오늘은 Serialize에 대해 글을 작성하려고 합니다.
한글로는 직렬화입니다.
Sericalize(직렬화)
- 객체를 파일 등에 저장하거나 네트워크로 전송하기 위해 연속적인 데이터로 변환하는 것
- 반대의 경우는 역 직렬화(deserializatin)
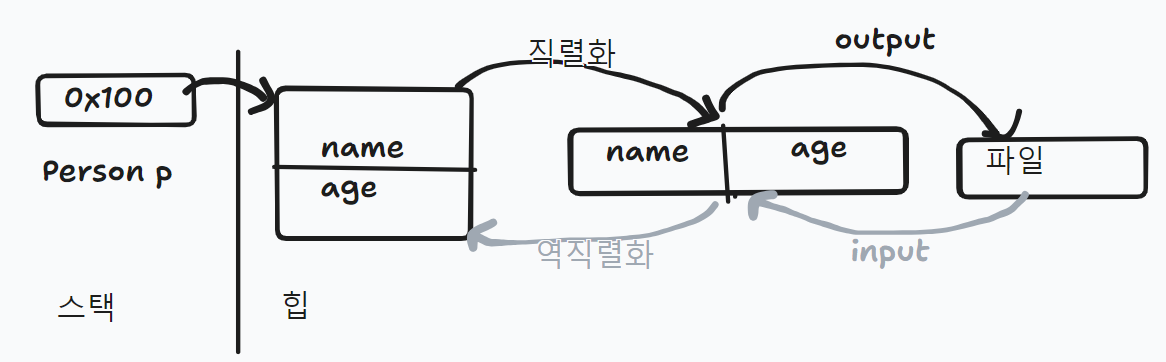
- 이렇게 그림처럼 내용을 연속적인 데이터로 변환하는 것을 직렬화라고 한다.
- 자바에서 직렬화를 하기 위해서는 Serializable 인터페이스를 구현해야만 한다. ex)
class Person implements Serializable - 직렬화에서 제외하려면 transiendt를 선언하면 된다. ex)
private transient int age;
직렬화 대상 클래스
ObjectOutputSteram()
- 객체를 직렬화 해서 출력하는 stream
- 출력하려는 객체가 Serializable 인터페이스를 구현 받지 않은 경우 Exception 발생
- static, transient 로 선언된 속성 정보는 출력되지 않는다.
ObjectInputStream()
- byte 배열 정보를 읽어서 해당 클래스의 객체로 복원
- transient 로 선언된 속성은 기본 값으로 복원
- static 으로 선언된 속성은 복원하는 쪽 JVM에 설정된 값으로 복원된다.
예제
public class ObjectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String file ="object.txt";
try(ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
oos.writeObject(new Employee("1","va",100000000));
Employee.salary = 5000000;
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}public class Employee implements Cloneable, Serializable{
private String empno;
private String ename;
public static int salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String empno, String ename, int salary) {
this.empno = empno;
this.ename = ename;
this.salary = salary;
}
}결과는

object.txt는

이렇게 연속적인 데이터로 파일에 저장이 된다.
어디에 사용하니?
근데 이걸 꼭 직렬화를 해야할까?
어디에서 사용되고 있을까?
직렬화: JVM의 힙(heap) 혹은 스택(stack) 메모리에 상주하고 있는 객체 데이터를 직렬화를 통해 바이트 형태로 변환하여 데이터베이스나 파일과 같은 외부 저장소로 저장해둔다.
역직렬화: 다른 컴퓨터에서 이 파일을 가져와 역직렬화를 통해 자바 객체로 변환해서 JVM 메모리에 적재한다.
직렬화를 응용한다면 휘발성이 있는 캐싱 데이터를 영구 저장이 필요할 때 사용할 수 있다.
서블릿 세션(Servlet Session)
- 단순히 세션을 서블릿 메모리 위에서 운용한다면 직렬화를 필요로 하지 않지만, 만일 세션 데이터를 저장, 공유가 필요할 때 직렬화를 이용한다.
- 세션 데이터를 데이터베이스에 저장할 때
- 톰캣의 세션 클러스터링을 통해 각 서버 간에 데이터 공유가 필요할 때
캐시(Cache)
- 데이터베이스로부터 조회한 객체 데이터를 다른 모듈에서도 필요할 때 재차 DB를 조회하는 것이 아닌, 객체를 직렬화하여 메모리나 외부 파일에 저장해두었다가 역직렬화하여 사용하는 캐시 데이터로서 이용이 가능하다.
- 물론 자바 직렬화를 이용해서만 캐시를 저장할 수 있는 것은 아니지만 자바 시스템에서만큼은 구현이 가장 간편하기 때문에 많이 사용된다고 보면 된다.
- 단, 요즘은 캐시 DB를 많이 사용하는 편이다.
