예외란 프로그램 실행 중 발생할 수 있는 예상치 못한 에러이다.
모든 에러와 예외 클래스는 Throwable 클래스를 상속받는다.
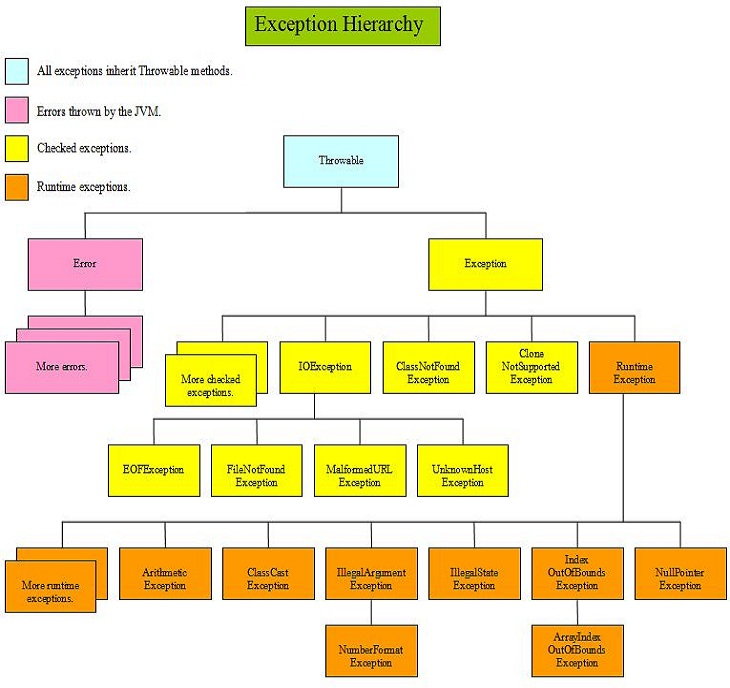
예외의 종류
Checked 예외
- 컴파일 시점에 체크
- 명시적인 예외 처리 필요
- 반드시 예외 처리(try/catch or throw)를 해야한다.
➡️ 안하게 되면 컴파일 에러 Exception클래스의 하위이면서RuntimeException클래스의 하위가 아님
ex)
FileNotFoundException
ClassNotFoundException
IOException
SQLException
NoSuchMetthodException
Unchecked 예외(RuntimeException)
- 런타임 시점에 체크
- 명시적인 예외 처리를 강제하지 않음
Exception클래스의 하위이며RuntimeException클래스의 하위이다.
ex)
ArithmeticException
NullPointerException
NumberFormatException
IndexOutOfBoundException
IllegalArgumentException
try / catch
기본적인 예외 처리 방법은 try / catch문을 쓰는 것이다.
예외가 발생할 수 있는 코드를 try 블록안에 작성 후
발생한 예외를 처리하는 코드를 catch 블록에 작성한다.
String str = "123";
try{
str.equals("111");
} catch (NullPointerException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch문에는 대비할 예외에 대한 알맞은 예외클래스를 아규먼트로 선언하여 예외 발생시 대비할 수 있다.
e.printStackTrace()는 예외 발생시 호출스택에 있던 메서드의 정보와 예외 메시지를 출력한다.
Throwable의 메서드이므로 모든 예외 클래스가 사용가능한 메서드이다.
finally
예외 발생 여부와 상관없이 실행되는 코드블록이다.
에러 발생 이후 프로그램을 종료해야 할 때 종료 전 처리해야할 프로세스를 진행할 수 있다.
주로 자원 해제와 같은 정리 작업에 활용한다.
try {
String str = br.readLine();
bw.write(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
bw.close();
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}IOException이 발생하여 프로그램이 종료 되더라도 finally 블럭안의 bw.close() br.close()가 실행되어 안전하게 자원이 해제될 수 있다.
하지만 이렇게 자원을 해제하게 되면 코드가 지저분해보인다.
try - with - resources
자동 자원 반환을 지원 AutoClosable 인터페이스 구현 객체
try(파일을 열거나 자원을 할당하는 명령어){
...
}괄호 안의 열린 파일이나 할당된 자원은 try 스코프를 벗어나면 자동으로 close()가 호출된다. 그 이후 catch 또는 finally가 실행된다.
try (BufferedReader br1 = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in))) {
String str = br1.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}자원이 자동으로 해제되어, 해제코드를 넣지 않았기 때문에 위의 finally 예시보다 코드가 간결해졌다.
throw / throws
throw
throw 키워드는 예외를 강제로 발생시킬 수 있다.
throw new RuntimeException("에러 발생");모든 예외 클래스는 Throwable을 상속 받으며 Throwable의 생성자중 하나는 아래와 같다.
Throwable(String message){
fillInstackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
}그리고 예외 발생시 이 detailMessage를 출력하기 때문에 개발자가 직접 에러메시지를 설정할 수 있다.
즉, 위에서 throw한 에러는 아래와 같이 나타난다.

throw를 할 때는 예외 또한 클래스임을 잊지말고 new로 생성해주자
throws
throws는 현재 위치에서 예외를 처리하지 않고 호출한 곳으로 예외 처리를 전가 시키는 것이다.
public void foo() throws IOException { }throws는 메서드의 선언부 끝에 작성된다.
public static void aaa(){
try{
throw new IOException("I/O exception");
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void bbb(){
try{
throw new ClassNotFoundException("class not found exception");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}위처럼 checked 예외를 발생시키는 메서드는 try - catch문을 이용해 예외 처리를 해줘야한다.
하지만 throws를 사용해준다면
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
aaa();
bbb();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void aaa() throws IOException{
throw new IOException("I/O exception");
}
public static void bbb() throws ClassNotFoundException{
throw new ClassNotFoundException("clas not found exception");
}위처럼 각 메서드마다 예외를 따로 처리하지 않고 메서드를 호출하는 곳에서 예외처리를 진행해준다.
main 메서드에
throwsException을 하게되면 예외처리를 JVM에 넘기는 것이다.
✨tip
- 구체적인 예외 처리를 우선
- 필요 이상의 예외는 던지지 않기
- 예외 메시지에 오류 분석에 도움이 되는 정보를 포함시켜야함
- 공통 예외 처리 로직은 별도 메서드로 정리
- 자원을 사용하는 경우 finally 보다 try - with - resource 권장
- Checked 예외가 단순히 발생할 수 있다는 것만으로도, 이를 어떻게 처리할지 명확히 해두는 것이 중요하므로 반드시 예외처리를 해준다.
