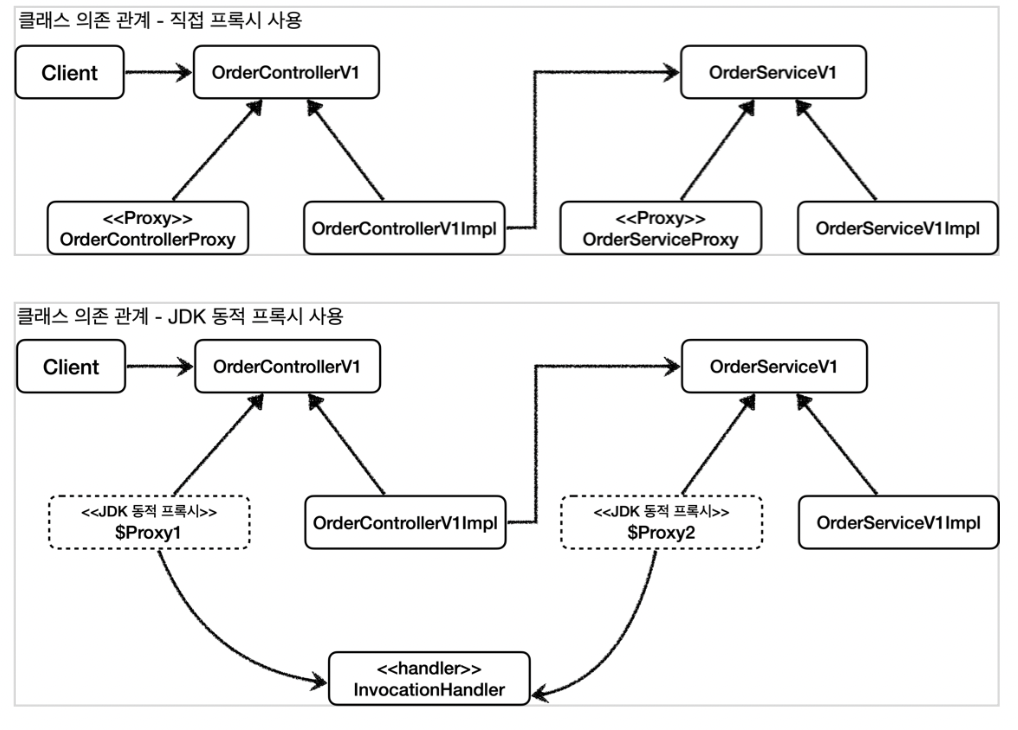
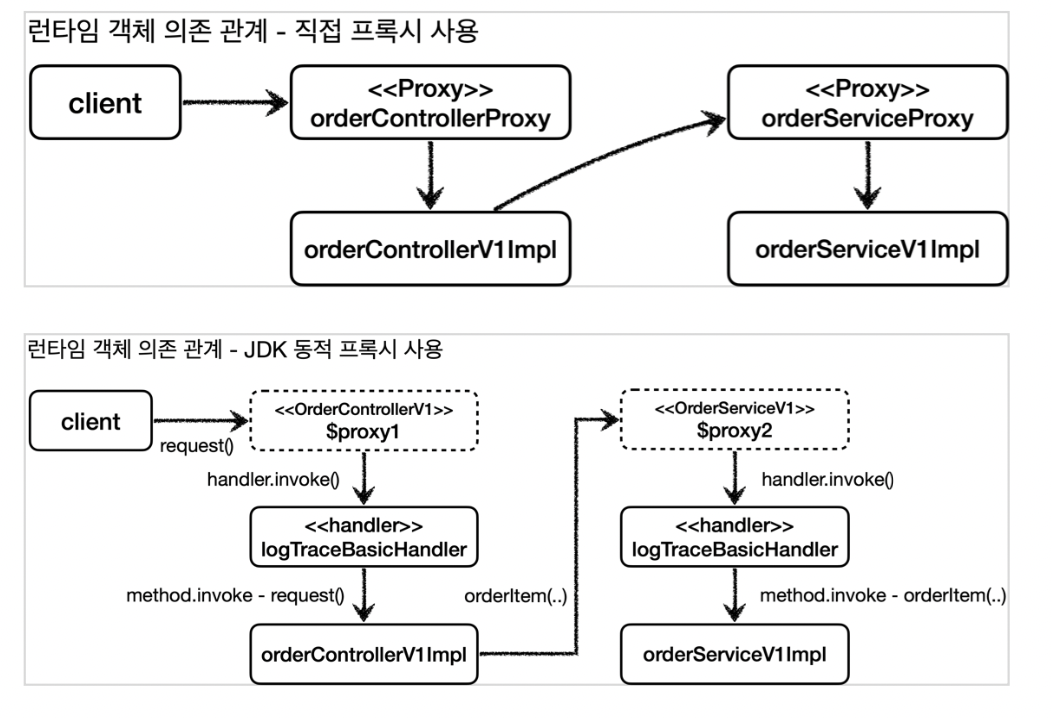
JDK 동적 프록시 기술은 개발자가 직접 프록시 클래스를 만들지 않고 런타임에 동적으로 생성되어 사용할 수 있습니다.
JDK 동적 프록시는 인터페이스를 기반으로 프록시를 동적으로 만들어준다.
따라서 인터페이스가 필수입니다.
AInterface
public interface AInterface {
String call();
}AImpl
@Slf4j
public class AImpl implements AInterface {
@Override
public String call() {
log.info("A 호출");
return "a";
}
}TimeInvocationHandler
@Slf4j
public class TimeInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
public TimeInvocationHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log.info("Time Proxy 실행");
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = method.invoke(target, args); //call
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("time->{}", endTime - startTime);
return result;
}
}Test Code
@Test
void dynamicA() {
//구현체 생성
AInterface target = new AImpl();
//핸들러 생성
TimeInvocationHandler handler = new TimeInvocationHandler(target);
//Proxy class 생성
AInterface proxyInstance = (AInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
AInterface.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{AInterface.class},
handler
);
//프록시 실행
proxyInstance.call(); //handler의 invoke가 실행되고 call이 넘어감
log.info("target class -> {}", target.getClass());
log.info("proxyInstance class -> {}", proxyInstance.getClass());
}실행 순서
- 클라이언트는 JDK 동적 프록시의 call() 을 실행한다.
- JDK 동적 프록시는 InvocationHandler.invoke() 를 호출한다.
TimeInvocationHandler 가 구현체로 있으로 TimeInvocationHandler.invoke() 가 호출된다.- TimeInvocationHandler 가 내부 로직을 수행하고, method.invoke(target, args) 를 호출해서 target 인 실제 객체( AImpl )를 호출한다.
- AImpl 인스턴스의 call() 이 실행된다.
- AImpl 인스턴스의 call() 의 실행이 끝나면 TimeInvocationHandler 로 응답이 돌아온다.
시간 로그를 출력하고 결과를 반환한다.
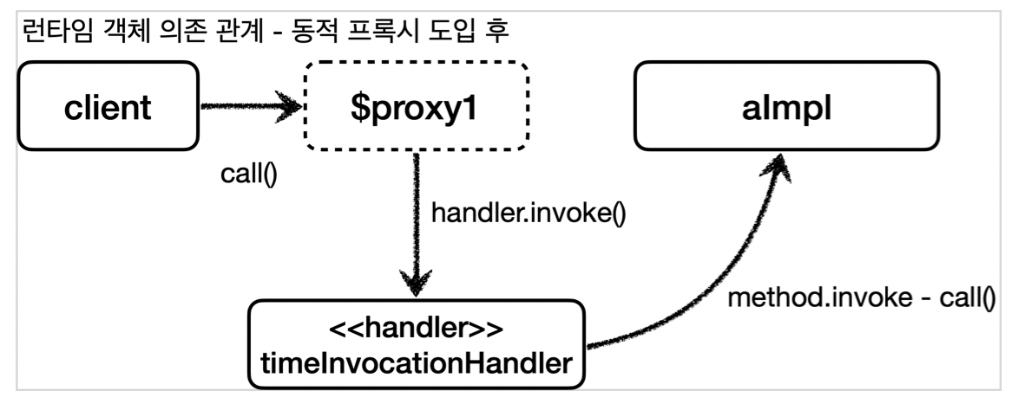
이로써 부가 기능 로직도 하나의 클래스에 모아서 단일 책임 원칙(SRP)도 지킬 수 있게 되었습니다.
reference : 김영한 선생님
