에러 처리
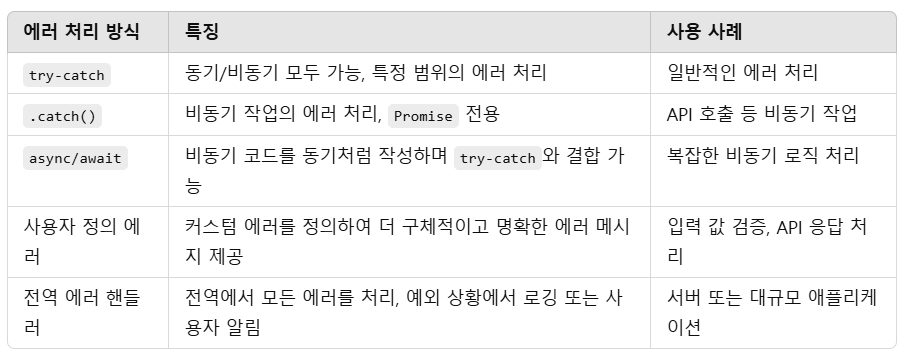
에러 종류
- 기본 에러 종류
Error: 기본 에러 객체. 모든 에러의 부모.SyntaxError: 문법 오류.ReferenceError: 존재하지 않는 변수를 참조할 때 발생.TypeError: 변수나 값의 타입이 유효하지 않을 때 발생.RangeError: 숫자 범위가 허용되지 않을 때 발생.URIError: decodeURI 또는 encodeURI 함수 사용 시 잘못된 URI가 제공될 때 발생.
- 사용자 정의 에러
- 필요에 따라 커스텀 에러를 정의하여 더 구체적인 에러 처리가 가능.
동기 코드에서의 에러 처리
try-catch 구조
try-catch는 에러를 감지하고 처리할 수 있는 기본 구조
try {
// 에러가 발생할 수 있는 코드
throw new Error("Something went wrong");
} catch (error) {
// 에러 처리
console.error("Caught an error:", error.message);
} finally {
// 항상 실행되는 블록 (선택적)
console.log("This runs no matter what.");
}- 에러는 명시적으로 throw를 사용하거나, 런타임 중 자연스럽게 발생할 수 있음.
- throw 뒤에는 문자열, 객체, Error 객체를 전달할 수 있음.
try {
throw new TypeError("Invalid type provided");
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.name); // TypeError
console.log(error.message); // Invalid type provided
}비동기 코드에서의 에러 처리
Promise와 .catch()
Promise에서 에러는 reject를 호출하거나 함수 내부에서 throw로 발생시킬 수 있음.
const asyncOperation = () =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error("Async error occurred"));
}, 1000);
});
asyncOperation()
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((error) => console.error("Caught error:", error.message));async/await와 try-catch
async/await를 사용하면 비동기 코드도 동기 코드처럼 try-catch로 에러를 처리할 수 있음.
const fetchData = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch("invalid-url");
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error during fetch:", error.message);
}
};
fetchData();사용자 정의 에러
사용자 정의 에러 생성
Error 클래스를 상속받아 특정 목적에 맞는 에러를 정의할 수 있음.
class ValidationError extends Error {
constructor(message) {
super(message);
this.name = "ValidationError";
}
}
try {
throw new ValidationError("Invalid data format");
} catch (error) {
console.error(`${error.name}: ${error.message}`); // ValidationError: Invalid data format
}정리