💐 동시성(concurrency) vs 병렬성(parallelism)
| 동시성 | 병렬성 |
|---|---|
| 한 번에 여러 작업을 동시에 다루는 것을 의미 동시성은 논리적 개념으로 멀티스레딩에서 사용되기도 하고 싱글 스레드에서 사용되기도 한다. 또한 싱글코어, 멀티코어에서도 사용된다 | 한번에 여러 작업을 병렬적으로 처리하는 것을 의미 병렬성은 물리적 개념으로 여러 로봇들이 여러 작업을 병렬로 수행한 것처럼 멀티코어에서 여러 작업을 병렬적으로 수행한다. |
- 동시성과 병렬성은 공존이 가능하다.
동시성
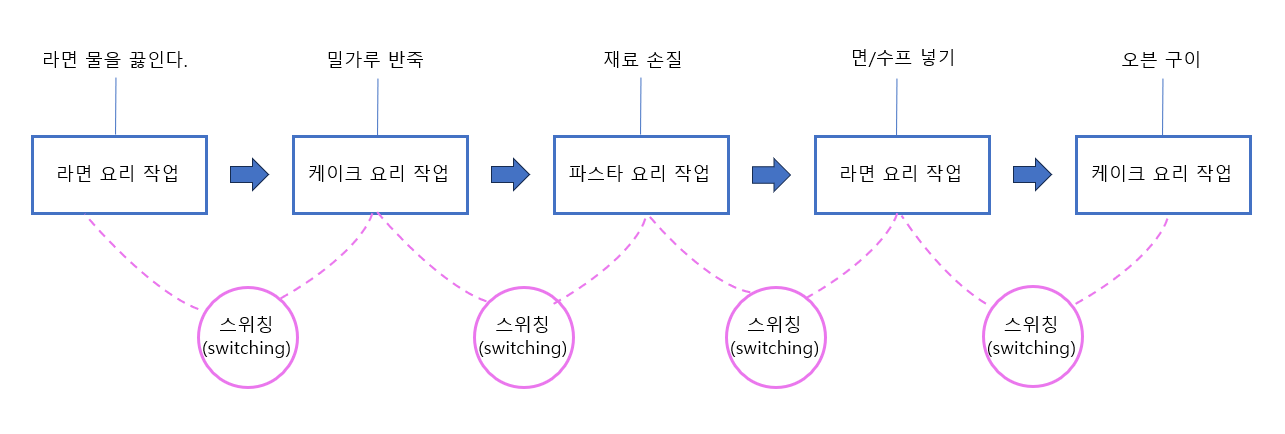
동시성에서는 스위칭이 핵심이다.
라면 요리작업을 시작하여, 라면 물을 끓이는 동안 스위칭하여 케이크 요리작업(밀가루 반죽)을 하고 밀가루 반죽이 다 끝났는데 아직도 라면 물을 끓이고 있다면 스위칭하여 파스타 요리작업(재료 손질)을 한다.
이렇게 한 번에 여러 작업을 동시에 하는 것을 동시성이라 한다.
병렬성
[싱글 스레드에서 동기 코드] → 14-15초 소요
import requests
import time
import os
import threading
def fetcher(session, url):
print(f"{os.getpid()} process | {threading.get_ident()} url: {url}")
with session.get(url) as response:
return response.text
def main():
urls = ["https://google.com", "https://apple.com"] * 50
with requests.Session() as session:
result = [fetcher(session,url) for url in urls]
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start =time.time()
main()
end = time.time()
print(end - start)def fetcher : 어떤 프로세스에서 어떤 스레드가 사용되는지 확인
os.getpid()는 현재 프로세스 ID이고,
threading.get_ident()는 현재 스레드 ID이다.
구글에 요청을 보내고 응답을 받을 때까지 기다림 → 응답을 받으면 애플로 넘어감 → 요청 → 기다림 → 응답 → ‥‥
[싱글 스레드에서 비동기 코드] → 0.9초 소요
import aiohttp
import time
import os
import asyncio
import threading
async def fetcher(session, url):
print(f"{os.getpid()} process | {threading.get_ident()} url: {url}")
async with session.get(url) as response:
return await response.text()
async def main():
urls = ["https://google.com", "https://apple.com"] * 50
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
result = await asyncio.gather(*[fetcher(session,url) for url in urls])
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start =time.time()
main()
end = time.time()
print(end - start)
구글에 요청 보냄 → await 통해 탈출 → 다른 코루틴 진입 (애플 코루틴)
→ 요청 보냄 → 탈출 → ‥‥ → 나중에 응답 받음
[멀티스레드에서 동기 코드] 동기적으로 코드를 작성하고 동시성 프로그래밍을 하려면 멀티스레딩을 사용하면 됨 → 시간 소요:4.2초
import requests
import time
import os
import threading
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def fetcher(params):
session = params[0]
url = params[1]
print(f"{os.getpid()} process| {threading.get_ident()} url: {url}")
with session.get(url) as response:
return response.text
def main():
urls = ["https://google.com", "https://apple.com"] * 50
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10)
with requests.Session() as session:
params = [(session, url) for url in urls]
results = list(executor.map(fetcher, params))
if __name__ == "__main__":
start = time.time()
main()
end = time.time()
print(end-start)max_workers는 최대 스레드 실행할 개수를 의미한다.
max_workers = 1이면 싱글스레드
max_workers >=2 이면 멀티스레딩이다.
▶ 스레드를 만들고 우선순위를 부여하는 것도 전부 다 연산과정이라 메모리 점유율이 많이 든다.

