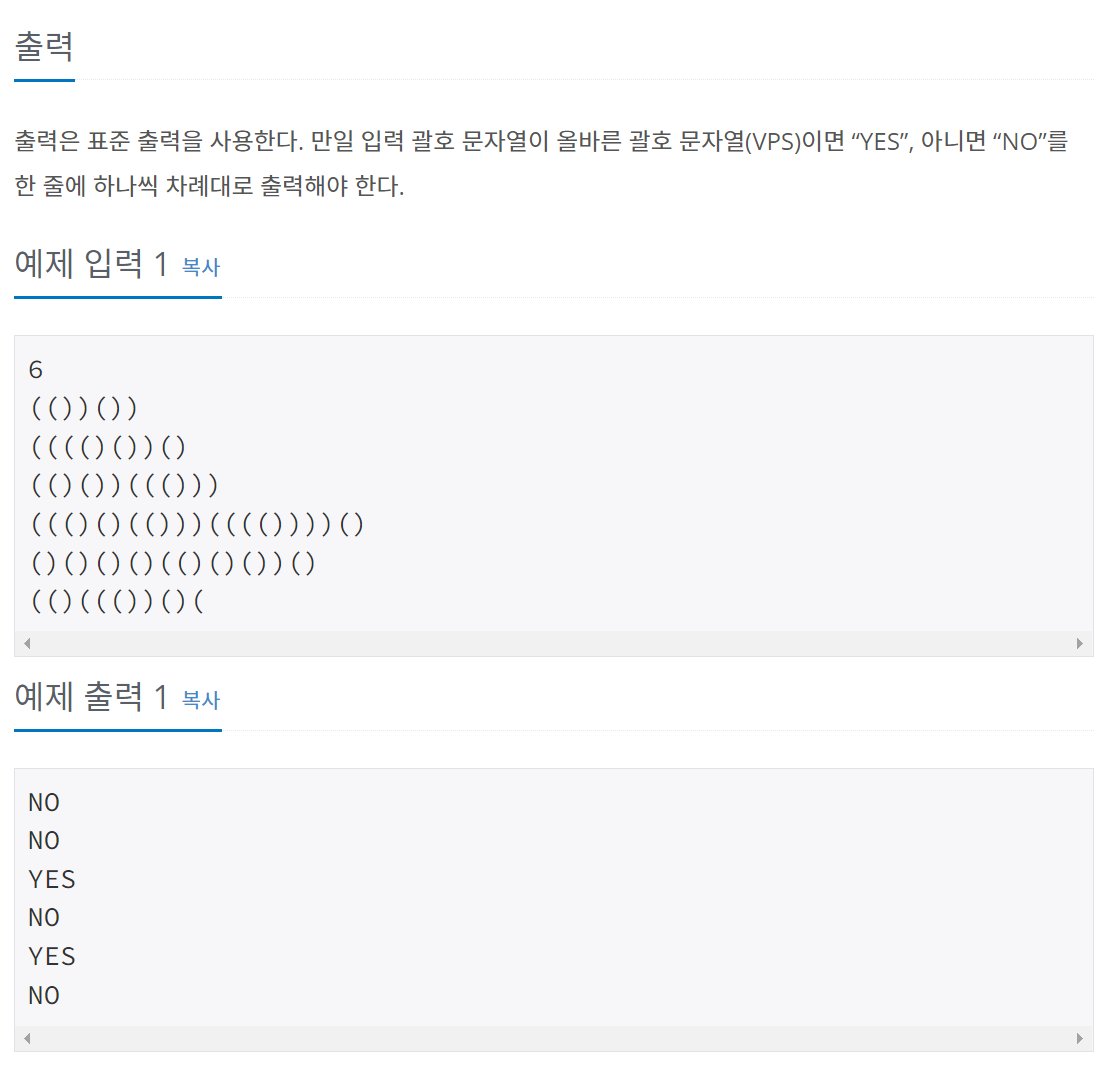
9012번 괄호
문제
풀이
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public String solution(String str) {
String answer = "YES";
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for(char x : str.toCharArray()) {
if(x == '(') {
stack.push(x);
} else {
// 닫는 괄호가 많은 상황
if(stack.isEmpty()) {
return "NO";
}
stack.pop();
}
}
// 여는 괄호가 많은 상황
if(!stack.isEmpty()) {
return "NO";
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main m = new Main();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(m.solution(sc.next()));
}
}
}해당 문제는 강의를 통해 풀었던 문제의 응용이라서 solution 함수는 그대로 쓰고 이 함수를 for문으로 여러번 사용하게 했다.
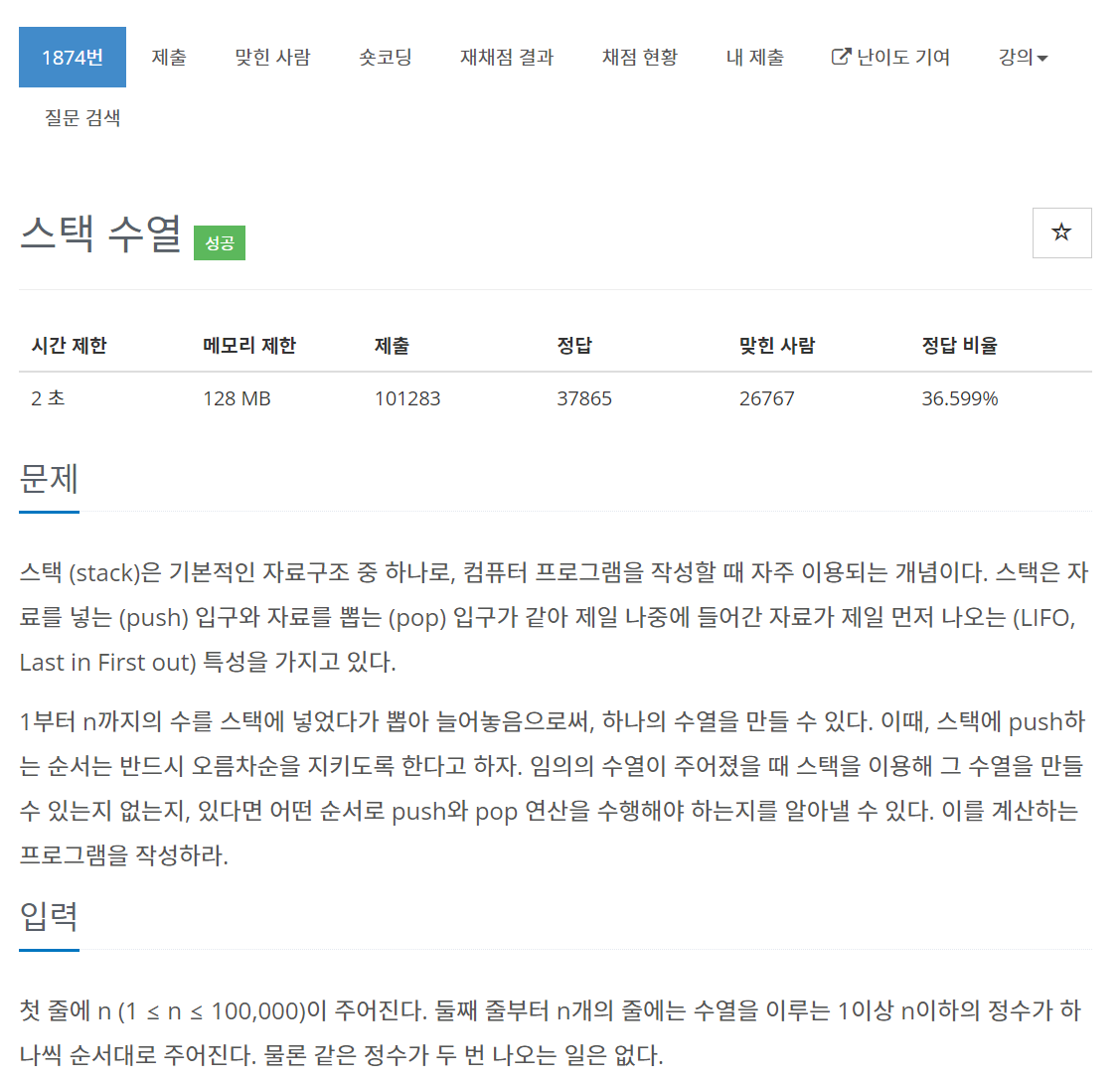
1874번 스택 수열
문제

풀이
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int start = 0;
while(n > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
if(a > start) {
for(int i = start + 1; i <= a; i++) {
stack.push(i);
sb.append('+').append('\n');
}
start = a;
} else if(stack.peek() != a) { // 스택에 넣어졌어야 했는데 다른 경우
System.out.println("NO"); // 수열을 만족하지 못하는 것임
return;
}
stack.pop();
sb.append('-').append('\n');
}
System.out.println(sb);
sc.close();
}
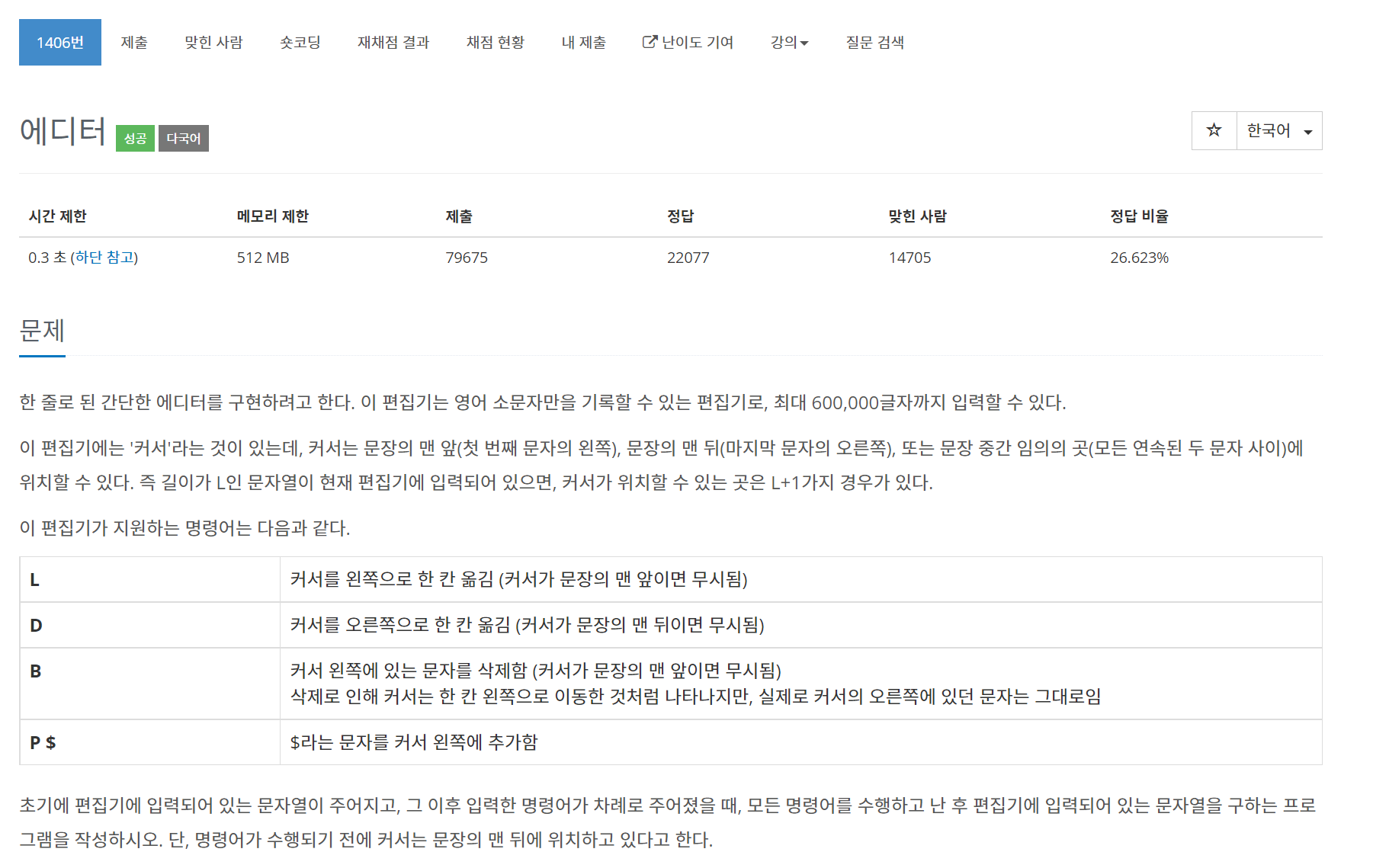
}1407번 에디터
문제

풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String str = br.readLine();
Stack<Character> lStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Character> rStack = new Stack<>();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
lStack.push(str.charAt(i));
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String cmd = br.readLine();
switch(cmd.charAt(0)) {
case 'L' : // 왼쪽 스택에서 pop한 값을 오른쪽 스택에 push
if(lStack.empty()) {
break;
}
rStack.push(lStack.pop());
break;
case 'D' : // 오른쪽 스택에서 pop한 값을 왼쪽 스택에 push
if(rStack.empty()) {
break;
}
lStack.push(rStack.pop());
break;
case 'B' : // 왼쪽 스택 pop
if(lStack.empty()) {
break;
}
lStack.pop();
break;
case 'P' : // 오른쪽 스택 push
lStack.push(cmd.charAt(2));
break;
}
}
while(!lStack.empty()) {
rStack.push(lStack.pop());
}
while(!rStack.empty()) {
sb.append(rStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
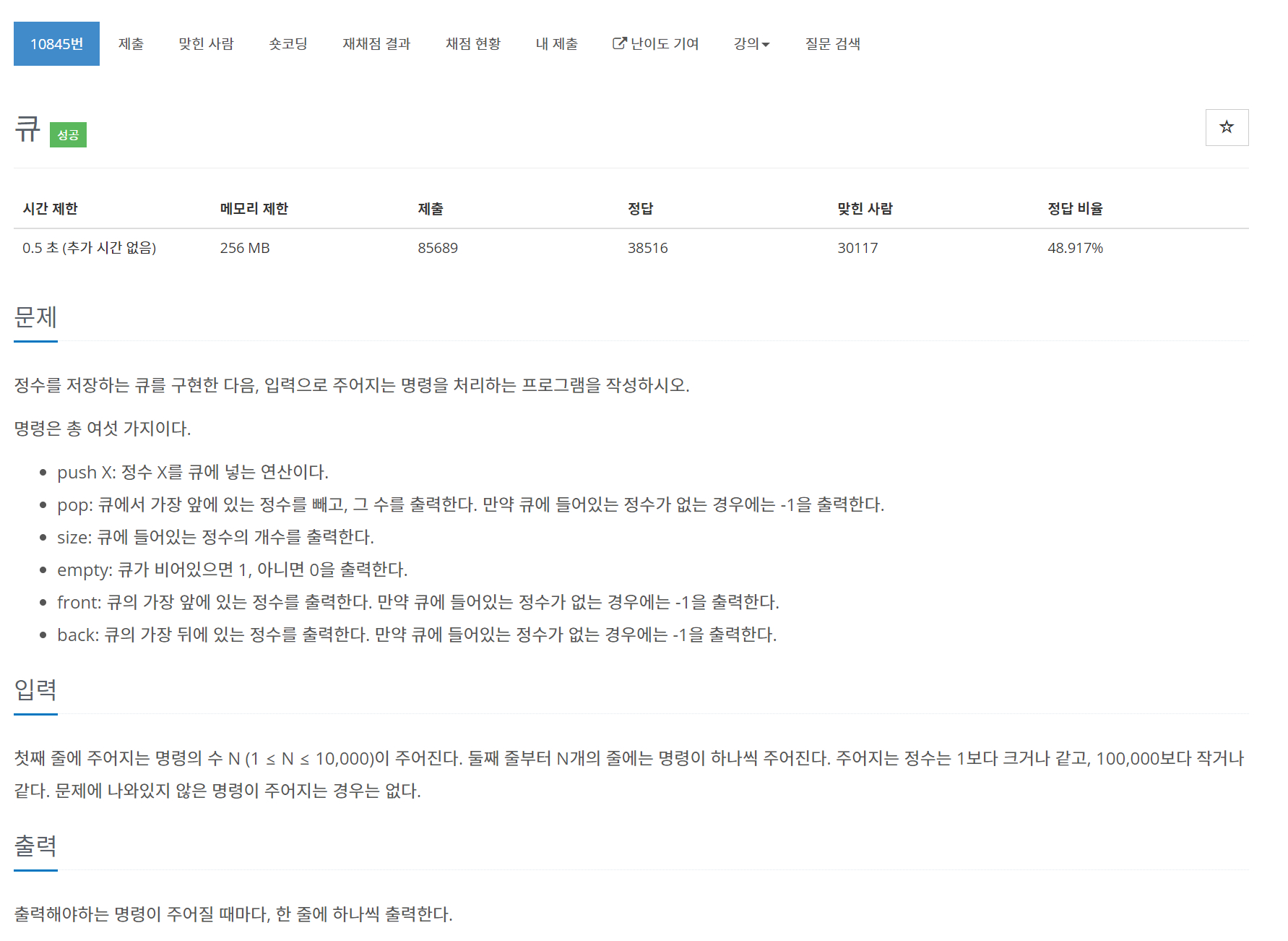
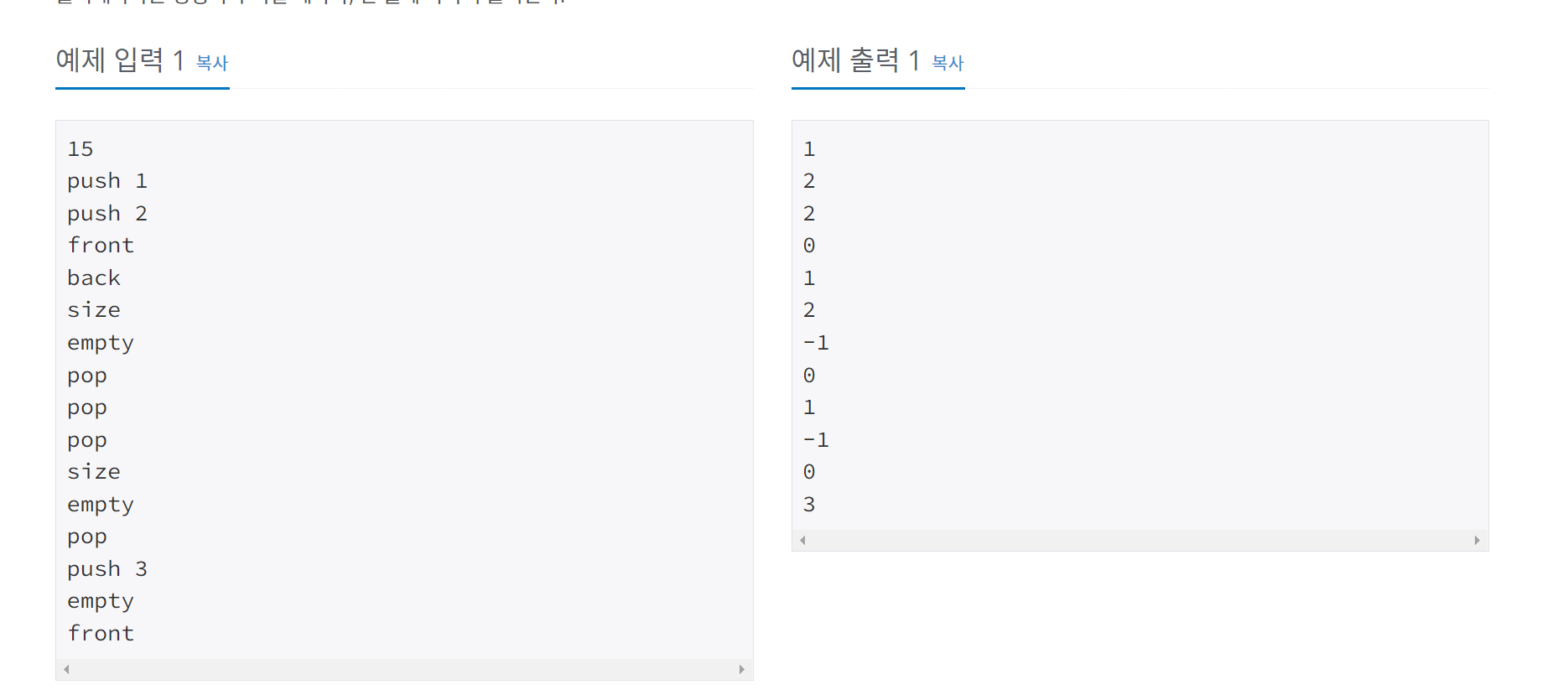
}10845번 큐
문제
풀이
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int a = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String str = st.nextToken();
switch(str) {
case "push" :
a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
queue.add(a);
break;
case "pop" :
if(queue.isEmpty()) {
sb.append("-1").append("\n");
break;
}
sb.append(queue.poll()).append("\n");
break;
case "size" :
sb.append(queue.size()).append("\n");
break;
case "empty" :
sb.append(queue.isEmpty() ? 1 : 0).append("\n");
break;
case "front" :
sb.append(queue.isEmpty() ? -1 : queue.peek()).append("\n");
break;
case "back" :
sb.append(queue.isEmpty() ? -1 : a).append("\n");
break;
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
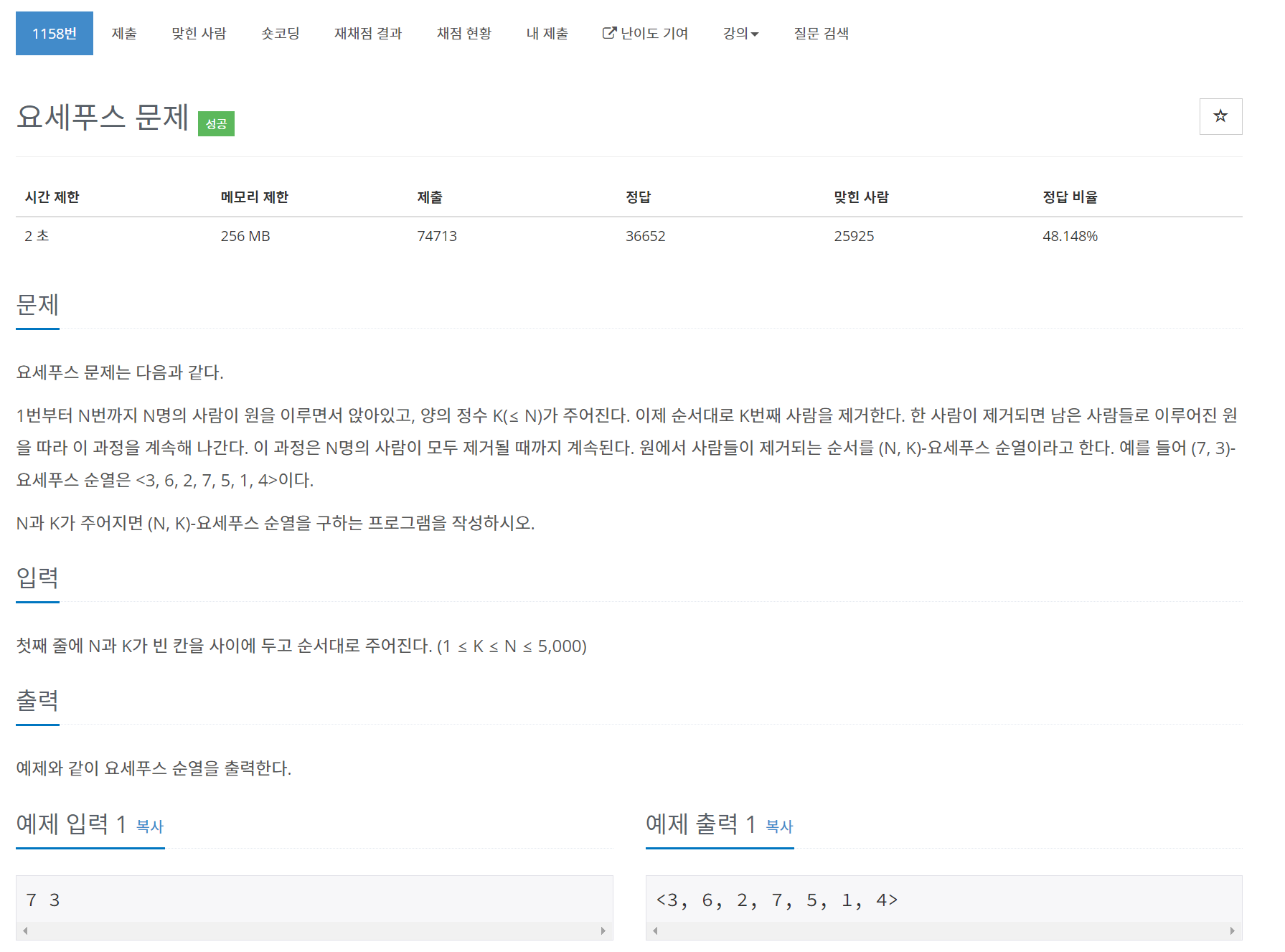
1158번 요세푸스 문제
문제
풀이
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.add(i + 1);
}
sb.append("<");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < k - 1; j++) {
queue.add(queue.poll());
}
sb.append(queue.poll() + ", ");
}
sb.setLength(sb.length() - 2); // 마지막 , 지우기
sb.append(">");
System.out.println(sb.toString());
sc.close();
}
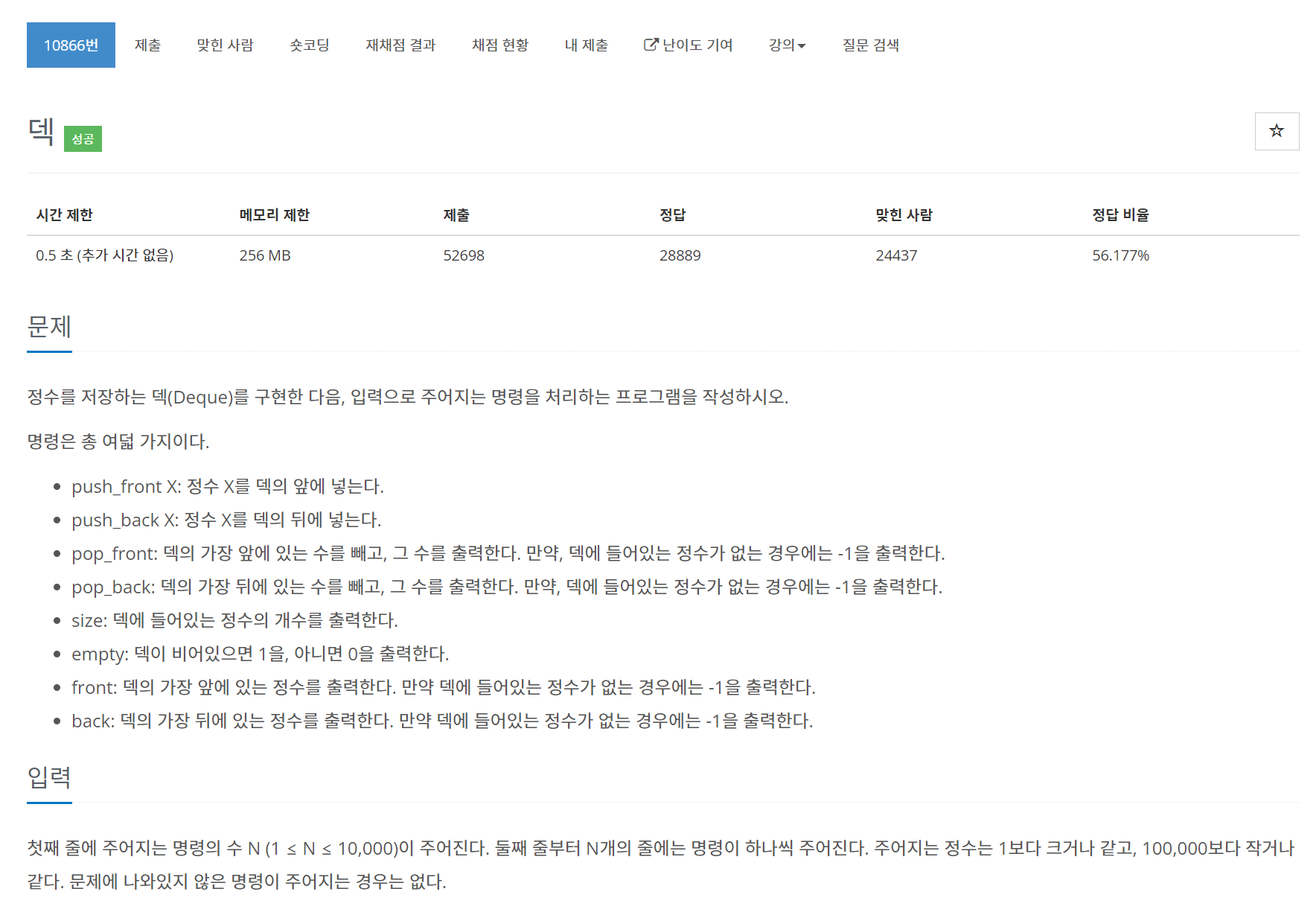
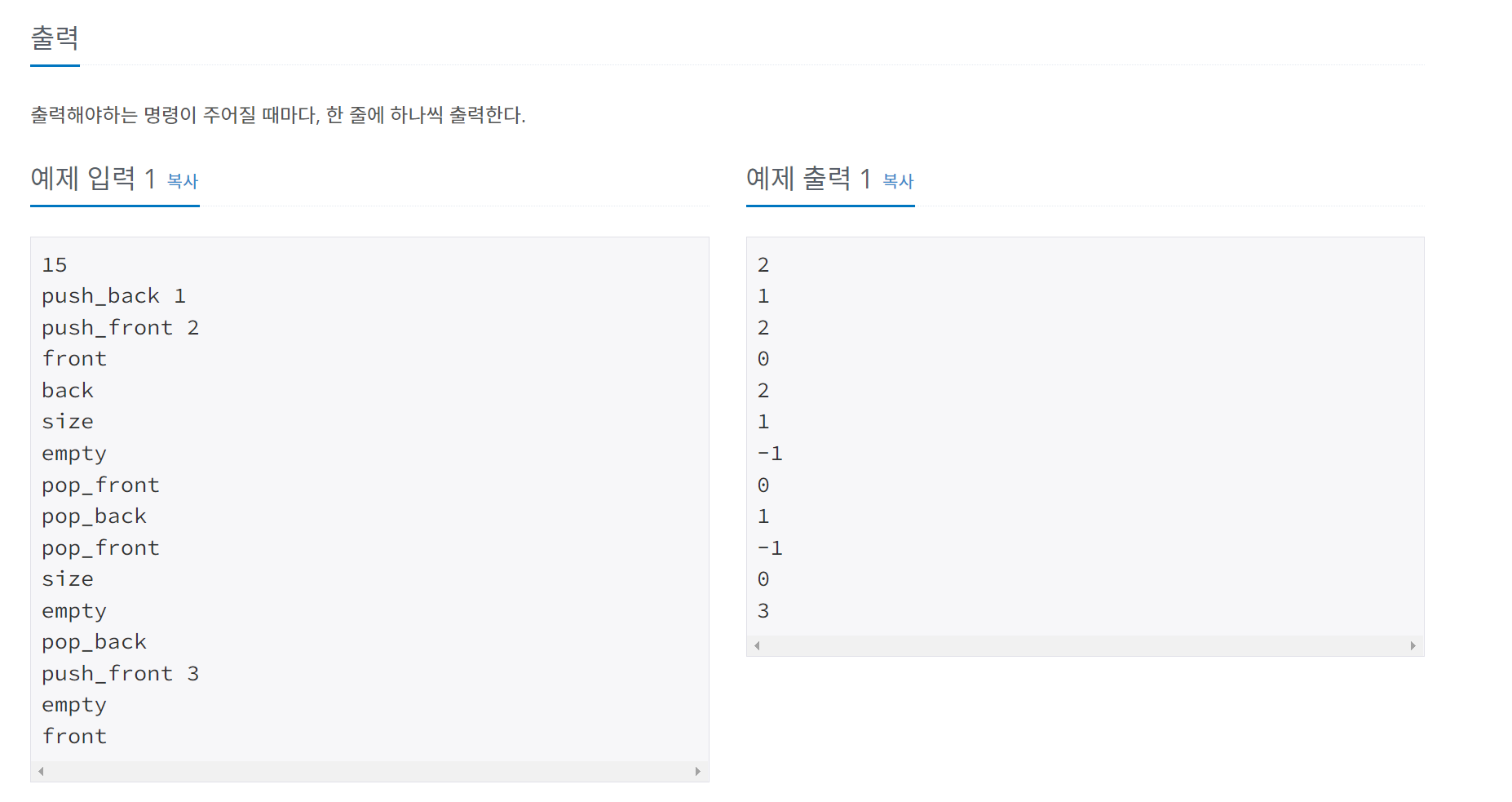
}10866번 덱
문제
풀이
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
ArrayDeque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String[] str = br.readLine().split(" ");
switch(str[0]) {
case "push_front":
deque.addFirst(Integer.parseInt(str[1]));
break;
case "push_back":
deque.addLast(Integer.parseInt(str[1]));
break;
case "pop_front":
if(deque.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(-1).append("\n");
}
else {
sb.append(deque.pollFirst()).append("\n");
}
break;
case "pop_back":
if(deque.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(-1).append("\n");
}
else {
sb.append(deque.pollLast()).append("\n");
}
break;
case "size":
sb.append(deque.size()).append("\n");
break;
case "empty":
if(deque.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(1).append("\n");
}
else {
sb.append(0).append("\n");
}
break;
case "front":
if(deque.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(-1).append("\n");
}
else { // 덱의 가장 앞에 있는 정수를 출력만 하고 빼지는 않음
sb.append(deque.peekFirst()).append("\n");
}
break;
case "back":
if(deque.isEmpty()) {
sb.append(-1).append("\n");
}
else { // 덱의 가장 뒤에 있는 정수를 출력만 하고 빼지는 않음
sb.append(deque.peekLast()).append("\n");
}
break;
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}