1. 예외 전파란 무엇인가?
상위 계층으로 예외가 전달될때마다 새로운 예외에 포함시켜 다시 던지는 과정
예외 체이닝, 예외 래핑이라고 불리기도 한다
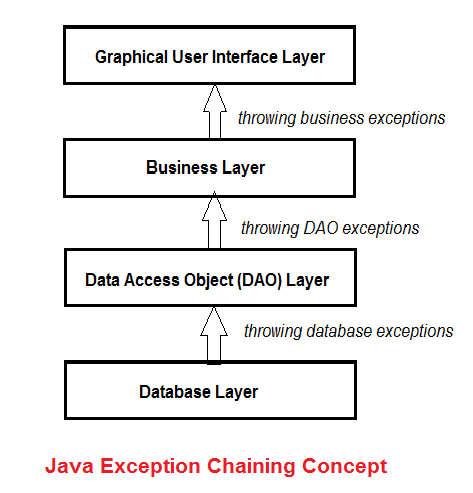
- 위 그림에서 나타나듯이 예외가 다른 계층으로 전달될때, 이전 예외를 원인으로 가지는 새로운 예외를 던지는 것을 예외 전파라고 한다
2. 왜 예외 전파를 하는가?
-
예외 전파의 가장 큰 목적은 첫 예외부터 전파되는 과정을 통해 거치는 예외들을 보존하기 위해서 이다. 아래와 같은 예외가 발생한다면 문제의 원인을 알 수가 없다
-
예외 전파를 통해 stack trace를 쌓고 예외가 어디서부터 어떤 과정을 거쳐 전달됐는지 확인할 수 있다
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Exception: 무슨 예외지???
at Main.main(Main.java:13)public class Main {
static Service service = new Service();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try {
service.get();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new Exception("무슨 예외지???");
}
}
}- 계층별 예외로 체이닝하지 않고 단순히 상위 계층으로 던질 수도 있겠지만, 이같은 경우 계층별 로직을 이해하기가 어렵다
Exception in thread "main" java.sql.SQLException: SQL이 잘못되었습니다
at Persistence.get(Persistence.java:5)
at Service.get(Service.java:7)
at Main.main(Main.java:10)public class Main {
static Service service = new Service();
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLExcpetion {
service.get();
}
}3. 예외 전파 예시
Exception in thread "main" MainException: 데이터를 가져오는데 실패했습니다
at Main.main(Main.java:12)
Caused by: exceptions.ServiceException: 데이터를 DB에서 질의하는데 실패했습니다
at Service.get(Service.java:13)
at Main.main(Main.java:10)
Caused by: java.sql.SQLException: SQL이 잘못되었습니다
at Persistence.get(Persistence.java:5)
at Service.get(Service.java:11)
... 1 morepublic class Main {
static Service service = new Service();
public static void main(String[] args) throws MainException {
try {
service.get();
} catch (ServiceException e) {
throw new MainException("데이터를 가져오는데 실패했습니다", e);
}
}
}public class Service {
Persistence persistence = new Persistence();
public void get() throws ServiceException {
try {
persistence.get();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new ServiceException("데이터를 DB에서 질의하는데 실패했습니다", e);
}
}
}public class Persistence {
public void get() throws SQLException {
throw new SQLException("SQL이 잘못되었습니다");
}
}- 계층에서 발생한 예외를 더 잘 표현하기 위해, 별도 Exception 클래스를 작성하는 것이 도움이 될 수도 있다
public class MainException extends Exception {
public MainException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}public class ServiceException extends Exception {
public ServiceException (String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}