📝 요구사항
- 간단한 사칙연산
- 양수로만 계산 가능
- 나눗셈에서 0으로 나누는 경우 IllegalArgument 예외 발생
📂 코드
ArithmeticOperator : enum
- 사칙 연산 수행 enum
- 코드
public enum ArithmeticOperator {
// enum 선언
// ADDITION("+"), SUBTRACTION("-"), MULTIPLICATION("*"), DIVISION("/");
// 추상 메소드 구현
ADDITION("+") {
@Override
public int calculate(final int operand1, final int operand2) {
return operand1 + operand2;
}
},
SUBTRACTION("-") {
@Override
public int calculate(final int operand1, final int operand2) {
return operand1 - operand2;
}
},
MULTIPLICATION("*") {
@Override
public int calculate(final int operand1, final int operand2) {
return operand1 * operand2;
}
},
DIVISION("/") {
@Override
public int calculate(final int operand1, final int operand2) {
if (operand2 == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
}
return operand1 / operand2;
}
};
// 각각의 산술 연산자를 operator로 명령하겠다는 코드.
private final String operator;
// ArithmeticOperator 생성자
ArithmeticOperator(String operator) {
this.operator = operator;
}
// 추상 메소드
public abstract int arithmeticCalculate(final int operand1, final int operand2);
public static int calculate(int operand1, String operator, int operand2) {
// 해당 연산자에 일치하는 enum 값을 가져온다.
ArithmeticOperator arithmeticOperator = Arrays.stream(ArithmeticOperator.values())
.filter(v -> v.operator.equals(operator))
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("올바른 사칙연산이 아닙니다."));
// enum 값에 해당하는 enum의 메소드 실행
return arithmeticOperator.calculate(operand1, operand2);
}
}Calculator : class
- 직접 사칙 연산을 수행하는 것이 아닌 ArithmeticOperator에게 사칙 연산 작업을 요청
- 코드
public class Calculator {
public static int calculate(int operand1, String operator, int operand2) {
return ArithmeticOperators.calculate(operand1, operator, operand2);
}CalculatorTest : class
- Test class
- 코드
- @MethodSource를 통해 하나의 테스트 코드로 4가지 연산을 수행 가능하다.
- formulaAndResult()은 "static"이어야 한다.
public class CalculatorTest {
@DisplayName("덧셈 연산을 정상적으로 수행한다.")
@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource("formulaAndResult")
void calculateTest(int operand1, String operator, int operand2, int result) {
int calculateResult = Calculator.calculate(operand1, operator, operand2);
assertThat(calculateResult).isEqualTo(result);
}
// static이어야 한다!
private static Stream<Arguments> formulaAndResult(){
return Stream.of(
arguments(1, "+", 2, 3),
arguments(1, "-", 2, -1),
arguments(4, "*", 2, 8),
arguments(4, "/", 2, 2)
);
}
}🔗 흐름 구조
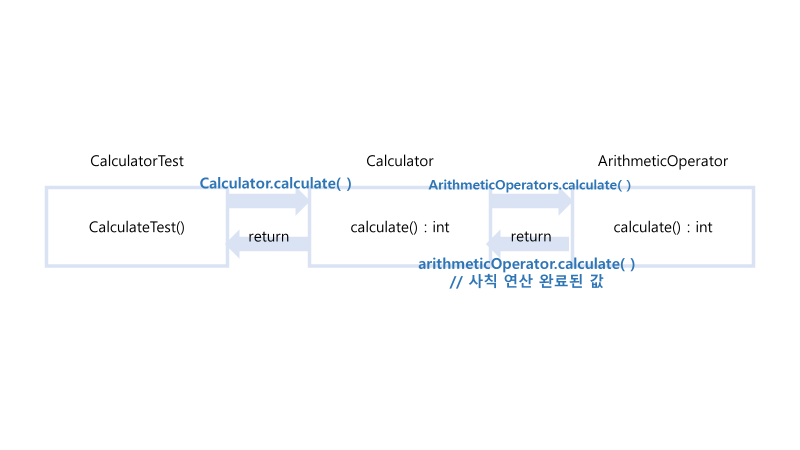
1. Test code에서 Calculator에게 작업을 위임
2. Calculator은 enum인 ArithmeticOperator에게 해당 연산 작업을 다시 한번 작업 위임
3. enum ArithmeticOperator에게 연산 작업을 수행 및 결과값 전달
-> 객체들이 협력을 해 결과값을 리턴해주는 구조
PositiveNumber : class
- 피연산자의 양음수 판단 class
NewArithmeticOperator : interface
- 인터페이스
public interface NewArithmeticOperator {
boolean supports(String operator);
int calculate(int operand1, int operand2);
}NewArithmeticOperator 구현 class
1. AdditionOperator
- 덧셈 연산 class
- 코드
public class AdditionOperator implements NewArithmeticOperator {
// operator와 해당 연산자가 같는지 비교값을 boolean 타입으로 반환
@Override
public boolean supports(String operator) {
return "+".equals(operator);
}
// 만약 같다면, 피연산자의 사칙 연산 값을 반환
@Override
public int calculate(int operand1, int operand2) {
return operand1 + operand2;
}
}- SubstractOperator
- 뺄셈 연산 class
- DivisionOperator
- 나누셈 연산 class
- MultiplicationOperator
- 곱셈 연산 class
<수정 중>
인터페이스를 가지는
각각의 구현체들을 상위 인터페이스인 __를 통해서 받는다.
operator에 해당하는 실제 구현체를 필터링해서
선택받은 오퍼레이터에 해당 calculate() 호출
만약 찾기 못하면 예외발생
4개의 구현체를 리스트로 받는다. 오퍼레이터에 맞는 구현체를 찾은 다음
구현체의 calculate() 작업 위임
int로 받기 위해 map
IF 0으로 나눠야 하는 경우에는?
@DisplayName("나눗셈에서 0으로 나누는 경우 IllegalArgument 예외를 발생시킨다.")
@Test
void CalculateExceptionTest() {
assertThatCode(() -> Calculator.calculate(10,"/",0))
.isInstanceOf(IllegalArgumentException.class);
}BUT IllegalArgumentException이 발생하지 않는다.
@Override
public int calculate(int operand1, int operand2) {
if (operand2 == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
}
return operand1 / operand2;
}양수로만 계산 가능하다
public class PositiveNumber {
private final int value;
public PositiveNumber(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
private void validate(int value){
if(isNegativeNumber(value)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("0 또는 음수를 전달할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
private boolean isNegativeNumber(int value){
return value <= 0;
}
}- 0 또는 음수면 IllegalArgumentException 예외 발생
- 양수면 객체 생성 -> 양수라는 것을 보장!
public class Calculator {
public static int calculate(int num1, String operator, int num2) {...}
}public class Calculator {
public static int calculate(PositiveNumber num1, String operator, PositiveNumber num2) {...}
}나머지 인자도 int 타입에서 PositiveNumber으로 변경
