1. Synchronization이 필요한 이유
멀티스레드 프로그램에서는 여러 thread가 동시에 실행된다.
이때 global variable, heap object, kernel data structure와 같은
shared resource에 동시에 접근하면 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
이러한 문제를 방지하기 위한 메커니즘이 바로 Synchronization이다.
핵심 목적:
한 시점에 오직 하나의 execution context만
critical code를 실행하도록 보장하는 것
2. Critical Section이란?
Critical Section이란 여러 thread 또는 execution context가
공유 자원에 접근하는 코드 영역을 의미한다.
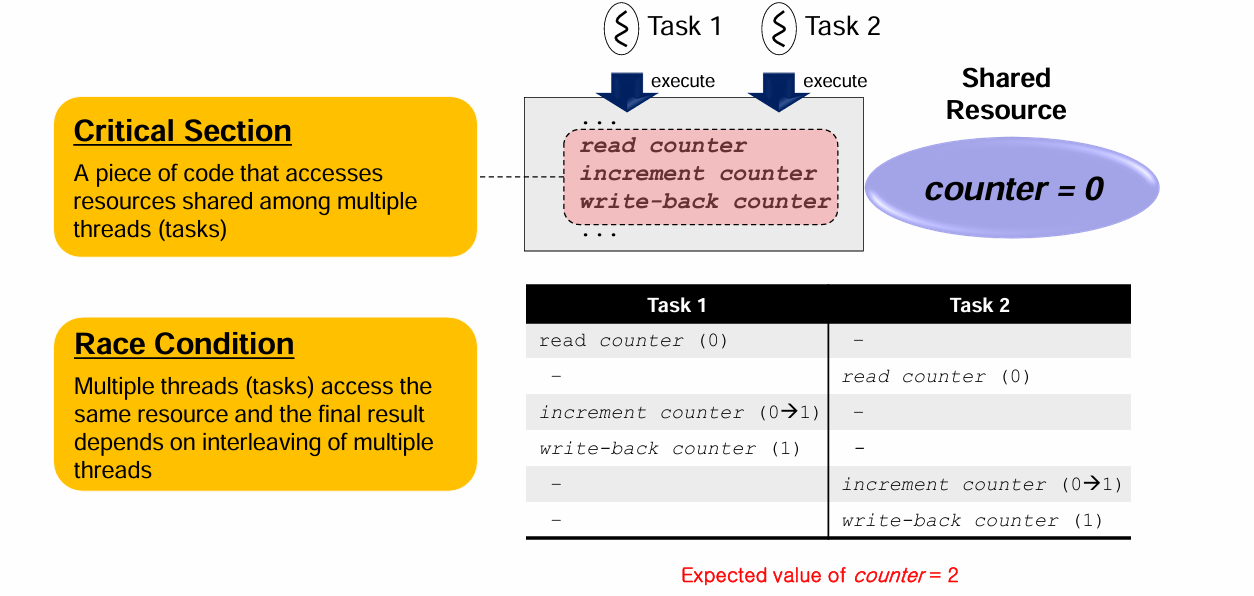
이 영역은 반드시 atomic하게 실행되어야 한다.
핵심 조건
- 한 시점에 only one thread
- 다른 thread는 wait
- 중간에 끼어들 수 없음 (no interleaving)
3. Critical Section의 일반적인 구조
do {
entry section // lock 획득
critical section // shared resource 접근
exit section // lock 해제
remainder section // 나머지 코드
} while (true);- entry section: critical section 진입 제어
- exit section: 다른 thread에게 기회 제공
- remainder section: 공유 자원과 무관한 코드
4. Sharing Resources
✅ Local variable (공유되지 않음)
- 각 thread는 자신만의 stack을 가짐
- local variable은 stack에 저장됨
void foo() {
int a = 0;
a++;
}👉 Synchronization 불필요
❌ Global variable (공유됨)
- data segment에 저장됨
- 모든 thread가 접근 가능
int i; // global variable👉 Critical Section 필요
❌ Dynamic object (공유됨)
- heap에 저장됨
- pointer를 통해 여러 thread가 공유
👉 Critical Section 필요
5. 왜 i++는 atomic하지 않은가?
int i;
void foo() {
i++;
}i++는 한 줄 코드지만 실제로는 다음 단계로 실행된다.
- memory에서
i값을 register로 load - register 값 increment
- 결과를 다시 memory에 store
👉 여러 instruction으로 구성
👉 atomic operation 아님
6. An Example of Critical Section
🟢 정상 동작하는 경우 (우연)
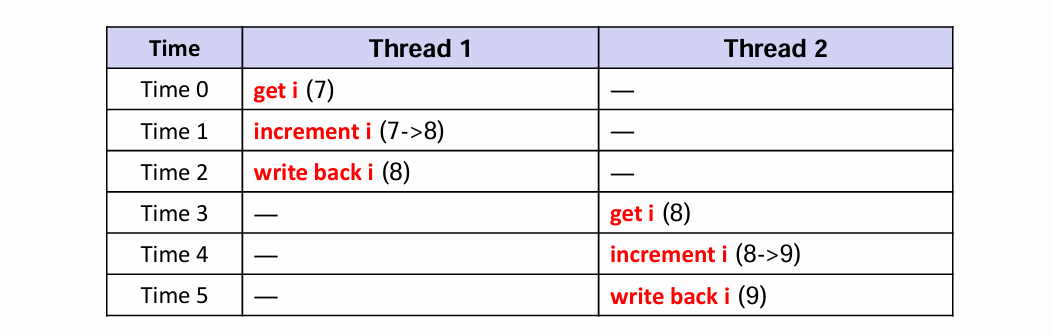
- 초기값:
i = 7 - Thread 1 실행 완료 후 Thread 2 실행
결과: i = 9
❌ Race Condition 발생

- 두 thread가 동시에
i = 7을 read - 각각 increment 후 write-back
결과: i = 8 (incorrect)
7. Linux Kernel에서의 Critical Section
Linux kernel에서는 단순히 thread만 고려하면 안 된다.
Kernel execution context
- process context
- interrupt context (ISR)
- kernel preemption
- multi-core execution
👉 kernel에서는 훨씬 더 많은 race scenario가 존재
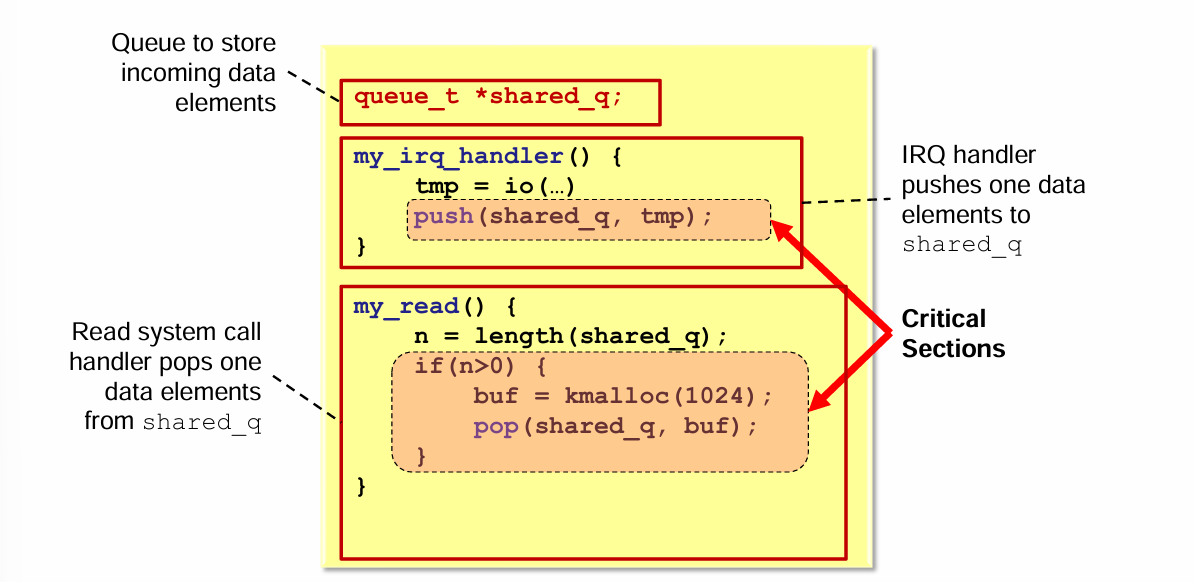
8. Linux Kernel Device Driver 예제
queue_t *shared_q;
my_irq_handler() {
tmp = io(...);
push(shared_q, tmp);
}
my_read() {
n = length(shared_q);
if (n > 0) {
buf = kmalloc(1024);
pop(shared_q, buf);
}
}shared_q는 shared resource- ISR과 system call handler가 동시에 접근
👉 push, pop, length 모두 critical section
9. Kernel에서의 Race Condition 시나리오
1️⃣ Interrupt
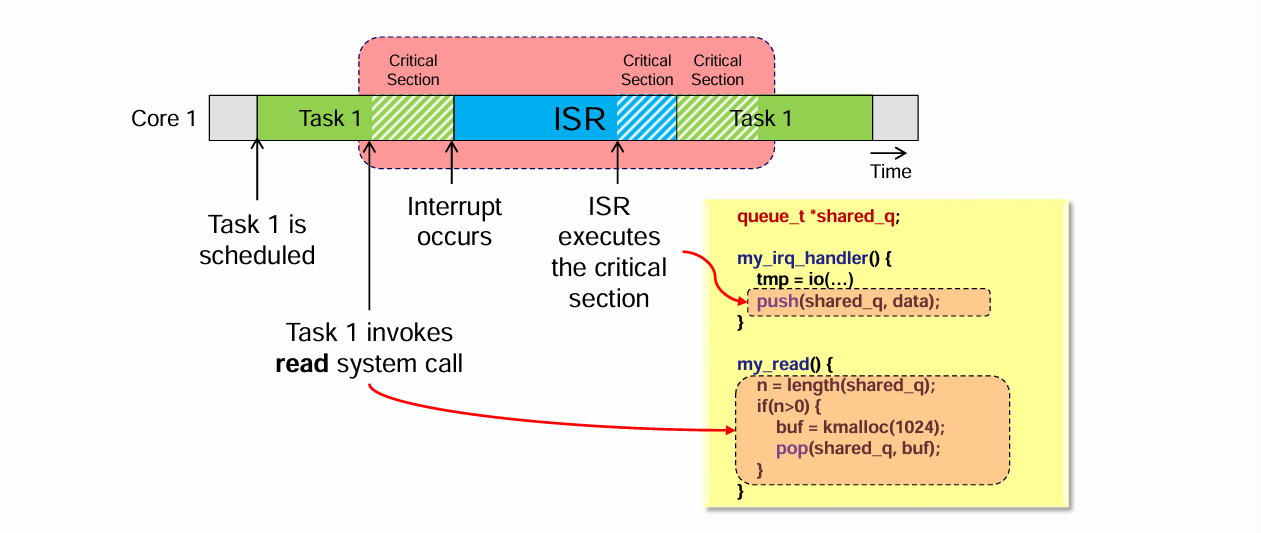
- task 실행 중 interrupt 발생
- ISR이 동일한 shared resource 접근
2️⃣ Kernel preemption
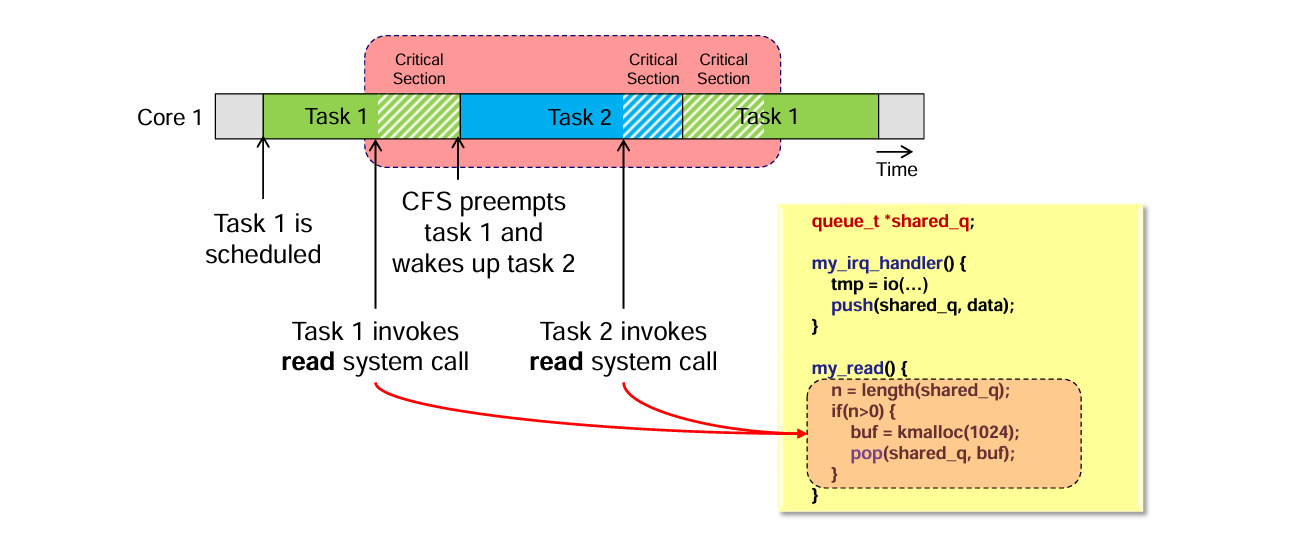
- scheduler가 task를 선점
- 다른 task가 같은 kernel code 실행
3️⃣ Sleeping
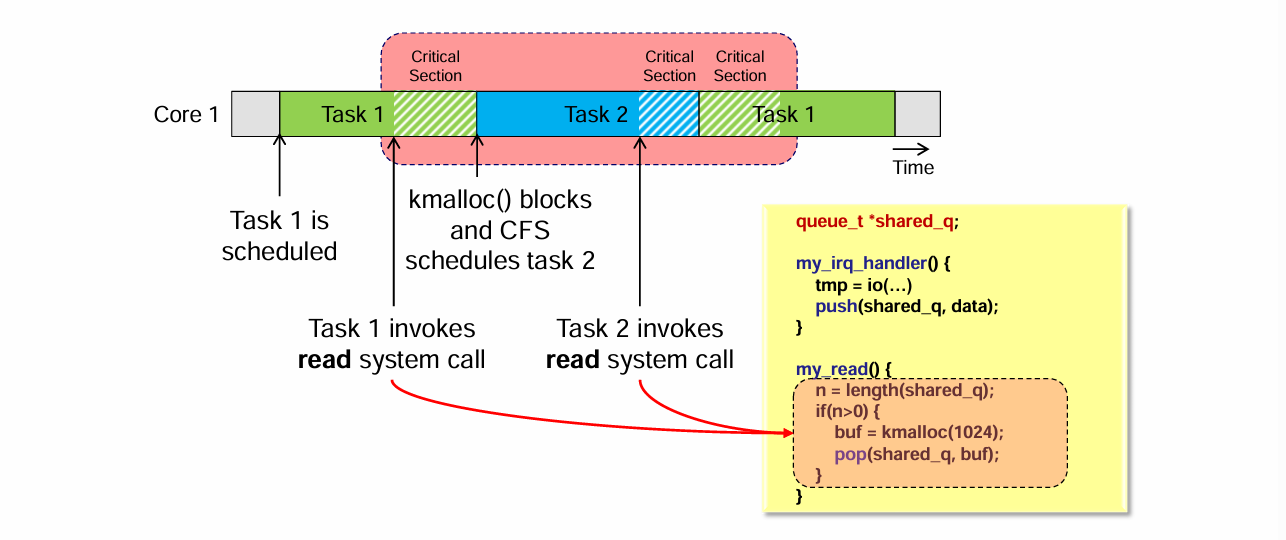
buf = kmalloc(1024); // sleep 가능- critical section 중 sleep 발생
- 다른 task가 실행됨
👉 상태 불일치 위험
10. 해결책
Single-core 환경
- preemption disable
- interrupt disable
Multi-core 환경
- atomic operation
- spinlock
- mutex
- semaphore
