그래프를 탐색하는 방법 중 BFS(넓이 우선 탐색)와 DFS(깊이 우선 탐색) 두 가지를 비교 해보겠습니다.
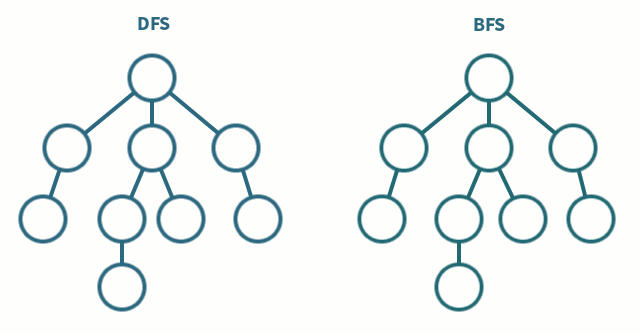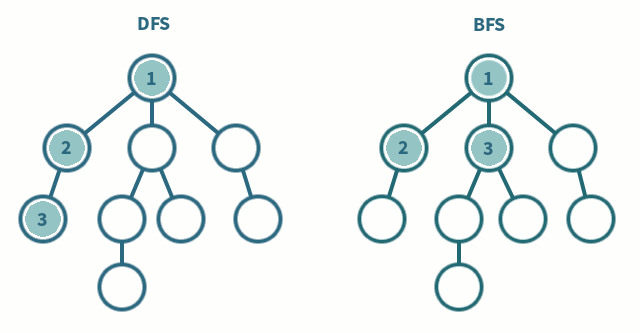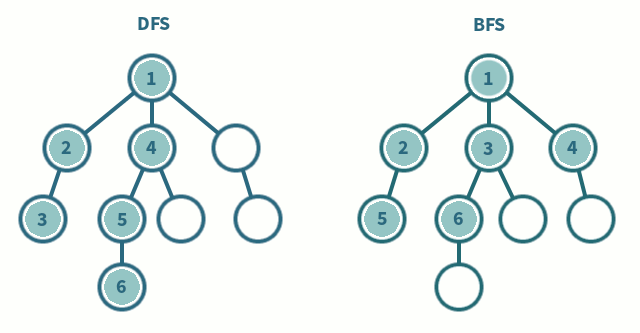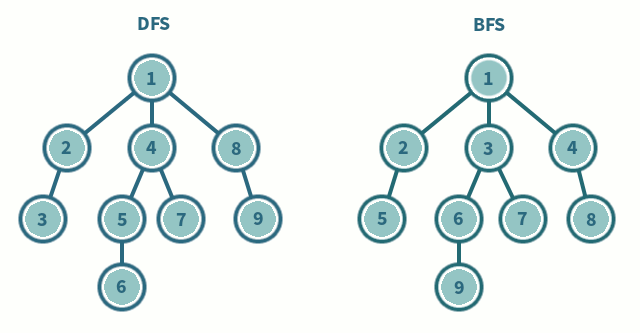
BFS - 루트를 시작으로 주변에 있는 정점들을 먼저 방문하는 방법으로 트리의 레벨 순회와 같습니다.
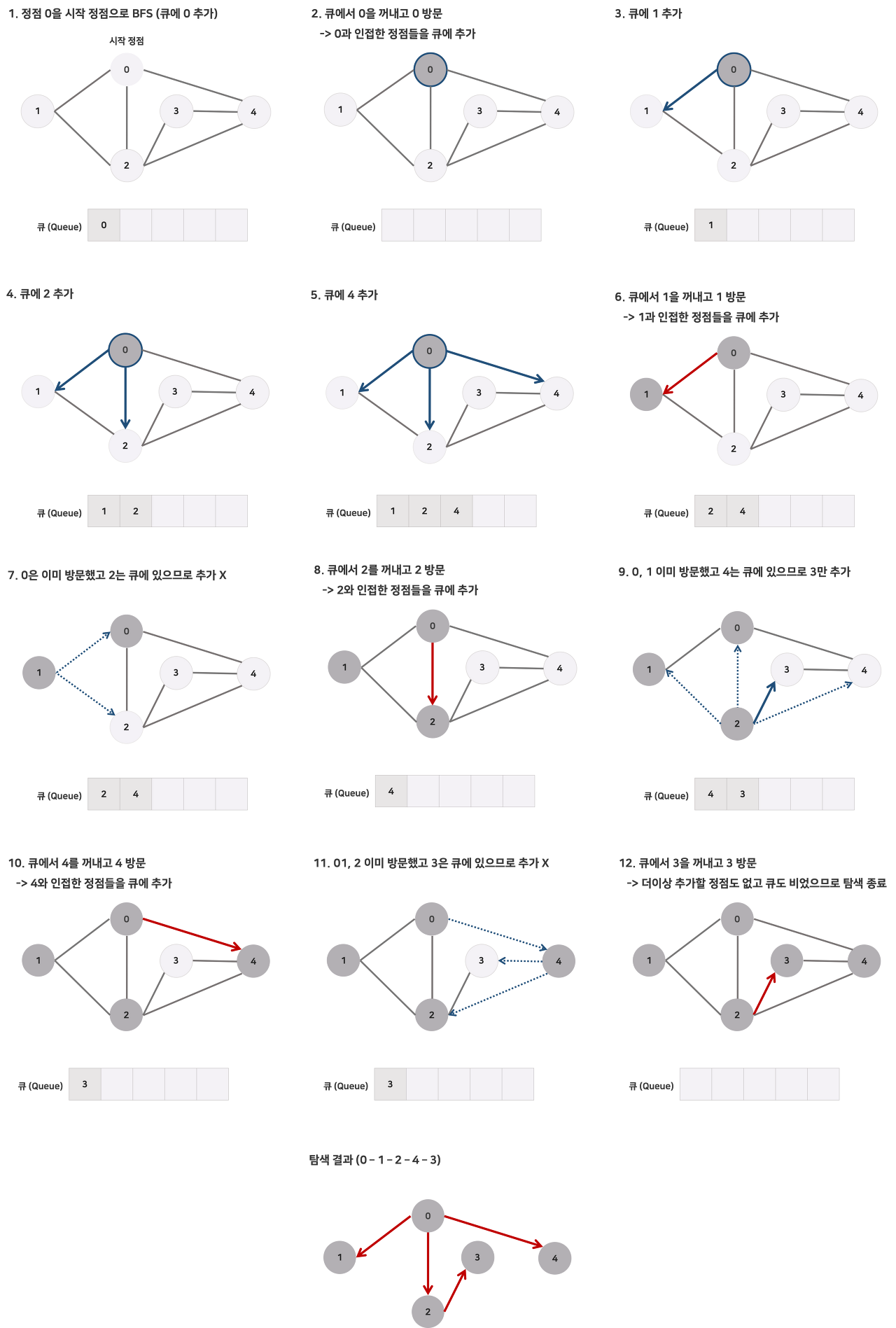
[출처] https://minhamina.tistory.com/36?category=837168
DFS - 한 번 갔던 방향으로 계속해서 정점들을 방문하는 방법으로 트리의 전위 순회와 같습니다.
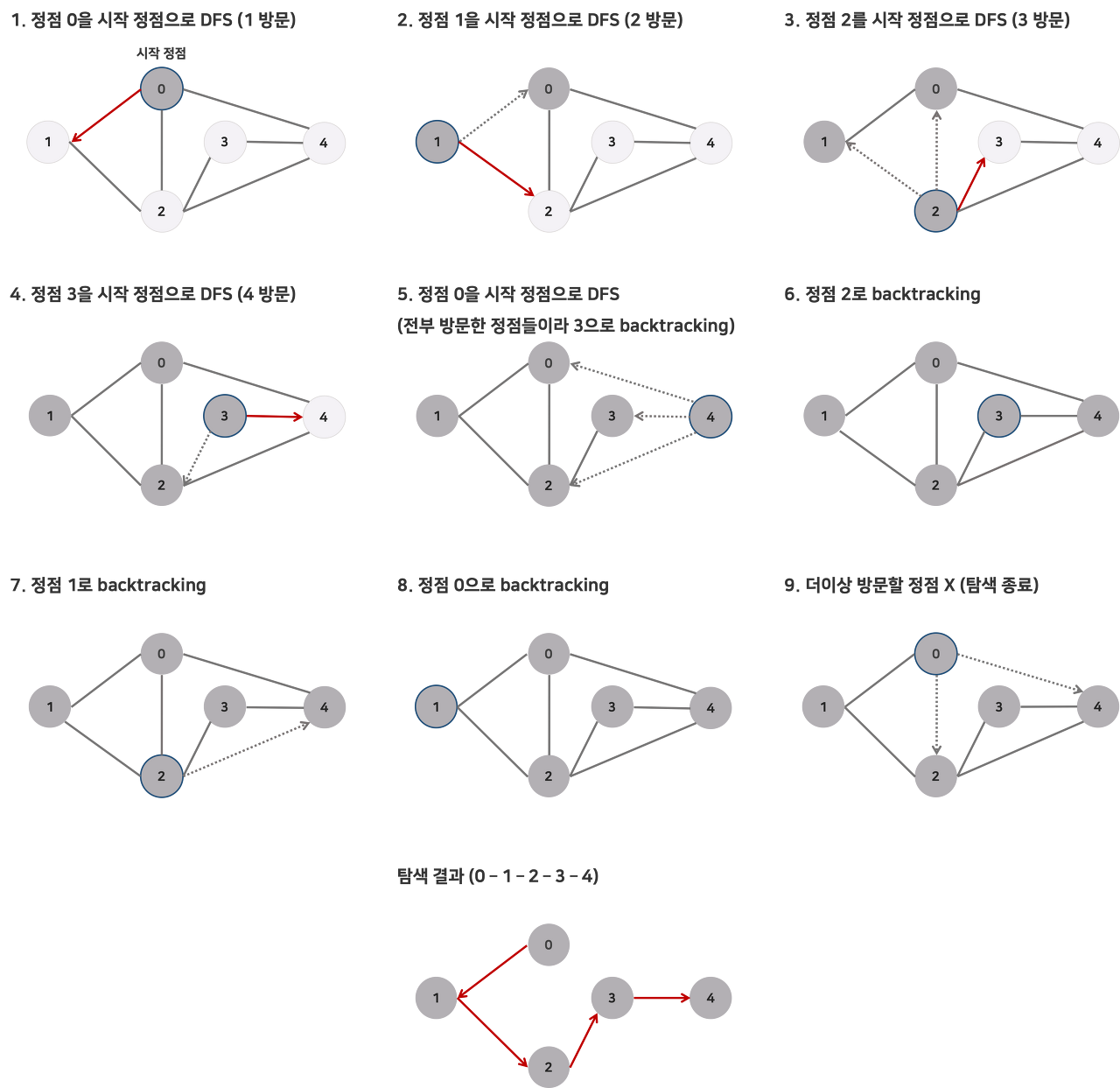
[출처] https://minhamina.tistory.com/22?category=837168
BFS 장단점
장점
- 너비를 우선으로 탐색하므로 답이 되는 경로가 여러 개인 경우에도 최단경로를 얻을 수 있다.
- 경로가 무한히 깊어져도 최단경로를 반드시 찾을 수 있다.
- 노드 수가 적고 깊이가 얕은 해가 존재할 때 유리하다.
단점
- DFS와 달리 큐를 이용하여 다음에 탐색할 정점들을 저장하기 때문에 더 큰 저장공간을 필요로 한다.
- 노드의 수가 늘어나면 탐색해야 하는 노드가 많아지기 때문에 비효율적이다.
DFS의 장단점
장점
- 현 경로상의 노드들만 기억하면 되기 때문에 저장공간 수요가 비교적 적다.
- 목표 노드가 깊은 단계에 있을 경우 해를 빨리 구할 수 있다.
단점
- 해가 없는 경로가 깊을 경우 탐색시간이 오래 걸릴 수 있다.
- 얻어진 해가 최단 경로가 된다는 보장이 없다.
- 깊이가 무한히 깊어지면 스택오버플로우가 날 위험이 있기 때문에 깊이에 제한을 줌으로써 이를 해결한다.
BFS vs DFS 정리
| BFS | DFS |
|---|---|
| 큐로 구현한다. | 스택 또는 재귀 함수로 구현한다. |
| 루트를 시작으로 주변에 있는 정점들을 먼저 방문한다. | 한 번 갔던 방향으로 계속해서 정점들을 방문한다. |
BFS vs DFS 코드 작성법
BFS
n: 정점의 수, e: 간선의 수
인접 리스트 : 리스트로 그래프의 연결 관계를 표현하는 방식 O(n+e)
인접 행렬 : 2차원 배열로 그래프의 연결 관계를 표현하는 방식 O(n^2)
1. 인접 리스트로 BFS 구현
import java.util.*;
public class BFS_List {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 개수
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 개수
int v = sc.nextInt(); // 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호
boolean visited[] = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 여부를 검사할 배열
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// 간선의 개수 만큼 반복, 입력으로 주어지는 간선은 양방향
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjList[v1].add(v2);
adjList[v2].add(v1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Collections.sort(adjList[i]); // 방문 순서를 위해 오름차순 정렬
}
System.out.println("[인접리스트 활용 BFS 큐로 구현]");
bfs_list(v, adjList, visited);
}
// 인접리스트를 활용한 BFS
public static void bfs_list(int v, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
visited[v] = true; // 방문 처리
queue.add(v); // 큐에 넣기
while(queue.size() != 0) {
v = queue.poll();
System.out.print(v + " ");
Iterator<Integer> iter = adjList[v].listIterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
int nextV = iter.next();
if(!visited[nextV]) {
visited[nextV] = true;
queue.add(nextV);
}
}
}
}
}[input]
5 5 3
5 4
5 2
1 2
3 4
3 1
[Output]
[인접리스트 활용 BFS 큐로 구현]
3 1 4 2 5 2. 인접 행렬로 BFS 구현
import java.util.*;
public class BFS_Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 개수
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 개수
int v = sc.nextInt(); // 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호
boolean visited[] = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 여부를 검사할 배열
int[][] adjArray = new int[n+1][n+1];
// 간선의 개수 만큼 반복, 입력으로 주어지는 간선은 양방향
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjArray[v1][v2] = 1;
adjArray[v2][v1] = 1;
}
System.out.println("[인접행렬 활용 BFS 큐로 구현]");
bfs_array(v, adjArray, visited);
}
// 인접행렬을 활용한 BFS
public static void bfs_array(int v, int[][] adjArray, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
int n = adjArray.length - 1;
q.add(v);
visited[v] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
v = q.poll(); // 큐에서 하나씩 꺼냄.
System.out.print(v + " ");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (adjArray[v][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
q.add(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}[input]
5 5 3
5 4
5 2
1 2
3 4
3 1
[Output]
[인접행렬 활용 BFS 큐로 구현]
3 1 4 2 5 DFS
구현 방법 2가지
- 재귀함수 활용
- 스택 활용
n: 정점의 수, e: 간선의 수
인접 리스트 : 리스트로 그래프의 연결 관계를 표현하는 방식 O(n+e)
인접 행렬 : 2차원 배열로 그래프의 연결 관계를 표현하는 방식 O(n^2)
1. 인접 리스트로 DFS 구현
import java.util.*;
public class DFS_List_Recursion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 개수
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 개수
int v = sc.nextInt(); // 시작 정점
boolean visited[] = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 여부 확인 배열
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// 간선의 개수 만큼 반복, 입력으로 주어지는 간선은 양방향
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjList[v1].add(v2);
adjList[v2].add(v1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 방문 순서는 작은거 우선적으로 큐에서 뽑기 위해 오름차순 정렬
Collections.sort(adjList[i]);
}
System.out.println("[인접리스트 활용 DFS 스택으로 구현]");
dfs_list_recursion(v, adjList, visited);
}
// 인접 리스트를 활용한 재귀문으로 구현
public static void dfs_list_recursion(int v, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, boolean[] visited) {
visited[v] = true; // 정점 방문 Check
System.out.print(v + " "); // 정점 출력
Iterator<Integer> iter = adjList[v].listIterator(); // 정점 인접리스트 순회
while (iter.hasNext()) {
int nextV = iter.next();
if (!visited[nextV]) // 방문하지 않은 정점이라면
dfs_list_recursion(nextV, adjList, visited); // 다시 DFS 실행
}
}
}[input]
5 5 3
5 4
5 2
1 2
3 4
3 1
[Output]
[인접리스트 활용 DFS 스택으로 구현]
3 1 2 5 4 2. 인접 행렬로 DFS 구현
import java.util.*;
public class DFS_Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 개수
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 개수
int v = sc.nextInt(); // 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호
boolean visited[] = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 여부를 검사할 배열
int[][] adjArray = new int[n+1][n+1];
// 간선의 개수 만큼 반복, 입력으로 주어지는 간선은 양방향
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjArray[v1][v2] = 1;
adjArray[v2][v1] = 1;
}
System.out.println("[인접행렬 활용 DFS 재귀로 구현]");
dfs_array_recursion(v, adjArray, visited);
// DFS 스택으로 구현하기 위해 visited 배열 초기화
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
System.out.println("\n[인접행렬 활용 DFS 스택으로 구현]");
dfs_array_stack(v, adjArray, visited, true);
}
// 인접 행렬을 활용한 DFS 재귀로 구현
public static void dfs_array_recursion(int v, int[][] adjArray, boolean[] visited) {
int l = adjArray.length-1;
visited[v] = true;
System.out.print(v + " ");
for(int i = 1; i <= l; i++) {
if(adjArray[v][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
dfs_array_recursion(i, adjArray, visited);
}
}
}
// 인접 행렬을 활용한 DFS 스택으로 구현
public static void dfs_array_stack(int v, int[][] adjArray, boolean[] visited, boolean flag) {
int l = adjArray.length-1;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(v);
visited[v] = true;
System.out.print(v + " ");
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
int w = stack.peek(); // stack의 맨 위에 있는 요소 반환
flag = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= l; i++) {
if(adjArray[w][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
stack.push(i);
System.out.print(i + " ");
visited[i] = true;
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(!flag) {
stack.pop();
}
}
}
}[Input]
5 5 3
5 4
5 2
1 2
3 4
3 1
[Output]
[인접행렬 활용 DFS 재귀로 구현]
3 1 2 5 4
[인접행렬 활용 DFS 스택으로 구현]
3 1 2 5 4 [참고자료]
https://minhamina.tistory.com/36
https://minhamina.tistory.com/22
