Loops
- 자바스크립트에서 루프를 사용하여 코드 블록을 여러 번 실행 가능
for
for: 코드 블록을 여러 번 반복
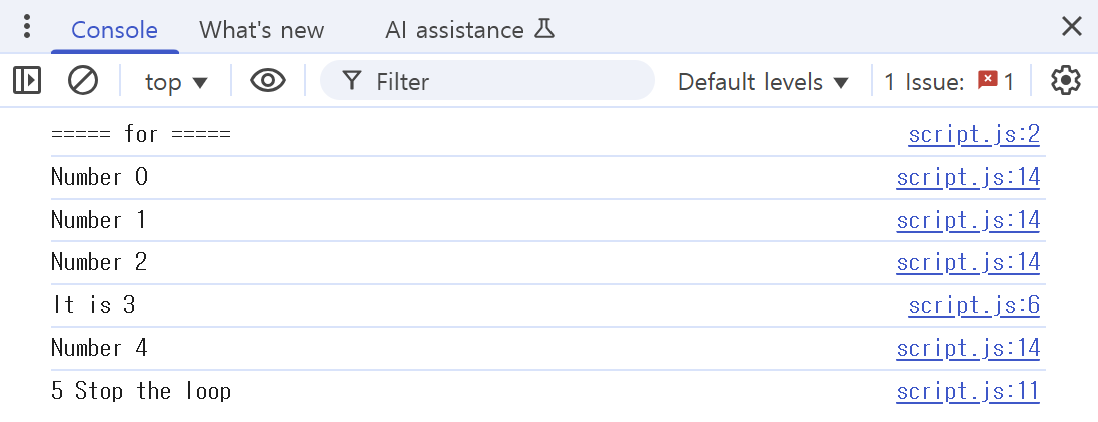
for(let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if(i === 3) {
console.log("It is 3");
continue; // 해당 턴은 여기까지 실행하고, 다음 턴으로(바로 i = 4 실행)
}
if(i === 5) {
console.log("5 Stop the loop");
break; // 반복문을 끝냄
}
console.log("Number " + i);
}
continue: 이번 반복은 건너뛰고, 다음 반복으로 넘어감
break: 반복을 완전 중단하고, 반복문을 빠져나감
for...in
for/in: 객체의 속성을 따라 반복
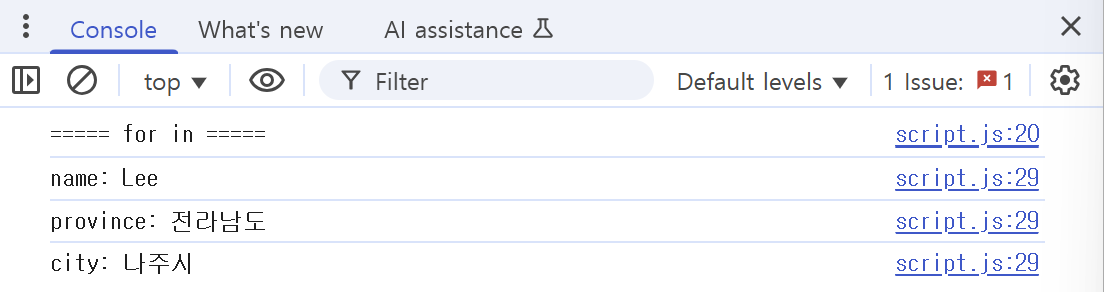
const user = {
name: "Lee",
province: "전라남도",
city: "나주시",
};
for(let item in user) {
console.log(`${item}: ${user[item]}`);
}
while
while: 지정된 조건이 true인 동안 코드 블록 반복
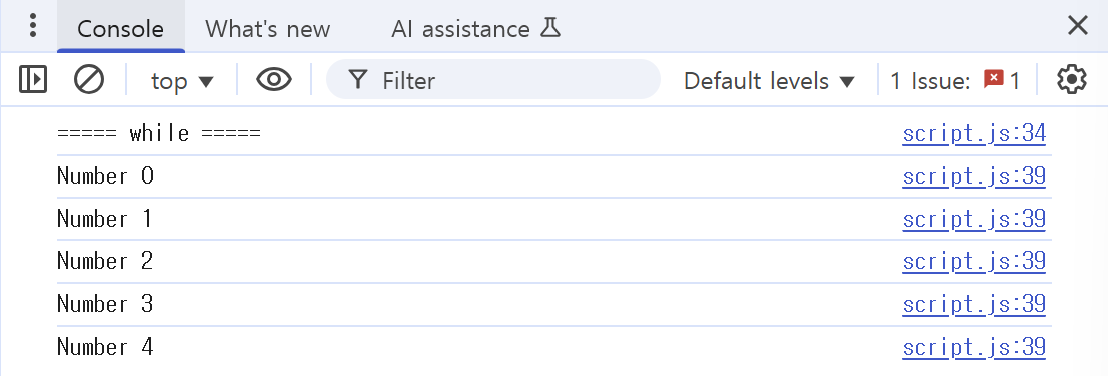
let i = 0;
while(i < 5) {
console.log("Number " + i);
i++;
}
do...while
do/while: 코드 블록을 한 번 실행한 뒤, 조건이 true인 동안 루프 반복
let j = 0;
do {
console.log("Number " + j);
j++
} while(j < 5);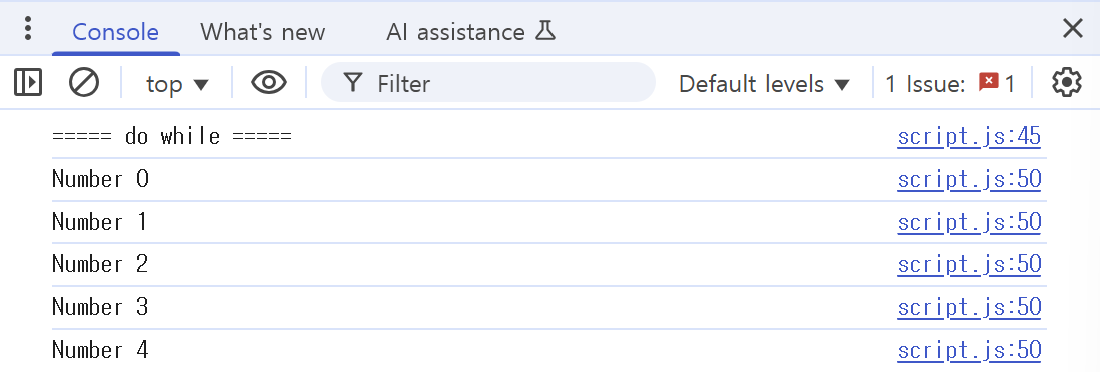
let j = 100;
do {
console.log("Number " + j);
j++
} while(j < 5);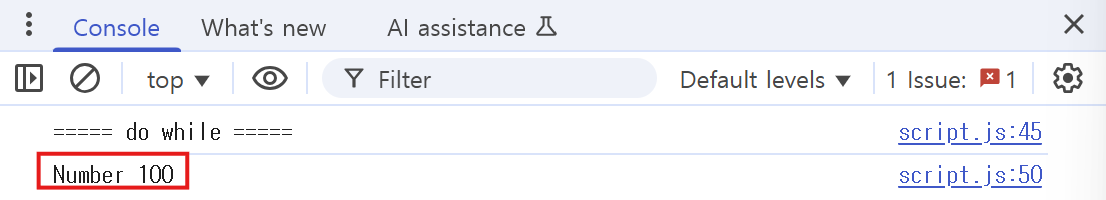
do-while은 무조건 1번은 실행한다는 점을 제외하고 while과 동일함
배열과 loop
length로 횟수 정하기
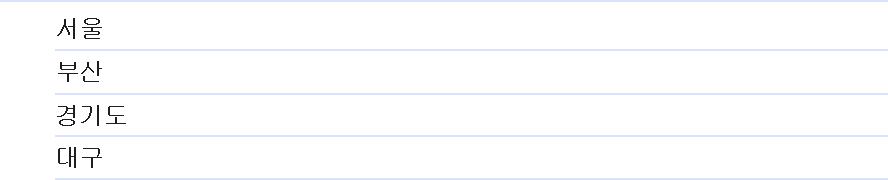
const locations = ['서울', '부산', '경기도', '대구'];
for(let i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
console.log(locations[i]);
}
array.forEach() 메소드
locations.forEach(function(location, index, array) {
console.log(`${index} : ${location}`);
console.log(array);
});
array.map() 메소드
-
map()메서드: 배열 내의 모든 요소 각각에 대하여 주어진 함수를 호출한 결과를 모아 새로운 배열 반환 -
array.map(callback(element, index, array), thisArg) -
예시 코드
const array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16]; const map1 = array1.map(x => x * 2); console.log("map1", map1); const map2 = array1.map(function(item, index, array) { console.log(item, index, array, this); return (item * 2); }, { a: 'a'}); console.log("map2", map2);
map()의 첫 번째 인수는 함수, 두번째 인수는 함수 내에서 this로 무엇을 접근할 건지를 넣어준다.- 만약 첫 번째 인수로 화살표 함수를 넣는다면, 두 번째 인수는 사용하지 않음
array.filter() 메소드
-
filter()메소드: 주어진 함수의 테스트를 통과하는 모든 요소를 모아 새로운 배열로 반환 -
array.filter(callback(element, index, array), thisArg) -
예시 코드
const words = ["spray", "limit", "elite", "exuberant", "destruction", "present"]; const result1 = words.filter(word => word.length > 6); console.log("result1", result1); const result2 = words.filter(function(word, index, array){ console.log(word, index, array, this); return word.length > 6 }, {a: 'a'}); console.log("result2", result2);
array.reduce() 메소드
reduce()메소드: 배열의 각 요소에 대해 주어진 리듀서(reducer) 함수를 실행하고, 하나의 결과값을 반환함array.reduce(reducer 함수(acc, cur, idx, src), initialValue)- 리듀서 함수는 네 개의 인자를 가짐
- 누산기(acc)
- 현재 값(cur)
- 현재 인덱스(idx)
- 원본 배열(src)
- 기본값 없는 경우
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4].reduce(function(accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, array){ return accumulator + currentValue; });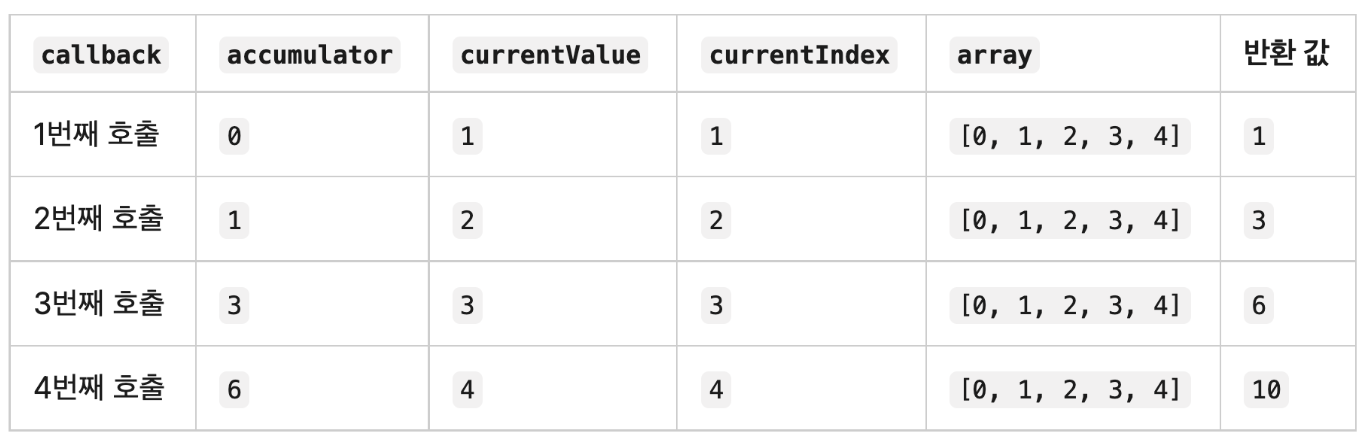
- 기본값 있는 경우
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4].reduce(function(accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, array){ return accumulator + currentValue; }, 10);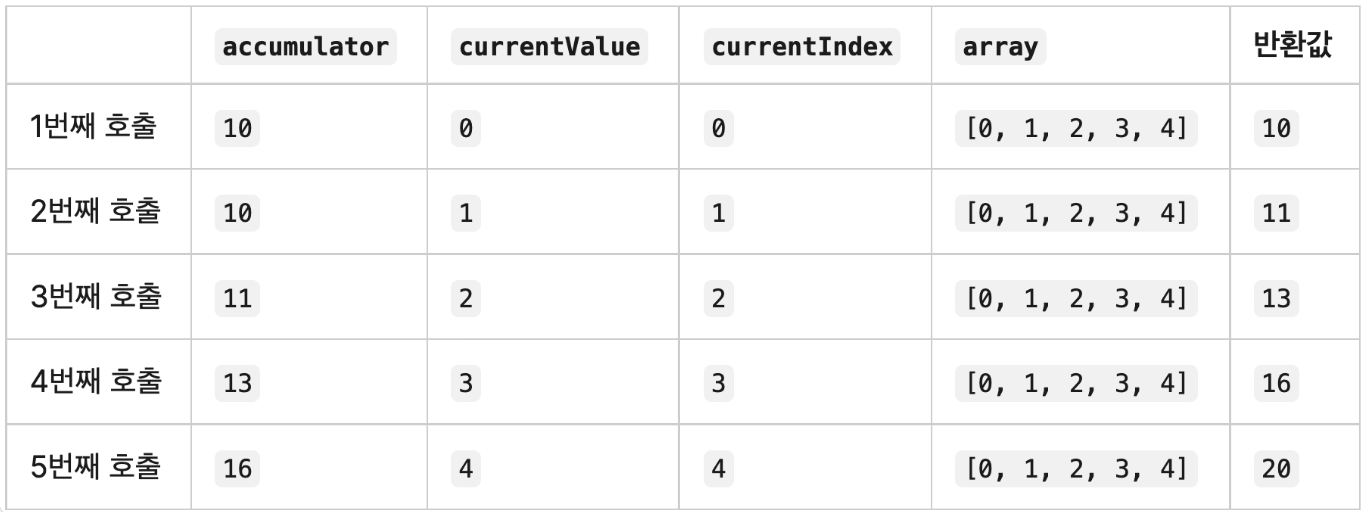
루프 비교
자료 구조와 loop
for..in: 객체에 사용
- 순회 대상: key
- 배열에도 사용 가능하나, 순서가 없어 지양
for..of: 배열와 같은 이터러블에 사용
- 순회 대상: value
break,continue사용 Oasync/await사용 OforEach: 배열
- 순회 대상: value
- 값, 인덱스, 배열을 콜백함수 인자로 받음 로직이 콜백 안에 있으면 복잡해질 수 있음
break,continue사용 Xasync/await사용 X
forEach() | map() | |
|---|---|---|
| 목적 | 반복하며 부수 효과 수행 | 배열을 변환하여 생성 |
| 반환값 | X(undefined) | O(새 배열) |
| 원본 배열 변경 | O | X |
| 체이닝 가능 여부 | X(undefined 반환됨) | O(map().filter().reduce()) |
for() | forEach() | |
|---|---|---|
| 방식 | 원래 사용됨 | 배열 요소 반복 |
| break 사용 가능 여부 | O | X |
| await() | O | X |
| 성능 | 빠름 | 느림 |