👉 전체코드보기
많은 참고가 되었던 포스팅입니다.
https://lamarr.dev/codingtest/2020/04/14/01-stack_postfix_notation.html
💡 결과물
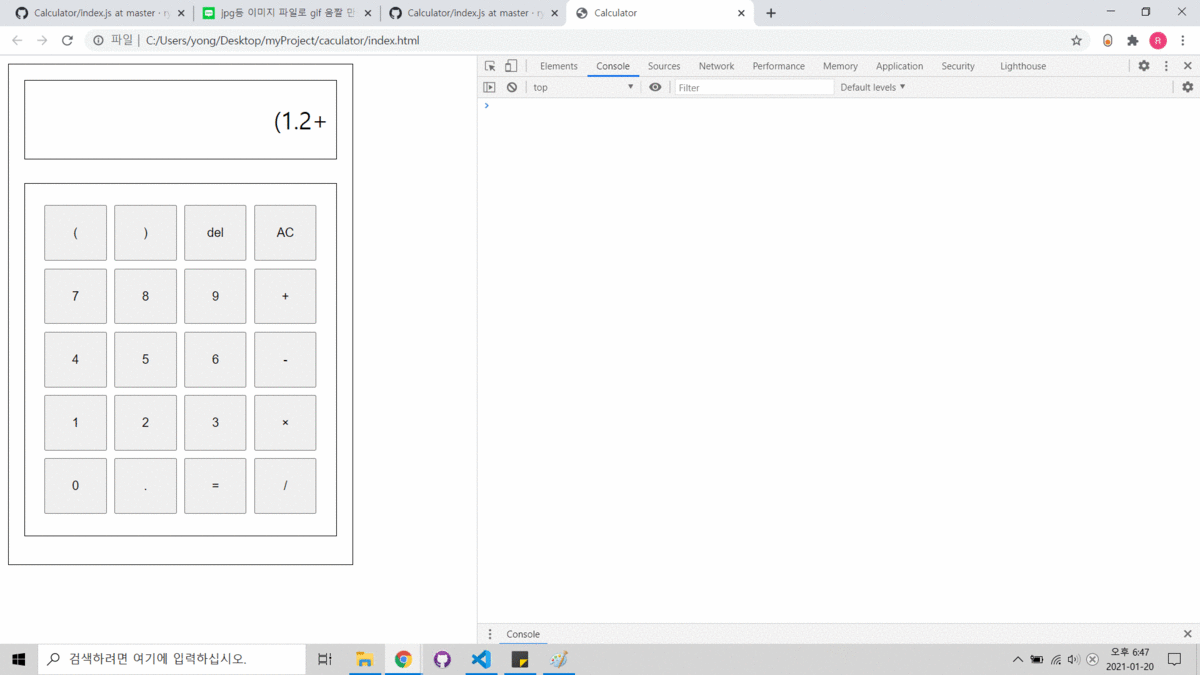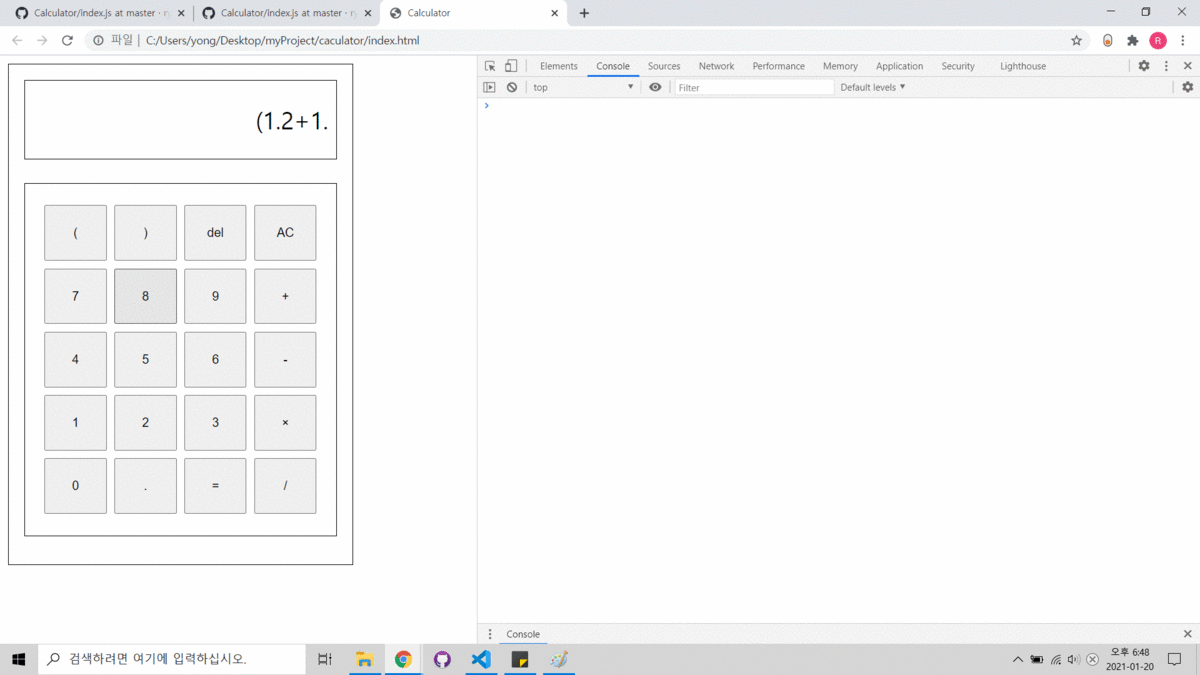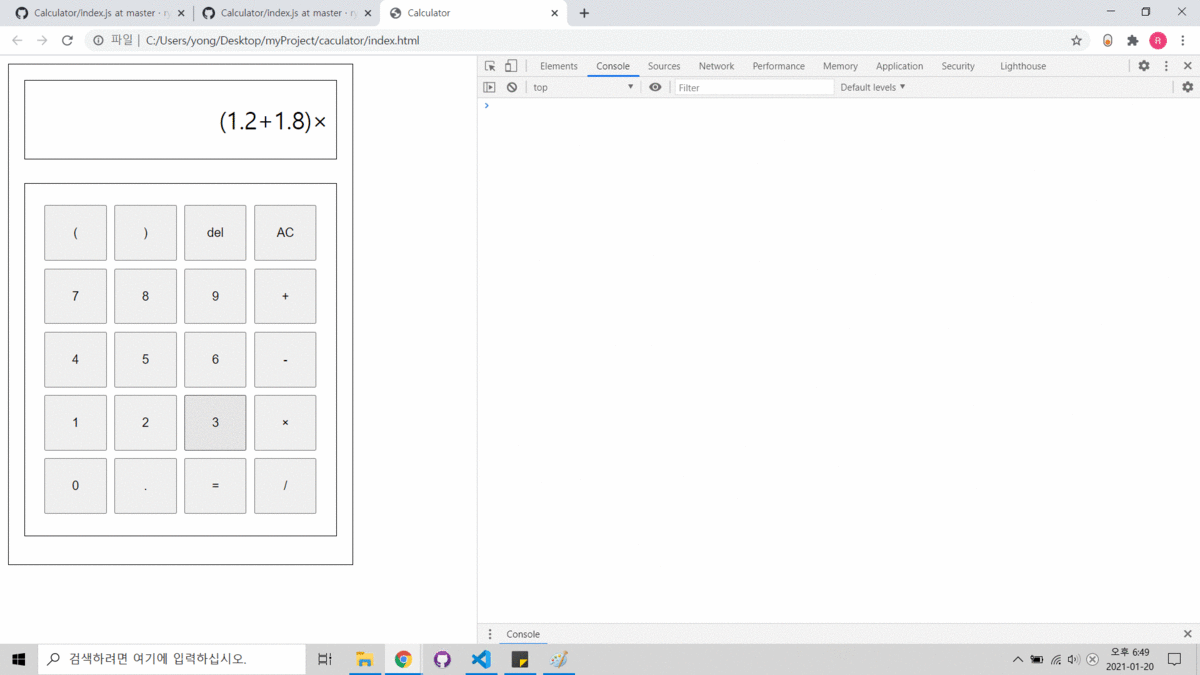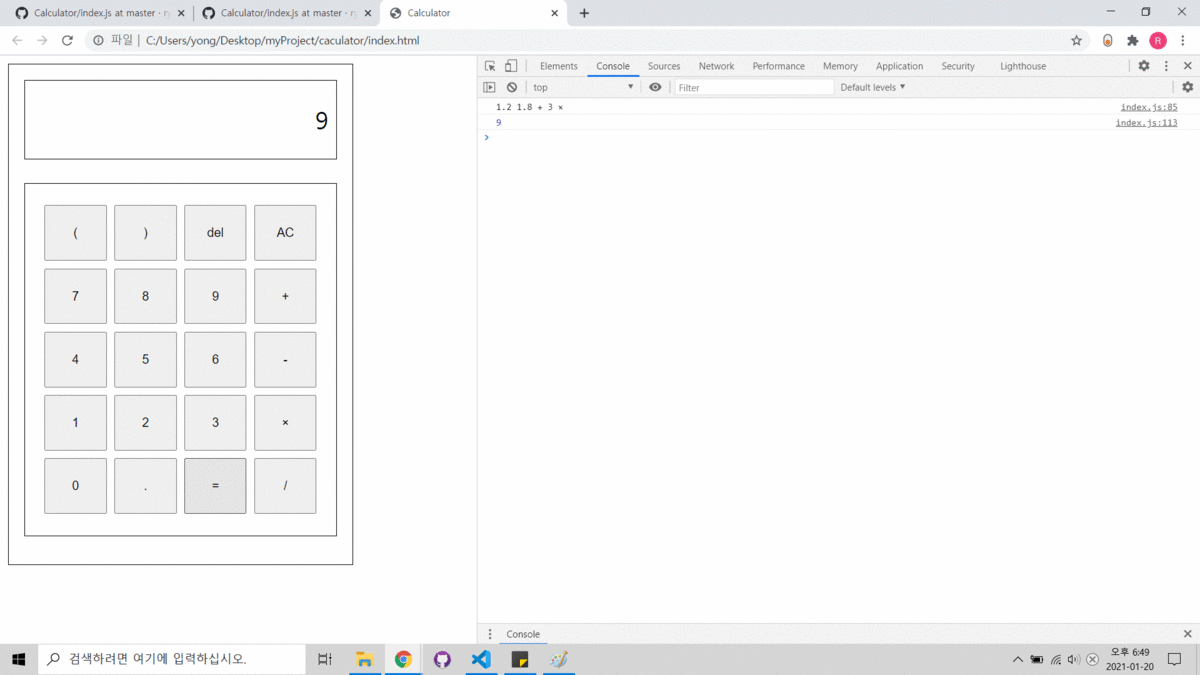
- Html, CSS, JS를 사용하였습니다.
Console에 변환된 후위표기식과 결과를 출력합니다.
📌 연산자 우선순위설정
우선순위 : (, ) > ×,÷ > +,-
function prec(op) {
switch(op) {
case '(':
case ')':
return 0;
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '×':
case '/':
return 2;
}
return 999;
}이 함수는 입력받은 식을 계산할 때 사용됩니다.
📌 후위표기법 변환
중위표기식(infix) → 후위표기식(postfix) 변환
- 연산자, 피연산자의 자료형은 모두
string이므로charAT함수를 활용합니다. - 자료구조 Stack 과
push(),pop()함수를 활용합니다.
infix ) 1 + 2
👉 1 2 +
- 피연산자는 그대로
console.log() - 연산자는 Stack에
push()
infix ) 1 + 2 * 3
👉 1 2 3 * +
- Stack 안의 연산자들의 우선순위를 비교합니다. 이때는
*의 우선순위가+보다 높으므로 그냥pop()을 합니다.
infix ) ( A + B ) * C + ( D + E )
👉 A B + C * D E + +
(는 무조건push()합니다.(,)는 출력하지 않습니다.
📌 code
let stack = [];
let convert = [];
let temp = ""; // 두자리수 이상의 숫자를 저장할 임시변수
function resultBtn(){
const f = resultScreen.textContent; //식
for(let i = 0; i<f.length; i++) {
const char = f.charAt(i);
switch(char) {
case '(' :
stack.push(char);
break;
case '+' : case '-' : case '×' : case '/' :
while(stack[stack.length - 1] != null &&
prec(char) <= prec(stack[stack.length - 1]) ){
convert.push(stack.pop());
}
stack.push(char);
break;
case ')' :
let returned_op = stack.pop();
while(returned_op != '('){
temp += returned_op;
returned_op = stack.pop();
if(isNaN(stack[stack.length - 1])){
convert.push(temp);
temp = "";
}
}
break;
default :
temp += char; // isNaN(f.charAt(i+1)) : 다음에 연산자가 나오면
if(isNaN(f.charAt(i+1)) || ( (i+1) == f.length )){
if(f.charAt(i+1) == '.'){ //소수점처리
continue;
} else {
convert.push(temp);
temp="";
}
}
break;
}
}
while(stack[stack.length - 1] != null){
convert.push(stack.pop());
}
//후위표기식 숫자와 연산자는 convert에 모두 담기게 됨.
// 후위표기식 출력코드
let result = "";
for(let i in convert){
result += convert[i];
result += " ";
}
console.log(result);
// 후위표기식 계산
for(let i in convert){
if(!isNaN(convert[i])){
stack.push(convert[i]);
} else{
const b = parseFloat(stack.pop());
const a = parseFloat(stack.pop());
switch(convert[i]){
case '+' : stack.push(a+b);
break;
case '-' : stack.push(a-b);
break;
case '×' : stack.push(a*b);
break;
case '/' : stack.push(a/b);
break;
}
}
}
console.log(+stack); //최종적으로 stack에 남아있는 값이 계산결과
resultScreen.innerText = +stack;
}
