1. Query DSL vs Query String
there are 2 ways of querying
1. using query DSL
2. using query string
1-1. Using query DSL
2 types
1. leaf query : search for values within particular fields
2. compound query : contain multiple leaf queries or compound queries
- most flexible and common way of writing search query
GET /product/_search
{
"query" : {
"match" : {
"description" : {
"value" : "red wine"
}
}
}
}- query object in _search API contains query definition
1-2. Using query string
GET /product/_search?q=name:pastaname = field name
pasta = value
2. How search query works

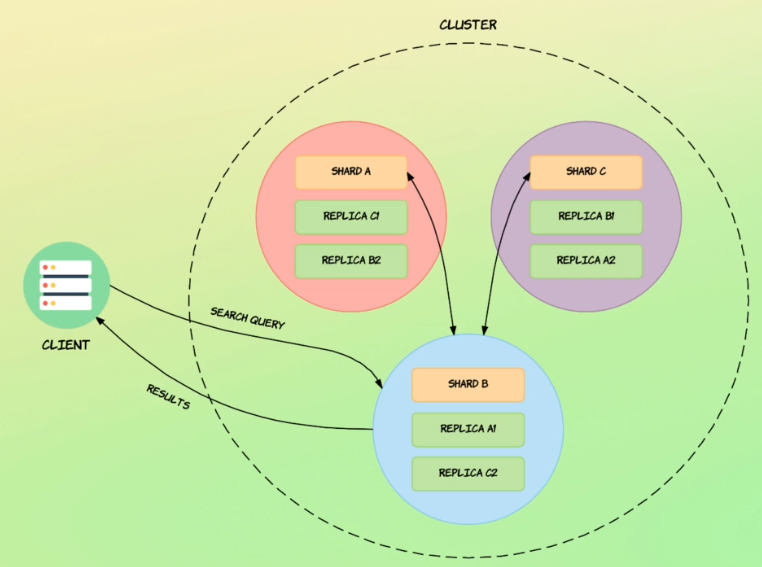
- search query reaches node with shard b, which becomes coordinating node
- coordinating node then queries nodes with different shards
2-1. Relevance Scoring
full text search results are sorted by their relevance score
- relevance scoring is what differenciates Elasticsearch from RDB
- until recently TF/IDF was used, but now BM 25 is used
- better handling of stop words using nonlinear term frequency saturation
- improving field-length norm factor by treating each field separately instead of just treating a field in the same way across all docs
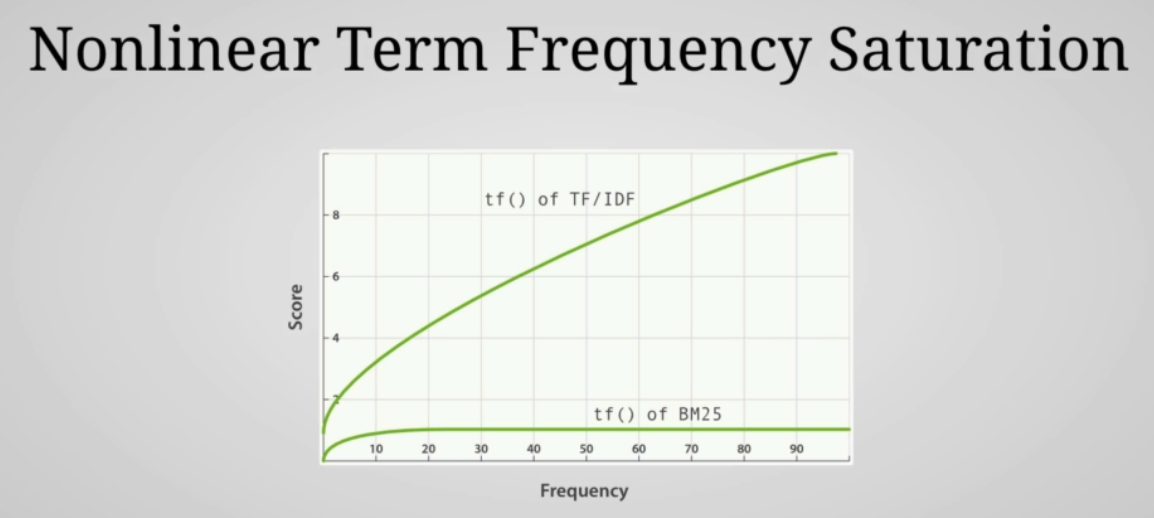
⚠️ IDF might be different for relevance scoring as by default, scoring is per shard based
3. Search Contexts
- query clause can be executed on 2 contexts
- Query Context : how well do docs match the query (match + relevance scoring)
- Filter Context : do docs match? (only match)
4. Full text vs term search
-
term level : search for exact value, input is not processed by analyzer
-
full text : search query is analyzed before matching. Analyzer specified by the field is used, if none, standard analyzer is used
