문제
[문제4] 사용자 입력을 받는 프롬프트에 현재 작업중인 폴더(디렉토리)의 경로를 표시하는 예제의 코드를 완성하세요.
[예제ConsoleEx4.java]
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class ConsoleEx4 {
static String[] argArr; // 입력한 매개변수를 담기위한 문자열배열
static LinkedList q = new LinkedList(); // 사용자가 입력한 내용을 저장할 큐(Queue)
static final int MAX_SIZE = 5; // Queue에 최대 5개까지만 저장되도록 한다.
static File curDir; // 현재 디렉토리
static {
/*
다음의 코드를 완성하세요.
1. 시스템속성 "user.dir"값을 읽어서 File객체를 만들고, curDir에 할당하세요.
2. 1의 코드를 간단히 예외처리하세요.
*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); // 한번만 생성해서 재사용하면 되므로 반복문 밖으로 이동
while(true) {
try {
String prompt = curDir.getCanonicalPath() + ">>";
System.out.print(prompt);
// 화면으로부터 라인단위로 입력받는다.
String input = s.nextLine();
save(input);
input = input.trim(); // 입력받은 값에서 불필요한 앞뒤 공백을 제거한다.
argArr = input.split(" +");
String command = argArr[0].trim();
if("".equals(command)) continue;
command = command.toLowerCase(); // 명령어를 소문자로 바꾼다.
if(command.equals("q")) { // q 또는 Q를 입력하면 실행종료한다.
System.exit(0);
} else if(command.equals("history")) {
history();
} else {
for(int i=0; i < argArr.length;i++) {
System.out.println(argArr[i]);
}
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("입력오류입니다.");
}
} // while(true)
} // main
public static void save(String input) {
if(input==null || "".equals(input)) return;
q.add(input); // queue에 저장한다.
// queue의 최대크기를 넣으면 제일 오래된 저장값을 삭제한다.
if(((LinkedList)q).size() > MAX_SIZE)
q.remove();
}
public static void history() {
int i=0;
// LinkedList의 내용을 보여준다.
ListIterator it =q.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(++i+"."+it.next());
}
}
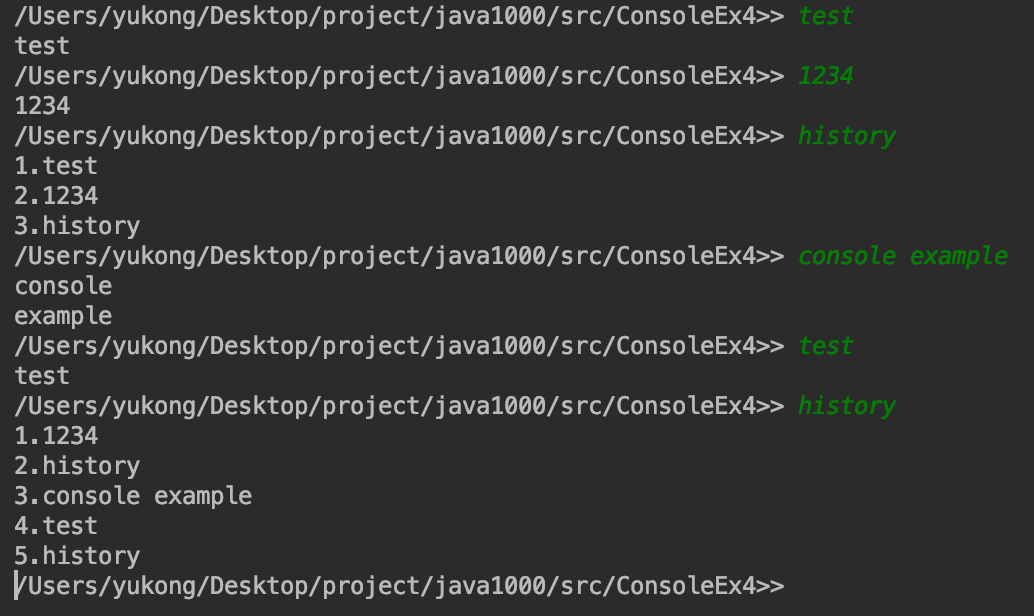
} // class[실행결과] - 현재 작업중인 폴더가 C:\java1000\work\Console일 경우
C:\java1000\work\Console>>history
1.history
C:\java1000\work\Console>>hello
hello
C:\java1000\work\Console>>q
https://cafe.naver.com/javachobostudy/24693
나의 풀이
문제에서 간단한 예외처리를 하라고 하였으나 어떤 것을 예외처리해야하는지 모르겠어서 일단 넘겼다. 현재 실행중인 디렉토리의 경로를 알기 위해 System.getProperty() 메소드를 이용하였다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.io.*;
class ConsoleEx4 {
static String[] argArr; // 입력한 매개변수를 담기위한 문자열배열
static LinkedList<String> q = new LinkedList<String>(); // 사용자가 입력한 내용을 저장할 큐(Queue)
static final int MAX_SIZE = 5; // Queue에 최대 5개까지만 저장되도록 한다.
static File curDir; // 현재 디렉토리
static {
curDir = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); // 한번만 생성해서 재사용하면 되므로 반복문 밖으로 이동
while(true) {
try {
String prompt = curDir.getCanonicalPath() + ">> ";
System.out.print(prompt);
String input = s.nextLine();
save(input);
input = input.trim(); // 입력받은 값에서 불필요한 앞뒤 공백을 제거한다.
argArr = input.split("\\s+");
String command = argArr[0].trim();
if("".equals(command)) continue;
command = command.toLowerCase(); // 명령어를 소문자로 바꾼다.
if(command.equals("q")) { // q 또는 Q를 입력하면 실행종료한다.
System.exit(0);
} else if(command.equals("history")) {
history();
} else {
for(int i=0; i < argArr.length;i++) {
System.out.println(argArr[i]);
}
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("입력오류입니다.");
}
}
}
public static void save(String input) {
if(input==null || "".equals(input)) return;
q.add(input);
if (q.size() > MAX_SIZE) {
q.remove();
}
}
public static void history() {
int i=0;
ListIterator it = q.listIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(++i + "." + it.next());
}
}
}
저자 풀이
답을 알기 위해 5번 문제를 가져왔다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
class ConsoleEx5 {
static String[] argArr; // 입력한 매개변수를 담기위한 문자열배열
static LinkedList q = new LinkedList(); // 사용자가 입력한 내용을 저장할 큐(Queue)
static final int MAX_SIZE = 5; // Queue에 최대 5개까지만 저장되도록 한다.
static File curDir;
static {
try {
curDir = new File(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
} catch(Exception e) {}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); // 한번만 생성해서 재사용하면 되므로 반복문 밖으로 이동
while(true) {
try {
String prompt = curDir.getCanonicalPath() + ">>";
System.out.print(prompt);
// 화면으로부터 라인단위로 입력받는다.
String input = s.nextLine();
save(input);
input = input.trim(); // 입력받은 값에서 불필요한 앞뒤 공백을 제거한다.
argArr = input.split(" +");
String command = argArr[0].trim();
if("".equals(command)) continue;
command = command.toLowerCase(); // 명령어를 소문자로 바꾼다.
if(command.equals("q")) { // q 또는 Q를 입력하면 실행종료한다.
System.exit(0);
} else if(command.equals("history")) {
history();
} else if(command.equals("dir")) {
dir();
} else {
for(int i=0; i < argArr.length;i++) {
System.out.println(argArr[i]);
}
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("입력오류입니다.");
}
} // while(true)
} // main
public static void save(String input) {
if(input==null || "".equals(input)) return;
q.offer(input); // queue에 저장한다.
// queue의 최대크기를 넣으면 제일 오래된 저장값을 삭제한다.
if(((LinkedList)q).size() > MAX_SIZE)
q.remove();
}
public static void history() {
int i=0;
// LinkedList의 내용을 보여준다.
LinkedList tmp = (LinkedList)q;
ListIterator it = tmp.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(++i+"."+it.next());
}
}
public static void dir() {
String pattern = "";
switch(argArr.length) {
case 1 : // dir만 입력한 경우 현재 디렉토리의 모든 파일과 디렉토리를 보여준다.
/*
다음의 코드를 완성하세요.
1. 반복문을 이용해서 현재디렉토리의 모든 파일의 목록을 출력한다.(File클래스의 listFiles()사용)
2. 조건문을 같이 사용해서 디렉토리(폴더)인 경우, 이름의 앞뒤에 '[' 와 ']'를 붙여서 출력한다.
(File클래스의 isDirectory()를 사용해서 체크)
' */
break;
case 2 : // dir과 패턴을 같이 입력한 경우, 예를 들면 dir *.class
pattern = argArr[1];
pattern = pattern.toUpperCase(); // 패턴에서 대소문자를 구별하지 않도록 대문자로 변경한다.
/*
다음의 코드를 완성하세요.
1. 입력된 패턴(pattern)을 정규식 표현(Regular Expression)에 알맞게 치환한다.
String클래스의 String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement)를 사용하자.
예를 들면, pattern = pattern.replace("A","AA")는 pattern의 "A"를 "AA"로 치환한다.
2. 반복문을 이용해서 현재 디렉토리 중, 입력된 패턴과 일치하는 것들만 출력한다.
이때, 조건문을 같이 사용해서 디렉토리(폴더)인 경우, 이름의 앞뒤에 '[' 와 ']'를 붙여서 출력한다.
(File클래스의 isDirectory()를 사용해서 체크)
대소문자구별을 하지 않기 위해서, 패턴과 마찬가지로 파일이나 디렉토리명을 대문자로 변경해야한다.
String tmp = f.getName().toUpperCase();
*/
break;
default :
System.out.println("USAGE : dir [FILENAME]");
} // switch
} // dir()
} // class